深度优先搜索
广度优先搜索
并查集
数组
二分查找
矩阵
堆(优先队列)
题目描述
在一个 n x n 的整数矩阵 grid 中,每一个方格的值 grid[i][j] 表示位置 (i, j) 的平台高度。
当开始下雨时,在时间为 t 时,水池中的水位为 t 。你可以从一个平台游向四周相邻的任意一个平台,但是前提是此时水位必须同时淹没这两个平台。假定你可以瞬间移动无限距离,也就是默认在方格内部游动是不耗时的。当然,在你游泳的时候你必须待在坐标方格里面。
你从坐标方格的左上平台 (0,0) 出发。返回 你到达坐标方格的右下平台 (n-1, n-1) 所需的最少时间 。
示例 1:
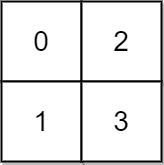
输入: grid = [[0,2],[1,3]]
输出: 3
解释:
时间为0时,你位于坐标方格的位置为 (0, 0)。
此时你不能游向任意方向,因为四个相邻方向平台的高度都大于当前时间为 0 时的水位。
等时间到达 3 时,你才可以游向平台 (1, 1). 因为此时的水位是 3,坐标方格中的平台没有比水位 3 更高的,所以你可以游向坐标方格中的任意位置
示例 2:
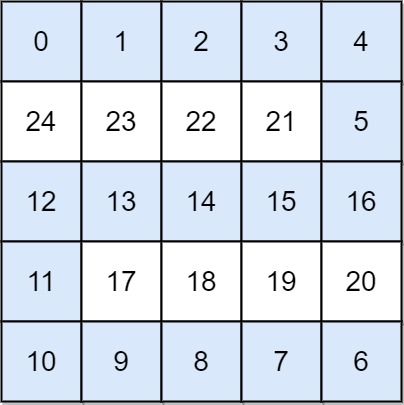
输入: grid = [[0,1,2,3,4],[24,23,22,21,5],[12,13,14,15,16],[11,17,18,19,20],[10,9,8,7,6]]
输出: 16
解释: 最终的路线用加粗进行了标记。
我们必须等到时间为 16,此时才能保证平台 (0, 0) 和 (4, 4) 是连通的
提示:
n == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= n <= 500 <= grid[i][j] < n2 grid[i][j] 中每个值 均无重复
解法
方法一
Python3 Java C++ Go TypeScript Rust
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22 class Solution :
def swimInWater ( self , grid : List [ List [ int ]]) -> int :
def find ( x ):
if p [ x ] != x :
p [ x ] = find ( p [ x ])
return p [ x ]
n = len ( grid )
p = list ( range ( n * n ))
hi = [ 0 ] * ( n * n )
for i , row in enumerate ( grid ):
for j , h in enumerate ( row ):
hi [ h ] = i * n + j
for t in range ( n * n ):
i , j = hi [ t ] // n , hi [ t ] % n
for a , b in [( 0 , - 1 ), ( 0 , 1 ), ( 1 , 0 ), ( - 1 , 0 )]:
x , y = i + a , j + b
if 0 <= x < n and 0 <= y < n and grid [ x ][ y ] <= t :
p [ find ( x * n + y )] = find ( hi [ t ])
if find ( 0 ) == find ( n * n - 1 ):
return t
return - 1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40 class Solution {
private int [] p ;
public int swimInWater ( int [][] grid ) {
int n = grid . length ;
p = new int [ n * n ] ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < p . length ; ++ i ) {
p [ i ] = i ;
}
int [] hi = new int [ n * n ] ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; ++ i ) {
for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j ) {
hi [ grid [ i ][ j ]] = i * n + j ;
}
}
int [] dirs = { - 1 , 0 , 1 , 0 , - 1 };
for ( int t = 0 ; t < n * n ; ++ t ) {
int i = hi [ t ] / n ;
int j = hi [ t ] % n ;
for ( int k = 0 ; k < 4 ; ++ k ) {
int x = i + dirs [ k ] ;
int y = j + dirs [ k + 1 ] ;
if ( x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < n && grid [ x ][ y ] <= t ) {
p [ find ( x * n + y ) ] = find ( i * n + j );
}
if ( find ( 0 ) == find ( n * n - 1 )) {
return t ;
}
}
}
return - 1 ;
}
private int find ( int x ) {
if ( p [ x ] != x ) {
p [ x ] = find ( p [ x ] );
}
return p [ x ] ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30 class Solution {
public :
vector < int > p ;
int swimInWater ( vector < vector < int >>& grid ) {
int n = grid . size ();
p . resize ( n * n );
for ( int i = 0 ; i < p . size (); ++ i ) p [ i ] = i ;
vector < int > hi ( n * n );
for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; ++ i )
for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j )
hi [ grid [ i ][ j ]] = i * n + j ;
vector < int > dirs = { -1 , 0 , 1 , 0 , -1 };
for ( int t = 0 ; t < n * n ; ++ t ) {
int i = hi [ t ] / n , j = hi [ t ] % n ;
for ( int k = 0 ; k < 4 ; ++ k ) {
int x = i + dirs [ k ], y = j + dirs [ k + 1 ];
if ( x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < n && grid [ x ][ y ] <= t )
p [ find ( x * n + y )] = find ( hi [ t ]);
if ( find ( 0 ) == find ( n * n - 1 )) return t ;
}
}
return -1 ;
}
int find ( int x ) {
if ( p [ x ] != x ) p [ x ] = find ( p [ x ]);
return p [ x ];
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34 func swimInWater ( grid [][] int ) int {
n := len ( grid )
p := make ([] int , n * n )
for i := range p {
p [ i ] = i
}
hi := make ([] int , n * n )
for i , row := range grid {
for j , h := range row {
hi [ h ] = i * n + j
}
}
var find func ( x int ) int
find = func ( x int ) int {
if p [ x ] != x {
p [ x ] = find ( p [ x ])
}
return p [ x ]
}
dirs := [] int { - 1 , 0 , 1 , 0 , - 1 }
for t := 0 ; t < n * n ; t ++ {
i , j := hi [ t ] / n , hi [ t ] % n
for k := 0 ; k < 4 ; k ++ {
x , y := i + dirs [ k ], j + dirs [ k + 1 ]
if x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < n && grid [ x ][ y ] <= t {
p [ find ( x * n + y )] = find ( hi [ t ])
}
if find ( 0 ) == find ( n * n - 1 ) {
return t
}
}
}
return - 1
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29 function swimInWater ( grid : number [][]) : number {
const m = grid . length ,
n = grid [ 0 ]. length ;
let visited = Array . from ({ length : m }, () => new Array ( n ). fill ( false ));
let ans = 0 ;
let stack = [[ 0 , 0 , grid [ 0 ][ 0 ]]];
const dir = [
[ 0 , 1 ],
[ 0 , - 1 ],
[ 1 , 0 ],
[ - 1 , 0 ],
];
while ( stack . length ) {
let [ i , j ] = stack . shift ();
ans = Math . max ( grid [ i ][ j ], ans );
if ( i == m - 1 && j == n - 1 ) break ;
for ( let [ dx , dy ] of dir ) {
let x = i + dx ,
y = j + dy ;
if ( x < m && x > - 1 && y < n && y > - 1 && ! visited [ x ][ y ]) {
visited [ x ][ y ] = true ;
stack . push ([ x , y , grid [ x ][ y ]]);
}
}
stack . sort (( a , b ) => a [ 2 ] - b [ 2 ]);
}
return ans ;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78 const DIR : [( i32 , i32 ); 4 ] = [
( - 1 , 0 ),
( 1 , 0 ),
( 0 , - 1 ),
( 0 , 1 ),
];
impl Solution {
#[allow(dead_code)]
pub fn swim_in_water ( grid : Vec < Vec < i32 >> ) -> i32 {
let n = grid . len ();
let m = grid [ 0 ]. len ();
let mut ret_time = 0 ;
let mut disjoint_set : Vec < usize > = vec! [ 0 ; n * m ];
// Initialize the disjoint set
for i in 0 .. n * m {
disjoint_set [ i ] = i ;
}
loop {
if Self :: check_and_union ( & grid , & mut disjoint_set , ret_time ) {
break ;
}
// Otherwise, keep checking
ret_time += 1 ;
}
ret_time
}
#[allow(dead_code)]
fn check_and_union ( grid : & Vec < Vec < i32 >> , d_set : & mut Vec < usize > , cur_time : i32 ) -> bool {
let n = grid . len ();
let m = grid [ 0 ]. len ();
for i in 0 .. n {
for j in 0 .. m {
if grid [ i ][ j ] != cur_time {
continue ;
}
// Otherwise, let's union the square with its neighbors
for ( dx , dy ) in DIR {
let x = dx + ( i as i32 );
let y = dy + ( j as i32 );
if
Self :: check_bounds ( x , y , n as i32 , m as i32 ) &&
grid [ x as usize ][ y as usize ] <= cur_time
{
Self :: union ( i * m + j , ( x as usize ) * m + ( y as usize ), d_set );
}
}
}
}
Self :: find ( 0 , d_set ) == Self :: find ( n * m - 1 , d_set )
}
#[allow(dead_code)]
fn find ( x : usize , d_set : & mut Vec < usize > ) -> usize {
if d_set [ x ] != x {
d_set [ x ] = Self :: find ( d_set [ x ], d_set );
}
d_set [ x ]
}
#[allow(dead_code)]
fn union ( x : usize , y : usize , d_set : & mut Vec < usize > ) {
let p_x = Self :: find ( x , d_set );
let p_y = Self :: find ( y , d_set );
d_set [ p_x ] = p_y ;
}
#[allow(dead_code)]
fn check_bounds ( i : i32 , j : i32 , n : i32 , m : i32 ) -> bool {
i >= 0 && i < n && j >= 0 && j < m
}
}