
题目描述
给定一个 m x n 二维字符网格 board 和一个单词(字符串)列表 words, 返回所有二维网格上的单词 。
单词必须按照字母顺序,通过 相邻的单元格 内的字母构成,其中“相邻”单元格是那些水平相邻或垂直相邻的单元格。同一个单元格内的字母在一个单词中不允许被重复使用。
示例 1:
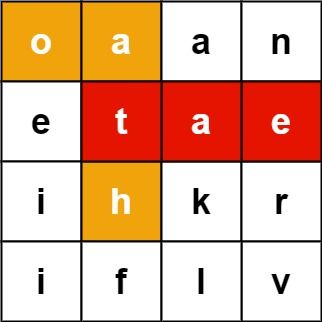
输入:board = [["o","a","a","n"],["e","t","a","e"],["i","h","k","r"],["i","f","l","v"]], words = ["oath","pea","eat","rain"]
输出:["eat","oath"]
示例 2:
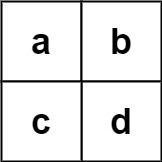
输入:board = [["a","b"],["c","d"]], words = ["abcb"]
输出:[]
提示:
m == board.lengthn == board[i].length1 <= m, n <= 12board[i][j] 是一个小写英文字母1 <= words.length <= 3 * 1041 <= words[i].length <= 10words[i] 由小写英文字母组成words 中的所有字符串互不相同
解法
方法一:前缀树 + DFS
我们首先将 words 中的单词构建成前缀树,前缀树的每个节点包含一个长度为 $26$ 的数组 children,表示该节点的子节点,数组的下标表示子节点对应的字符,数组的值表示子节点的引用。同时,每个节点还包含一个整数 ref,表示该节点对应的单词在 words 中的引用,如果该节点不是单词的结尾,则 ref 的值为 $-1$。
接下来,我们对于 board 中的每个单元格,从该单元格出发,进行深度优先搜索,搜索过程中,如果当前单词不是前缀树中的单词,则剪枝,如果当前单词是前缀树中的单词,则将该单词加入答案,并将该单词在前缀树中的引用置为 $-1$,表示该单词已经被找到,不需要再次搜索。
最后,我们将答案返回即可。
时间复杂度 $(m \times n \times 3^{l-1})$,空间复杂度 $(k \times l)$。其中 $m$ 和 $n$ 分别是 board 的行数和列数。而 $l$ 和 $k$ 分别是 words 中的单词的平均长度和单词的个数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42 | class Trie:
def __init__(self):
self.children: List[Trie | None] = [None] * 26
self.ref: int = -1
def insert(self, w: str, ref: int):
node = self
for c in w:
idx = ord(c) - ord('a')
if node.children[idx] is None:
node.children[idx] = Trie()
node = node.children[idx]
node.ref = ref
class Solution:
def findWords(self, board: List[List[str]], words: List[str]) -> List[str]:
def dfs(node: Trie, i: int, j: int):
idx = ord(board[i][j]) - ord('a')
if node.children[idx] is None:
return
node = node.children[idx]
if node.ref >= 0:
ans.append(words[node.ref])
node.ref = -1
c = board[i][j]
board[i][j] = '#'
for a, b in pairwise((-1, 0, 1, 0, -1)):
x, y = i + a, j + b
if 0 <= x < m and 0 <= y < n and board[x][y] != '#':
dfs(node, x, y)
board[i][j] = c
tree = Trie()
for i, w in enumerate(words):
tree.insert(w, i)
m, n = len(board), len(board[0])
ans = []
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
dfs(tree, i, j)
return ans
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60 | class Trie {
Trie[] children = new Trie[26];
int ref = -1;
public void insert(String w, int ref) {
Trie node = this;
for (int i = 0; i < w.length(); ++i) {
int j = w.charAt(i) - 'a';
if (node.children[j] == null) {
node.children[j] = new Trie();
}
node = node.children[j];
}
node.ref = ref;
}
}
class Solution {
private char[][] board;
private String[] words;
private List<String> ans = new ArrayList<>();
public List<String> findWords(char[][] board, String[] words) {
this.board = board;
this.words = words;
Trie tree = new Trie();
for (int i = 0; i < words.length; ++i) {
tree.insert(words[i], i);
}
int m = board.length, n = board[0].length;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
dfs(tree, i, j);
}
}
return ans;
}
private void dfs(Trie node, int i, int j) {
int idx = board[i][j] - 'a';
if (node.children[idx] == null) {
return;
}
node = node.children[idx];
if (node.ref != -1) {
ans.add(words[node.ref]);
node.ref = -1;
}
char c = board[i][j];
board[i][j] = '#';
int[] dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < board.length && y >= 0 && y < board[0].length && board[x][y] != '#') {
dfs(node, x, y);
}
}
board[i][j] = c;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62 | class Trie {
public:
vector<Trie*> children;
int ref;
Trie()
: children(26, nullptr)
, ref(-1) {}
void insert(const string& w, int ref) {
Trie* node = this;
for (char c : w) {
c -= 'a';
if (!node->children[c]) {
node->children[c] = new Trie();
}
node = node->children[c];
}
node->ref = ref;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> findWords(vector<vector<char>>& board, vector<string>& words) {
Trie* tree = new Trie();
for (int i = 0; i < words.size(); ++i) {
tree->insert(words[i], i);
}
vector<string> ans;
int m = board.size(), n = board[0].size();
function<void(Trie*, int, int)> dfs = [&](Trie* node, int i, int j) {
int idx = board[i][j] - 'a';
if (!node->children[idx]) {
return;
}
node = node->children[idx];
if (node->ref != -1) {
ans.emplace_back(words[node->ref]);
node->ref = -1;
}
int dirs[5] = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
char c = board[i][j];
board[i][j] = '#';
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && board[x][y] != '#') {
dfs(node, x, y);
}
}
board[i][j] = c;
};
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
dfs(tree, i, j);
}
}
return ans;
}
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55 | type Trie struct {
children [26]*Trie
ref int
}
func newTrie() *Trie {
return &Trie{ref: -1}
}
func (this *Trie) insert(w string, ref int) {
node := this
for _, c := range w {
c -= 'a'
if node.children[c] == nil {
node.children[c] = newTrie()
}
node = node.children[c]
}
node.ref = ref
}
func findWords(board [][]byte, words []string) (ans []string) {
trie := newTrie()
for i, w := range words {
trie.insert(w, i)
}
m, n := len(board), len(board[0])
var dfs func(*Trie, int, int)
dfs = func(node *Trie, i, j int) {
idx := board[i][j] - 'a'
if node.children[idx] == nil {
return
}
node = node.children[idx]
if node.ref != -1 {
ans = append(ans, words[node.ref])
node.ref = -1
}
c := board[i][j]
board[i][j] = '#'
dirs := [5]int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}
for k := 0; k < 4; k++ {
x, y := i+dirs[k], j+dirs[k+1]
if x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && board[x][y] != '#' {
dfs(node, x, y)
}
}
board[i][j] = c
}
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
dfs(trie, i, j)
}
}
return
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59 | class Trie {
children: Trie[];
ref: number;
constructor() {
this.children = new Array(26);
this.ref = -1;
}
insert(w: string, ref: number): void {
let node: Trie = this;
for (let i = 0; i < w.length; i++) {
const c = w.charCodeAt(i) - 97;
if (node.children[c] == null) {
node.children[c] = new Trie();
}
node = node.children[c];
}
node.ref = ref;
}
}
function findWords(board: string[][], words: string[]): string[] {
const tree = new Trie();
for (let i = 0; i < words.length; ++i) {
tree.insert(words[i], i);
}
const m = board.length;
const n = board[0].length;
const ans: string[] = [];
const dirs: number[] = [-1, 0, 1, 0, -1];
const dfs = (node: Trie, i: number, j: number) => {
const idx = board[i][j].charCodeAt(0) - 97;
if (node.children[idx] == null) {
return;
}
node = node.children[idx];
if (node.ref != -1) {
ans.push(words[node.ref]);
node.ref = -1;
}
const c = board[i][j];
board[i][j] = '#';
for (let k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
const x = i + dirs[k];
const y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && board[x][y] != '#') {
dfs(node, x, y);
}
}
board[i][j] = c;
};
for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
dfs(tree, i, j);
}
}
return ans;
}
|


