


题目描述
给你一个二维整数数组 stockPrices ,其中 stockPrices[i] = [dayi, pricei] 表示股票在 dayi 的价格为 pricei 。折线图 是一个二维平面上的若干个点组成的图,横坐标表示日期,纵坐标表示价格,折线图由相邻的点连接而成。比方说下图是一个例子:
请你返回要表示一个折线图所需要的 最少线段数 。
示例 1:
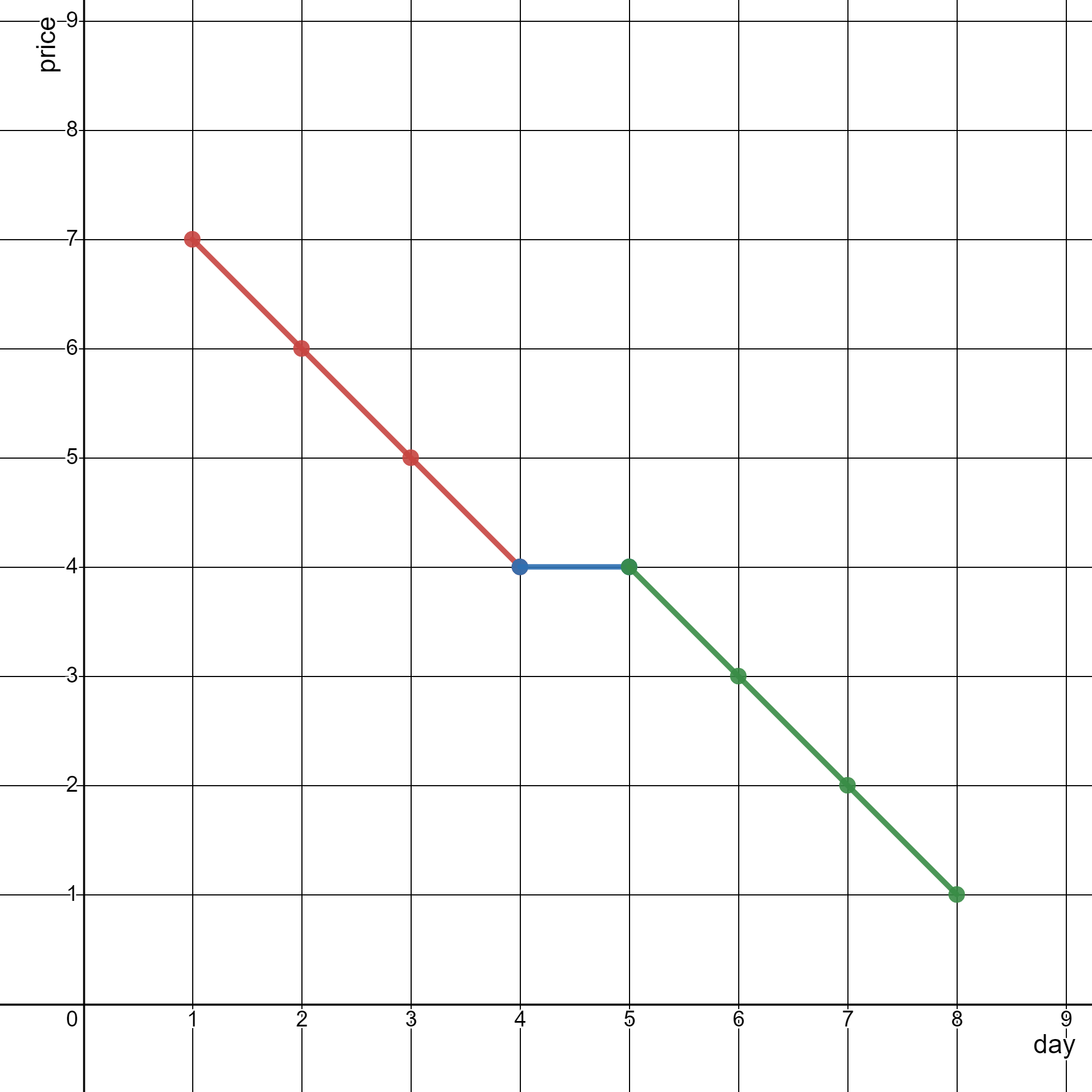
输入:stockPrices = [[1,7],[2,6],[3,5],[4,4],[5,4],[6,3],[7,2],[8,1]]
输出:3
解释:
上图为输入对应的图,横坐标表示日期,纵坐标表示价格。
以下 3 个线段可以表示折线图:
- 线段 1 (红色)从 (1,7) 到 (4,4) ,经过 (1,7) ,(2,6) ,(3,5) 和 (4,4) 。
- 线段 2 (蓝色)从 (4,4) 到 (5,4) 。
- 线段 3 (绿色)从 (5,4) 到 (8,1) ,经过 (5,4) ,(6,3) ,(7,2) 和 (8,1) 。
可以证明,无法用少于 3 条线段表示这个折线图。
示例 2:
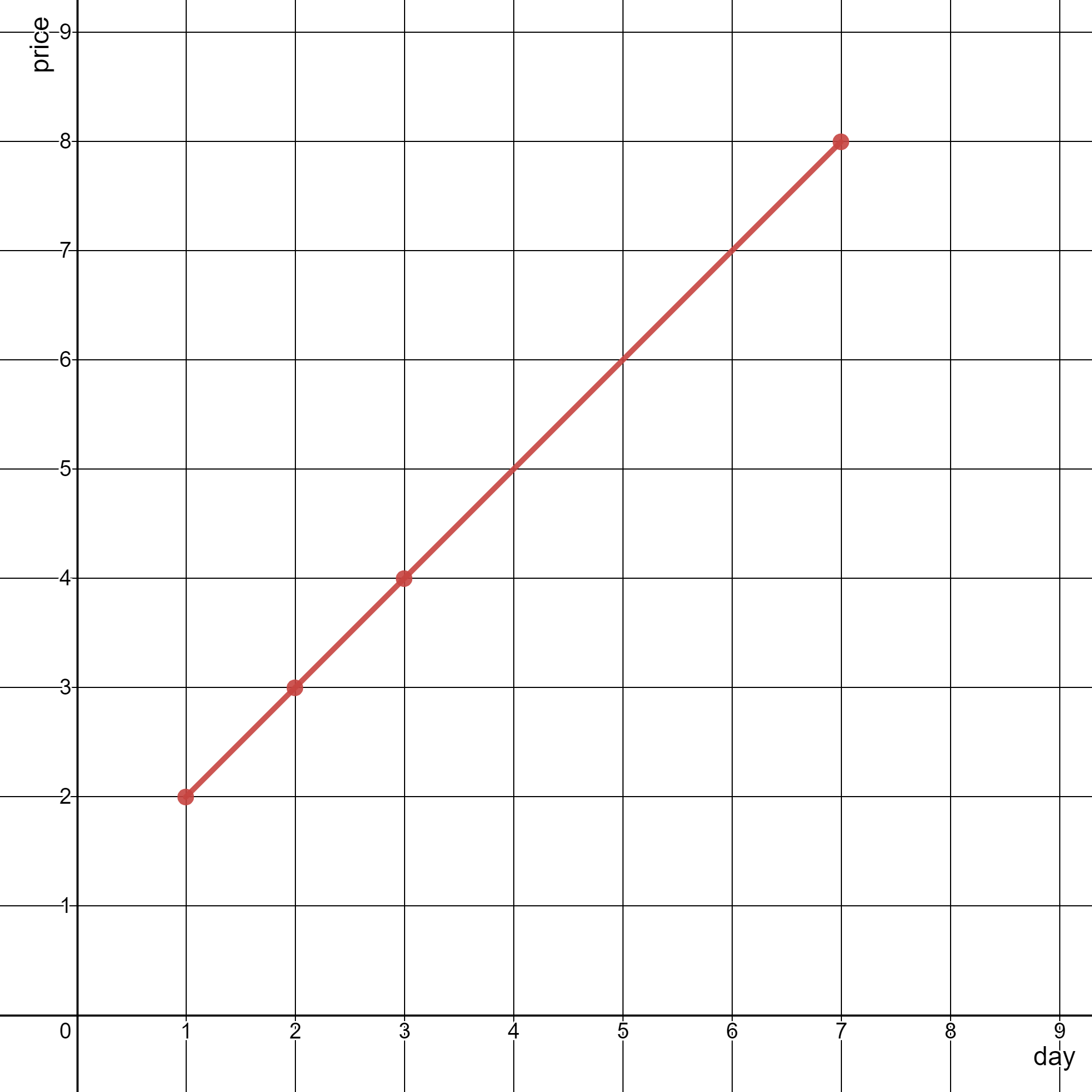
输入:stockPrices = [[3,4],[1,2],[7,8],[2,3]]
输出:1
解释:
如上图所示,折线图可以用一条线段表示。
提示:
1 <= stockPrices.length <= 105stockPrices[i].length == 21 <= dayi, pricei <= 109- 所有
dayi 互不相同 。
解法
方法一:斜率比较
需要注意:
- 只有一个点时,需要的线段数为 0;
- 利用除法计算斜率时,会有浮点误差,可以改成乘法比较。
| class Solution:
def minimumLines(self, stockPrices: List[List[int]]) -> int:
stockPrices.sort()
dx, dy = 0, 1
ans = 0
for (x, y), (x1, y1) in pairwise(stockPrices):
dx1, dy1 = x1 - x, y1 - y
if dy * dx1 != dx * dy1:
ans += 1
dx, dy = dx1, dy1
return ans
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18 | class Solution {
public int minimumLines(int[][] stockPrices) {
Arrays.sort(stockPrices, (a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
int dx = 0, dy = 1;
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < stockPrices.length; ++i) {
int x = stockPrices[i - 1][0], y = stockPrices[i - 1][1];
int x1 = stockPrices[i][0], y1 = stockPrices[i][1];
int dx1 = x1 - x, dy1 = y1 - y;
if (dy * dx1 != dx * dy1) {
++ans;
}
dx = dx1;
dy = dy1;
}
return ans;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17 | class Solution {
public:
int minimumLines(vector<vector<int>>& stockPrices) {
sort(stockPrices.begin(), stockPrices.end());
int dx = 0, dy = 1;
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < stockPrices.size(); ++i) {
int x = stockPrices[i - 1][0], y = stockPrices[i - 1][1];
int x1 = stockPrices[i][0], y1 = stockPrices[i][1];
int dx1 = x1 - x, dy1 = y1 - y;
if ((long long) dy * dx1 != (long long) dx * dy1) ++ans;
dx = dx1;
dy = dy1;
}
return ans;
}
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14 | func minimumLines(stockPrices [][]int) int {
ans := 0
sort.Slice(stockPrices, func(i, j int) bool { return stockPrices[i][0] < stockPrices[j][0] })
for i, dx, dy := 1, 0, 1; i < len(stockPrices); i++ {
x, y := stockPrices[i-1][0], stockPrices[i-1][1]
x1, y1 := stockPrices[i][0], stockPrices[i][1]
dx1, dy1 := x1-x, y1-y
if dy*dx1 != dx*dy1 {
ans++
}
dx, dy = dx1, dy1
}
return ans
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15 | function minimumLines(stockPrices: number[][]): number {
const n = stockPrices.length;
stockPrices.sort((a, b) => a[0] - b[0]);
let ans = 0;
let pre = [BigInt(0), BigInt(0)];
for (let i = 1; i < n; i++) {
const [x1, y1] = stockPrices[i - 1];
const [x2, y2] = stockPrices[i];
const dx = BigInt(x2 - x1),
dy = BigInt(y2 - y1);
if (i == 1 || dx * pre[1] !== dy * pre[0]) ans++;
pre = [dx, dy];
}
return ans;
}
|





