


题目描述
给你一棵 n 个节点的 无向 树,节点编号为 0 到 n - 1 ,树的根节点在节点 0 处。同时给你一个长度为 n - 1 的二维整数数组 edges ,其中 edges[i] = [ai, bi] 表示树中节点 ai 和 bi 之间有一条边。
给你一个长度为 n 下标从 0 开始的整数数组 cost ,其中 cost[i] 是第 i 个节点的 开销 。
你需要在树中每个节点都放置金币,在节点 i 处的金币数目计算方法如下:
- 如果节点
i 对应的子树中的节点数目小于 3 ,那么放 1 个金币。
- 否则,计算节点
i 对应的子树内 3 个不同节点的开销乘积的 最大值 ,并在节点 i 处放置对应数目的金币。如果最大乘积是 负数 ,那么放置 0 个金币。
请你返回一个长度为 n 的数组 coin ,coin[i]是节点 i 处的金币数目。
示例 1:
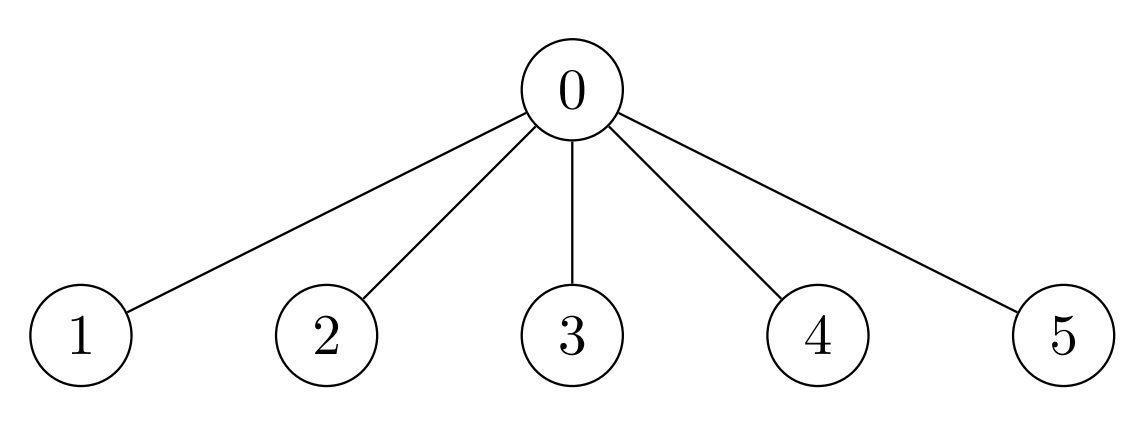
输入:edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3],[0,4],[0,5]], cost = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
输出:[120,1,1,1,1,1]
解释:在节点 0 处放置 6 * 5 * 4 = 120 个金币。所有其他节点都是叶子节点,子树中只有 1 个节点,所以其他每个节点都放 1 个金币。
示例 2:
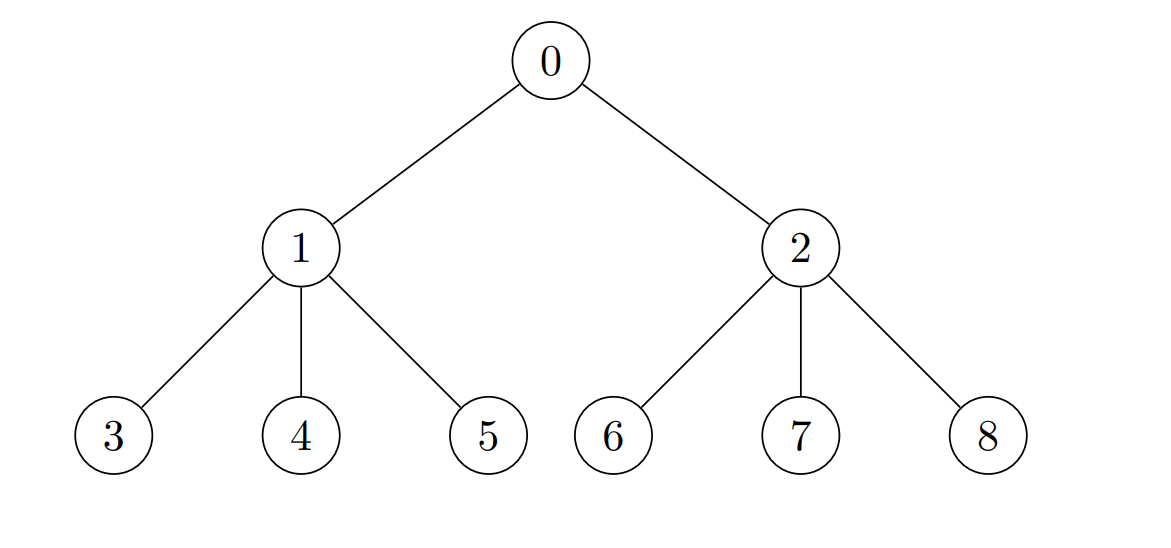
输入:edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,3],[1,4],[1,5],[2,6],[2,7],[2,8]], cost = [1,4,2,3,5,7,8,-4,2]
输出:[280,140,32,1,1,1,1,1,1]
解释:每个节点放置的金币数分别为:
- 节点 0 处放置 8 * 7 * 5 = 280 个金币。
- 节点 1 处放置 7 * 5 * 4 = 140 个金币。
- 节点 2 处放置 8 * 2 * 2 = 32 个金币。
- 其他节点都是叶子节点,子树内节点数目为 1 ,所以其他每个节点都放 1 个金币。
示例 3:
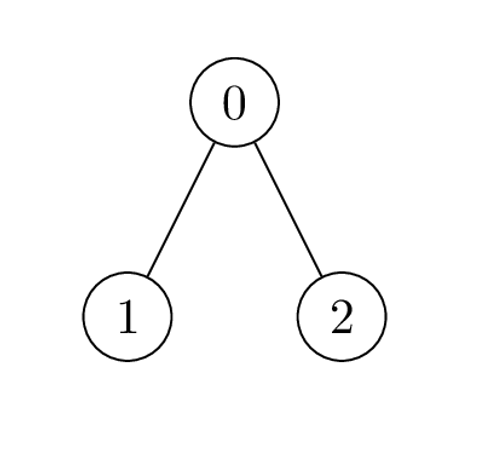
输入:edges = [[0,1],[0,2]], cost = [1,2,-2]
输出:[0,1,1]
解释:节点 1 和 2 都是叶子节点,子树内节点数目为 1 ,各放置 1 个金币。节点 0 处唯一的开销乘积是 2 * 1 * -2 = -4 。所以在节点 0 处放置 0 个金币。
提示:
2 <= n <= 2 * 104edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 20 <= ai, bi < ncost.length == n1 <= |cost[i]| <= 104edges 一定是一棵合法的树。
解法
方法一:DFS + 排序
根据题目描述,每个节点 $a$ 的放置的金币数有两种情况:
- 如果节点 $a$ 对应的子树中的节点数目小于 $3$,那么放 $1$ 个金币;
- 如果节点 $a$ 对应的子树中的节点数目大于等于 $3$,那么我们需要取出子树中的 $3$ 个不同节点,计算它们的开销乘积的最大值,然后在节点 $a$ 处放置对应数目的金币,如果最大乘积是负数,那么放置 $0$ 个金币。
第一种情况比较简单,我们只需要在遍历的过程中,统计每个节点的子树中的节点数目即可。
而对于第二种情况,如果开销都是正数,那么应该取开销最大的 $3$ 个节点;如果开销中有负数,那么应该取开销最小的 $2$ 个节点和开销最大的 $1$ 个节点。因此,我们需要维护每个子树最小的 $2$ 个开销和最大的 $3$ 个开销。
我们先根据题目给定的二维数组 $edges$ 构建邻接表 $g$,其中 $g[a]$ 表示节点 $a$ 的所有邻居节点。
接下来,我们设计一个函数 $dfs(a, fa)$,该函数返回一个数组 $res$,其中存储了节点 $a$ 的子树中最小的 $2$ 个开销和最大的 $3$ 个开销(可能不足 $5$ 个)。
在函数 $dfs(a, fa)$ 中,我们将节点 $a$ 的开销 $cost[a]$ 加入数组 $res$ 中,然后遍历节点 $a$ 的所有邻居节点 $b$,如果 $b$ 不是节点 $a$ 的父节点 $fa$,那么我们将 $dfs(b, a)$ 的结果加入数组 $res$ 中。
然后,我们对数组 $res$ 进行排序,然后根据数组 $res$ 的长度 $m$ 计算节点 $a$ 的放置金币数目,更新 $ans[a]$:
- 如果 $m \ge 3$,那么节点 $a$ 的放置金币数目为 $\max(0, res[m - 1] \times res[m - 2] \times res[m - 3], res[0] \times res[1] \times res[m - 1])$,否则节点 $a$ 的放置金币数目为 $1$;
- 如果 $m > 5$,那么我们只需要保留数组 $res$ 的前 $2$ 个元素和后 $3$ 个元素。
最后,我们调用函数 $dfs(0, -1)$,并且返回答案数组 $ans$ 即可。
时间复杂度 $O(n \times \log n)$,空间复杂度 $O(n)$。其中 $n$ 是节点的数目。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22 | class Solution:
def placedCoins(self, edges: List[List[int]], cost: List[int]) -> List[int]:
def dfs(a: int, fa: int) -> List[int]:
res = [cost[a]]
for b in g[a]:
if b != fa:
res.extend(dfs(b, a))
res.sort()
if len(res) >= 3:
ans[a] = max(res[-3] * res[-2] * res[-1], res[0] * res[1] * res[-1], 0)
if len(res) > 5:
res = res[:2] + res[-3:]
return res
n = len(cost)
g = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for a, b in edges:
g[a].append(b)
g[b].append(a)
ans = [1] * n
dfs(0, -1)
return ans
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42 | class Solution {
private int[] cost;
private List<Integer>[] g;
private long[] ans;
public long[] placedCoins(int[][] edges, int[] cost) {
int n = cost.length;
this.cost = cost;
ans = new long[n];
g = new List[n];
Arrays.fill(ans, 1);
Arrays.setAll(g, i -> new ArrayList<>());
for (int[] e : edges) {
int a = e[0], b = e[1];
g[a].add(b);
g[b].add(a);
}
dfs(0, -1);
return ans;
}
private List<Integer> dfs(int a, int fa) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
res.add(cost[a]);
for (int b : g[a]) {
if (b != fa) {
res.addAll(dfs(b, a));
}
}
Collections.sort(res);
int m = res.size();
if (m >= 3) {
long x = (long) res.get(m - 1) * res.get(m - 2) * res.get(m - 3);
long y = (long) res.get(0) * res.get(1) * res.get(m - 1);
ans[a] = Math.max(0, Math.max(x, y));
}
if (m >= 5) {
res = List.of(res.get(0), res.get(1), res.get(m - 3), res.get(m - 2), res.get(m - 1));
}
return res;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35 | class Solution {
public:
vector<long long> placedCoins(vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<int>& cost) {
int n = cost.size();
vector<long long> ans(n, 1);
vector<int> g[n];
for (auto& e : edges) {
int a = e[0], b = e[1];
g[a].push_back(b);
g[b].push_back(a);
}
function<vector<int>(int, int)> dfs = [&](int a, int fa) -> vector<int> {
vector<int> res = {cost[a]};
for (int b : g[a]) {
if (b != fa) {
auto t = dfs(b, a);
res.insert(res.end(), t.begin(), t.end());
}
}
sort(res.begin(), res.end());
int m = res.size();
if (m >= 3) {
long long x = 1LL * res[m - 1] * res[m - 2] * res[m - 3];
long long y = 1LL * res[0] * res[1] * res[m - 1];
ans[a] = max({0LL, x, y});
}
if (m >= 5) {
res = {res[0], res[1], res[m - 1], res[m - 2], res[m - 3]};
}
return res;
};
dfs(0, -1);
return ans;
}
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35 | func placedCoins(edges [][]int, cost []int) []int64 {
n := len(cost)
g := make([][]int, n)
for _, e := range edges {
a, b := e[0], e[1]
g[a] = append(g[a], b)
g[b] = append(g[b], a)
}
ans := make([]int64, n)
for i := range ans {
ans[i] = int64(1)
}
var dfs func(a, fa int) []int
dfs = func(a, fa int) []int {
res := []int{cost[a]}
for _, b := range g[a] {
if b != fa {
res = append(res, dfs(b, a)...)
}
}
sort.Ints(res)
m := len(res)
if m >= 3 {
x := res[m-1] * res[m-2] * res[m-3]
y := res[0] * res[1] * res[m-1]
ans[a] = max(0, int64(x), int64(y))
}
if m >= 5 {
res = append(res[:2], res[m-3:]...)
}
return res
}
dfs(0, -1)
return ans
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30 | function placedCoins(edges: number[][], cost: number[]): number[] {
const n = cost.length;
const ans: number[] = Array(n).fill(1);
const g: number[][] = Array.from({ length: n }, () => []);
for (const [a, b] of edges) {
g[a].push(b);
g[b].push(a);
}
const dfs = (a: number, fa: number): number[] => {
const res: number[] = [cost[a]];
for (const b of g[a]) {
if (b !== fa) {
res.push(...dfs(b, a));
}
}
res.sort((a, b) => a - b);
const m = res.length;
if (m >= 3) {
const x = res[m - 1] * res[m - 2] * res[m - 3];
const y = res[0] * res[1] * res[m - 1];
ans[a] = Math.max(0, x, y);
}
if (m > 5) {
res.splice(2, m - 5);
}
return res;
};
dfs(0, -1);
return ans;
}
|





