
题目描述
多项式链表是一种特殊形式的链表,每个节点表示多项式的一项。
每个节点有三个属性:
coefficient:该项的系数。项 9x4 的系数是 9 。power:该项的指数。项 9x4 的指数是 4 。next:指向下一个节点的指针(引用),如果当前节点为链表的最后一个节点则为 null 。
例如,多项式 5x3 + 4x - 7 可以表示成如下图所示的多项式链表:
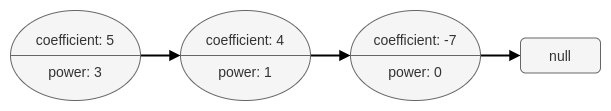
多项式链表必须是标准形式的,即多项式必须 严格 按指数 power 的递减顺序排列(即降幂排列)。另外,系数 coefficient 为 0 的项需要省略。
给定两个多项式链表的头节点 poly1 和 poly2,返回它们的和的头节点。
PolyNode 格式:
输入/输出格式表示为 n 个节点的列表,其中每个节点表示为 [coefficient, power] 。例如,多项式 5x3 + 4x - 7 表示为: [[5,3],[4,1],[-7,0]] 。
示例 1:
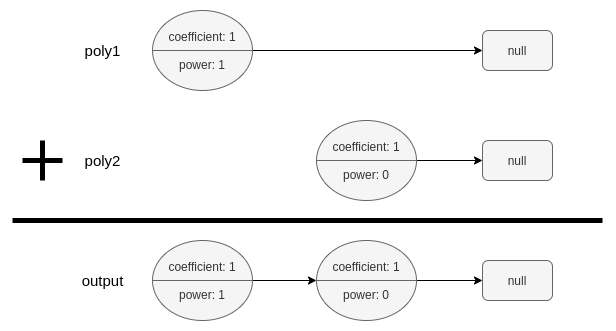
输入:poly1 = [[1,1]], poly2 = [[1,0]]
输出:[[1,1],[1,0]]
解释:poly1 = x. poly2 = 1. 和为 x + 1.
示例 2:
输入:poly1 = [[2,2],[4,1],[3,0]], poly2 = [[3,2],[-4,1],[-1,0]]
输出:[[5,2],[2,0]]
解释:poly1 = 2x2 + 4x + 3. poly2 = 3x2 - 4x - 1. 和为 5x2 + 2. 注意,我们省略 "0x" 项。
示例 3:
输入:poly1 = [[1,2]], poly2 = [[-1,2]]
输出:[]
解释:和为 0。我们返回空链表。
提示:
0 <= n <= 104-109 <= PolyNode.coefficient <= 109PolyNode.coefficient != 00 <= PolyNode.power <= 109PolyNode.power > PolyNode.next.power
解法
方法一:遍历链表
我们可以同时遍历两个链表,根据指数大小关系,将节点添加到结果链表中。
最后,如果链表 $1$ 或链表 $2$ 还有剩余节点,将其添加到结果链表中。
时间复杂度 $O(n)$,空间复杂度 $O(n)$。其中 $n$ 为两个链表中节点数的较大值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28 | # Definition for polynomial singly-linked list.
# class PolyNode:
# def __init__(self, x=0, y=0, next=None):
# self.coefficient = x
# self.power = y
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def addPoly(self, poly1: "PolyNode", poly2: "PolyNode") -> "PolyNode":
dummy = curr = PolyNode()
while poly1 and poly2:
if poly1.power > poly2.power:
curr.next = poly1
poly1 = poly1.next
curr = curr.next
elif poly1.power < poly2.power:
curr.next = poly2
poly2 = poly2.next
curr = curr.next
else:
if c := poly1.coefficient + poly2.coefficient:
curr.next = PolyNode(c, poly1.power)
curr = curr.next
poly1 = poly1.next
poly2 = poly2.next
curr.next = poly1 or poly2
return dummy.next
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45 | /**
* Definition for polynomial singly-linked list.
* class PolyNode {
* int coefficient, power;
* PolyNode next = null;
* PolyNode() {}
* PolyNode(int x, int y) { this.coefficient = x; this.power = y; }
* PolyNode(int x, int y, PolyNode next) { this.coefficient = x; this.power = y; this.next =
next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public PolyNode addPoly(PolyNode poly1, PolyNode poly2) {
PolyNode dummy = new PolyNode();
PolyNode curr = dummy;
while (poly1 != null && poly2 != null) {
if (poly1.power > poly2.power) {
curr.next = poly1;
poly1 = poly1.next;
curr = curr.next;
} else if (poly1.power < poly2.power) {
curr.next = poly2;
poly2 = poly2.next;
curr = curr.next;
} else {
int c = poly1.coefficient + poly2.coefficient;
if (c != 0) {
curr.next = new PolyNode(c, poly1.power);
curr = curr.next;
}
poly1 = poly1.next;
poly2 = poly2.next;
}
}
if (poly1 == null) {
curr.next = poly2;
}
if (poly2 == null) {
curr.next = poly1;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44 | /**
* Definition for polynomial singly-linked list->
* struct PolyNode {
* int coefficient, power;
* PolyNode *next;
* PolyNode(): coefficient(0), power(0), next(nullptr) {};
* PolyNode(int x, int y): coefficient(x), power(y), next(nullptr) {};
* PolyNode(int x, int y, PolyNode* next): coefficient(x), power(y), next(next) {};
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
PolyNode* addPoly(PolyNode* poly1, PolyNode* poly2) {
PolyNode* dummy = new PolyNode();
PolyNode* curr = dummy;
while (poly1 && poly2) {
if (poly1->power > poly2->power) {
curr->next = poly1;
poly1 = poly1->next;
curr = curr->next;
} else if (poly1->power < poly2->power) {
curr->next = poly2;
poly2 = poly2->next;
curr = curr->next;
} else {
int c = poly1->coefficient + poly2->coefficient;
if (c != 0) {
curr->next = new PolyNode(c, poly1->power);
curr = curr->next;
}
poly1 = poly1->next;
poly2 = poly2->next;
}
}
if (!poly1) {
curr->next = poly2;
}
if (!poly2) {
curr->next = poly1;
}
return dummy->next;
}
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39 | /**
* Definition for polynomial singly-linked list.
* function PolyNode(x=0, y=0, next=null) {
* this.coefficient = x;
* this.power = y;
* this.next = next;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {PolyNode} poly1
* @param {PolyNode} poly2
* @return {PolyNode}
*/
var addPoly = function (poly1, poly2) {
const dummy = new PolyNode();
let curr = dummy;
while (poly1 && poly2) {
if (poly1.power > poly2.power) {
curr.next = poly1;
poly1 = poly1.next;
curr = curr.next;
} else if (poly1.power < poly2.power) {
curr.next = poly2;
poly2 = poly2.next;
curr = curr.next;
} else {
const c = poly1.coefficient + poly2.coefficient;
if (c != 0) {
curr.next = new PolyNode(c, poly1.power);
curr = curr.next;
}
poly1 = poly1.next;
poly2 = poly2.next;
}
}
curr.next = poly1 || poly2;
return dummy.next;
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46 | /**
* Definition for polynomial singly-linked list.
* public class PolyNode {
* public int coefficient, power;
* public PolyNode next;
*
* public PolyNode(int x=0, int y=0, PolyNode next=null) {
* this.coefficient = x;
* this.power = y;
* this.next = next;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public PolyNode AddPoly(PolyNode poly1, PolyNode poly2) {
PolyNode dummy = new PolyNode();
PolyNode curr = dummy;
while (poly1 != null && poly2 != null) {
if (poly1.power > poly2.power) {
curr.next = poly1;
poly1 = poly1.next;
curr = curr.next;
} else if (poly1.power < poly2.power) {
curr.next = poly2;
poly2 = poly2.next;
curr = curr.next;
} else {
int c = poly1.coefficient + poly2.coefficient;
if (c != 0) {
curr.next = new PolyNode(c, poly1.power);
curr = curr.next;
}
poly1 = poly1.next;
poly2 = poly2.next;
}
}
if (poly1 == null) {
curr.next = poly2;
}
if (poly2 == null) {
curr.next = poly1;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
|


