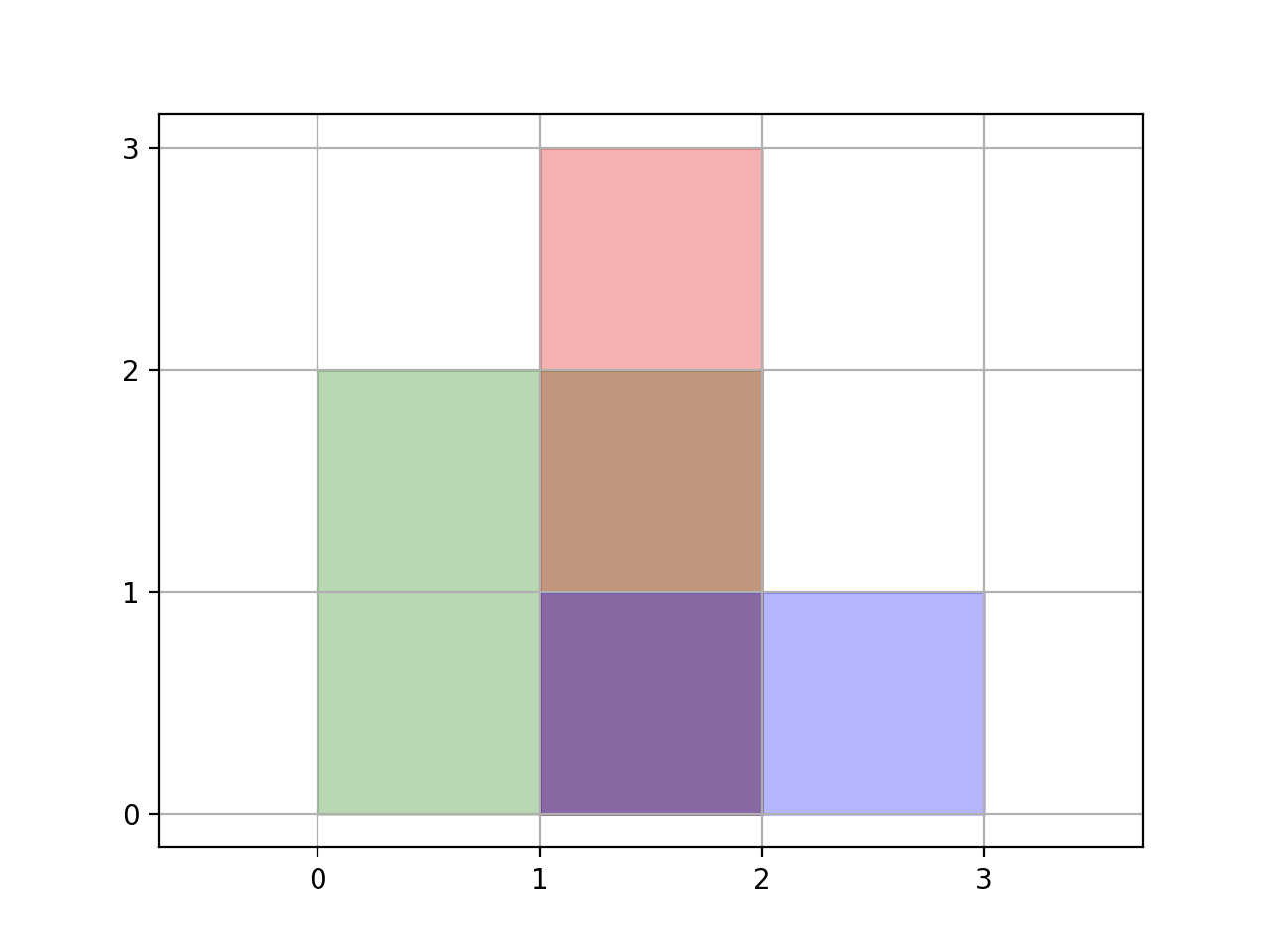Segment Tree
Array
Ordered Set
Line Sweep
Description
You are given a 2D array of axis-aligned rectangles. Each rectangle[i] = [xi1 , yi1 , xi2 , yi2 ] denotes the ith rectangle where (xi1 , yi1 ) are the coordinates of the bottom-left corner , and (xi2 , yi2 ) are the coordinates of the top-right corner .
Calculate the total area covered by all rectangles in the plane. Any area covered by two or more rectangles should only be counted once .
Return the total area . Since the answer may be too large, return it modulo 109 + 7.
Example 1:
Input: rectangles = [[0,0,2,2],[1,0,2,3],[1,0,3,1]]
Output: 6
Explanation: A total area of 6 is covered by all three rectangles, as illustrated in the picture.
From (1,1) to (2,2), the green and red rectangles overlap.
From (1,0) to (2,3), all three rectangles overlap.
Example 2:
Input: rectangles = [[0,0,1000000000,1000000000]]
Output: 49
Explanation: The answer is 1018 modulo (109 + 7), which is 49.
Constraints:
1 <= rectangles.length <= 200rectanges[i].length == 40 <= xi1 , yi1 , xi2 , yi2 <= 109 xi1 <= xi2 yi1 <= yi2
Solutions
Solution 1
Python3 Java C++ Go
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64 class Node :
def __init__ ( self ):
self . l = self . r = 0
self . cnt = self . length = 0
class SegmentTree :
def __init__ ( self , nums ):
n = len ( nums ) - 1
self . nums = nums
self . tr = [ Node () for _ in range ( n << 2 )]
self . build ( 1 , 0 , n - 1 )
def build ( self , u , l , r ):
self . tr [ u ] . l , self . tr [ u ] . r = l , r
if l != r :
mid = ( l + r ) >> 1
self . build ( u << 1 , l , mid )
self . build ( u << 1 | 1 , mid + 1 , r )
def modify ( self , u , l , r , k ):
if self . tr [ u ] . l >= l and self . tr [ u ] . r <= r :
self . tr [ u ] . cnt += k
else :
mid = ( self . tr [ u ] . l + self . tr [ u ] . r ) >> 1
if l <= mid :
self . modify ( u << 1 , l , r , k )
if r > mid :
self . modify ( u << 1 | 1 , l , r , k )
self . pushup ( u )
def pushup ( self , u ):
if self . tr [ u ] . cnt :
self . tr [ u ] . length = self . nums [ self . tr [ u ] . r + 1 ] - self . nums [ self . tr [ u ] . l ]
elif self . tr [ u ] . l == self . tr [ u ] . r :
self . tr [ u ] . length = 0
else :
self . tr [ u ] . length = self . tr [ u << 1 ] . length + self . tr [ u << 1 | 1 ] . length
@property
def length ( self ):
return self . tr [ 1 ] . length
class Solution :
def rectangleArea ( self , rectangles : List [ List [ int ]]) -> int :
segs = []
alls = set ()
for x1 , y1 , x2 , y2 in rectangles :
segs . append (( x1 , y1 , y2 , 1 ))
segs . append (( x2 , y1 , y2 , - 1 ))
alls . update ([ y1 , y2 ])
segs . sort ()
alls = sorted ( alls )
tree = SegmentTree ( alls )
m = { v : i for i , v in enumerate ( alls )}
ans = 0
for i , ( x , y1 , y2 , k ) in enumerate ( segs ):
if i :
ans += tree . length * ( x - segs [ i - 1 ][ 0 ])
tree . modify ( 1 , m [ y1 ], m [ y2 ] - 1 , k )
ans %= int ( 1e9 + 7 )
return ans
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96 class Node {
int l , r , cnt , length ;
}
class SegmentTree {
private Node [] tr ;
private int [] nums ;
public SegmentTree ( int [] nums ) {
this . nums = nums ;
int n = nums . length - 1 ;
tr = new Node [ n << 2 ] ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < tr . length ; ++ i ) {
tr [ i ] = new Node ();
}
build ( 1 , 0 , n - 1 );
}
private void build ( int u , int l , int r ) {
tr [ u ] . l = l ;
tr [ u ] . r = r ;
if ( l != r ) {
int mid = ( l + r ) >> 1 ;
build ( u << 1 , l , mid );
build ( u << 1 | 1 , mid + 1 , r );
}
}
public void modify ( int u , int l , int r , int k ) {
if ( tr [ u ] . l >= l && tr [ u ] . r <= r ) {
tr [ u ] . cnt += k ;
} else {
int mid = ( tr [ u ] . l + tr [ u ] . r ) >> 1 ;
if ( l <= mid ) {
modify ( u << 1 , l , r , k );
}
if ( r > mid ) {
modify ( u << 1 | 1 , l , r , k );
}
}
pushup ( u );
}
private void pushup ( int u ) {
if ( tr [ u ] . cnt > 0 ) {
tr [ u ] . length = nums [ tr [ u ] . r + 1 ] - nums [ tr [ u ] . l ] ;
} else if ( tr [ u ] . l == tr [ u ] . r ) {
tr [ u ] . length = 0 ;
} else {
tr [ u ] . length = tr [ u << 1 ] . length + tr [ u << 1 | 1 ] . length ;
}
}
public int query () {
return tr [ 1 ] . length ;
}
}
class Solution {
private static final int MOD = ( int ) 1e9 + 7 ;
public int rectangleArea ( int [][] rectangles ) {
int n = rectangles . length ;
int [][] segs = new int [ n << 1 ][ 4 ] ;
int i = 0 ;
TreeSet < Integer > ts = new TreeSet <> ();
for ( var e : rectangles ) {
int x1 = e [ 0 ] , y1 = e [ 1 ] , x2 = e [ 2 ] , y2 = e [ 3 ] ;
segs [ i ++] = new int [] { x1 , y1 , y2 , 1 };
segs [ i ++] = new int [] { x2 , y1 , y2 , - 1 };
ts . add ( y1 );
ts . add ( y2 );
}
Arrays . sort ( segs , ( a , b ) -> a [ 0 ] - b [ 0 ] );
Map < Integer , Integer > m = new HashMap <> ( ts . size ());
i = 0 ;
int [] nums = new int [ ts . size () ] ;
for ( int v : ts ) {
m . put ( v , i );
nums [ i ++] = v ;
}
SegmentTree tree = new SegmentTree ( nums );
long ans = 0 ;
for ( i = 0 ; i < segs . length ; ++ i ) {
var e = segs [ i ] ;
int x = e [ 0 ] , y1 = e [ 1 ] , y2 = e [ 2 ] , k = e [ 3 ] ;
if ( i > 0 ) {
ans += ( long ) tree . query () * ( x - segs [ i - 1 ][ 0 ] );
}
tree . modify ( 1 , m . get ( y1 ), m . get ( y2 ) - 1 , k );
}
ans %= MOD ;
return ( int ) ans ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86 class Node {
public :
int l , r , cnt , length ;
};
class SegmentTree {
public :
vector < Node *> tr ;
vector < int > nums ;
SegmentTree ( vector < int >& nums ) {
this -> nums = nums ;
int n = nums . size () - 1 ;
tr . resize ( n << 2 );
for ( int i = 0 ; i < tr . size (); ++ i ) tr [ i ] = new Node ();
build ( 1 , 0 , n - 1 );
}
void build ( int u , int l , int r ) {
tr [ u ] -> l = l ;
tr [ u ] -> r = r ;
if ( l != r ) {
int mid = ( l + r ) >> 1 ;
build ( u << 1 , l , mid );
build ( u << 1 | 1 , mid + 1 , r );
}
}
void modify ( int u , int l , int r , int k ) {
if ( tr [ u ] -> l >= l && tr [ u ] -> r <= r )
tr [ u ] -> cnt += k ;
else {
int mid = ( tr [ u ] -> l + tr [ u ] -> r ) >> 1 ;
if ( l <= mid ) modify ( u << 1 , l , r , k );
if ( r > mid ) modify ( u << 1 | 1 , l , r , k );
}
pushup ( u );
}
int query () {
return tr [ 1 ] -> length ;
}
void pushup ( int u ) {
if ( tr [ u ] -> cnt )
tr [ u ] -> length = nums [ tr [ u ] -> r + 1 ] - nums [ tr [ u ] -> l ];
else if ( tr [ u ] -> l == tr [ u ] -> r )
tr [ u ] -> length = 0 ;
else
tr [ u ] -> length = tr [ u << 1 ] -> length + tr [ u << 1 | 1 ] -> length ;
}
};
class Solution {
public :
const int mod = 1e9 + 7 ;
int rectangleArea ( vector < vector < int >>& rectangles ) {
int n = rectangles . size ();
vector < vector < int >> segs ( n << 1 );
set < int > ts ;
int i = 0 ;
for ( auto & e : rectangles ) {
int x1 = e [ 0 ], y1 = e [ 1 ], x2 = e [ 2 ], y2 = e [ 3 ];
segs [ i ++ ] = { x1 , y1 , y2 , 1 };
segs [ i ++ ] = { x2 , y1 , y2 , -1 };
ts . insert ( y1 );
ts . insert ( y2 );
}
sort ( segs . begin (), segs . end ());
unordered_map < int , int > m ;
i = 0 ;
for ( int v : ts ) m [ v ] = i ++ ;
vector < int > nums ( ts . begin (), ts . end ());
SegmentTree * tree = new SegmentTree ( nums );
long long ans = 0 ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < segs . size (); ++ i ) {
auto e = segs [ i ];
int x = e [ 0 ], y1 = e [ 1 ], y2 = e [ 2 ], k = e [ 3 ];
if ( i > 0 ) ans += ( long long ) tree -> query () * ( x - segs [ i - 1 ][ 0 ]);
tree -> modify ( 1 , m [ y1 ], m [ y2 ] - 1 , k );
}
ans %= mod ;
return ( int ) ans ;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95 func rectangleArea ( rectangles [][] int ) int {
var mod int = 1e9 + 7
segs := [][] int {}
alls := map [ int ] bool {}
for _ , e := range rectangles {
x1 , y1 , x2 , y2 := e [ 0 ], e [ 1 ], e [ 2 ], e [ 3 ]
segs = append ( segs , [] int { x1 , y1 , y2 , 1 })
segs = append ( segs , [] int { x2 , y1 , y2 , - 1 })
alls [ y1 ] = true
alls [ y2 ] = true
}
nums := [] int {}
for v := range alls {
nums = append ( nums , v )
}
sort . Ints ( nums )
sort . Slice ( segs , func ( i , j int ) bool { return segs [ i ][ 0 ] < segs [ j ][ 0 ] })
m := map [ int ] int {}
for i , v := range nums {
m [ v ] = i
}
tree := newSegmentTree ( nums )
ans := 0
for i , e := range segs {
x , y1 , y2 , k := e [ 0 ], e [ 1 ], e [ 2 ], e [ 3 ]
if i > 0 {
ans += tree . query () * ( x - segs [ i - 1 ][ 0 ])
ans %= mod
}
tree . modify ( 1 , m [ y1 ], m [ y2 ] - 1 , k )
}
return ans
}
type node struct {
l int
r int
cnt int
length int
}
type segmentTree struct {
tr [] * node
nums [] int
}
func newSegmentTree ( nums [] int ) * segmentTree {
n := len ( nums ) - 1
tr := make ([] * node , n << 2 )
for i := range tr {
tr [ i ] = & node {}
}
t := & segmentTree { tr , nums }
t . build ( 1 , 0 , n - 1 )
return t
}
func ( t * segmentTree ) build ( u , l , r int ) {
t . tr [ u ]. l , t . tr [ u ]. r = l , r
if l == r {
return
}
mid := ( l + r ) >> 1
t . build ( u << 1 , l , mid )
t . build ( u << 1 | 1 , mid + 1 , r )
}
func ( t * segmentTree ) modify ( u , l , r , k int ) {
if t . tr [ u ]. l >= l && t . tr [ u ]. r <= r {
t . tr [ u ]. cnt += k
} else {
mid := ( t . tr [ u ]. l + t . tr [ u ]. r ) >> 1
if l <= mid {
t . modify ( u << 1 , l , r , k )
}
if r > mid {
t . modify ( u << 1 | 1 , l , r , k )
}
}
t . pushup ( u )
}
func ( t * segmentTree ) query () int {
return t . tr [ 1 ]. length
}
func ( t * segmentTree ) pushup ( u int ) {
if t . tr [ u ]. cnt > 0 {
t . tr [ u ]. length = t . nums [ t . tr [ u ]. r + 1 ] - t . nums [ t . tr [ u ]. l ]
} else if t . tr [ u ]. l == t . tr [ u ]. r {
t . tr [ u ]. length = 0
} else {
t . tr [ u ]. length = t . tr [ u << 1 ]. length + t . tr [ u << 1 | 1 ]. length
}
}
GitHub