Tree
Depth-First Search
Binary Tree
Description
Given the root of a binary tree and an integer targetSum, return the number of paths where the sum of the values along the path equals targetSum.
The path does not need to start or end at the root or a leaf, but it must go downwards (i.e., traveling only from parent nodes to child nodes).
Example 1:
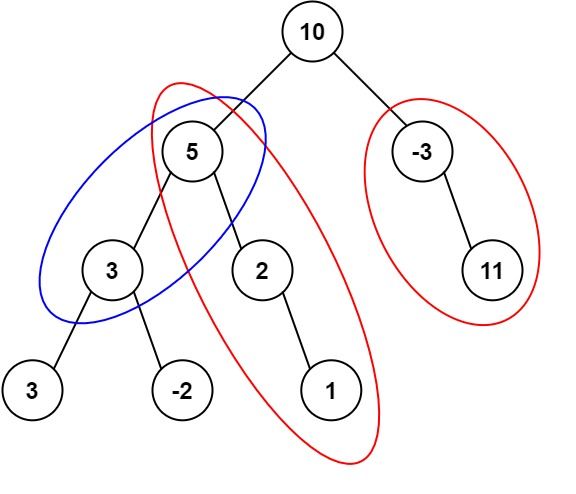
Input: root = [10,5,-3,3,2,null,11,3,-2,null,1], targetSum = 8
Output: 3
Explanation: The paths that sum to 8 are shown.
Example 2:
Input: root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1], targetSum = 22
Output: 3
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 1000].
-109 <= Node.val <= 109 -1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
Solutions
Solution 1
Python3 Java C++ Go TypeScript
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21 # Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution :
def pathSum ( self , root : Optional [ TreeNode ], targetSum : int ) -> int :
def dfs ( node , s ):
if node is None :
return 0
s += node . val
ans = cnt [ s - targetSum ]
cnt [ s ] += 1
ans += dfs ( node . left , s )
ans += dfs ( node . right , s )
cnt [ s ] -= 1
return ans
cnt = Counter ({ 0 : 1 })
return dfs ( root , 0 )
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private Map < Long , Integer > cnt = new HashMap <> ();
private int targetSum ;
public int pathSum ( TreeNode root , int targetSum ) {
cnt . put ( 0 L , 1 );
this . targetSum = targetSum ;
return dfs ( root , 0 );
}
private int dfs ( TreeNode node , long s ) {
if ( node == null ) {
return 0 ;
}
s += node . val ;
int ans = cnt . getOrDefault ( s - targetSum , 0 );
cnt . merge ( s , 1 , Integer :: sum );
ans += dfs ( node . left , s );
ans += dfs ( node . right , s );
cnt . merge ( s , - 1 , Integer :: sum );
return ans ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public :
int pathSum ( TreeNode * root , int targetSum ) {
unordered_map < long , int > cnt ;
cnt [ 0 ] = 1 ;
function < int ( TreeNode * , long ) > dfs = [ & ]( TreeNode * node , long s ) -> int {
if ( ! node ) return 0 ;
s += node -> val ;
int ans = cnt [ s - targetSum ];
++ cnt [ s ];
ans += dfs ( node -> left , s ) + dfs ( node -> right , s );
-- cnt [ s ];
return ans ;
};
return dfs ( root , 0 );
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func pathSum ( root * TreeNode , targetSum int ) int {
cnt := map [ int ] int { 0 : 1 }
var dfs func ( * TreeNode , int ) int
dfs = func ( node * TreeNode , s int ) int {
if node == nil {
return 0
}
s += node . Val
ans := cnt [ s - targetSum ]
cnt [ s ] ++
ans += dfs ( node . Left , s ) + dfs ( node . Right , s )
cnt [ s ] --
return ans
}
return dfs ( root , 0 )
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function pathSum ( root : TreeNode | null , targetSum : number ) : number {
const cnt : Map < number , number > = new Map ();
const dfs = ( node : TreeNode | null , s : number ) : number => {
if ( ! node ) {
return 0 ;
}
s += node . val ;
let ans = cnt . get ( s - targetSum ) ?? 0 ;
cnt . set ( s , ( cnt . get ( s ) ?? 0 ) + 1 );
ans += dfs ( node . left , s );
ans += dfs ( node . right , s );
cnt . set ( s , ( cnt . get ( s ) ?? 0 ) - 1 );
return ans ;
};
cnt . set ( 0 , 1 );
return dfs ( root , 0 );
}
GitHub