2711. Difference of Number of Distinct Values on Diagonals
Description
Given a 0-indexed 2D grid of size m x n, you should find the matrix answer of size m x n.
The value of each cell (r, c) of the matrix answer is calculated in the following way:
- Let
topLeft[r][c]be the number of distinct values in the top-left diagonal of the cell(r, c)in the matrixgrid. - Let
bottomRight[r][c]be the number of distinct values in the bottom-right diagonal of the cell(r, c)in the matrixgrid.
Then answer[r][c] = |topLeft[r][c] - bottomRight[r][c]|.
Return the matrix answer.
A matrix diagonal is a diagonal line of cells starting from some cell in either the topmost row or leftmost column and going in the bottom-right direction until reaching the matrix's end.
A cell (r1, c1) belongs to the top-left diagonal of the cell (r, c), if both belong to the same diagonal and r1 < r. Similarly is defined bottom-right diagonal.
Example 1:
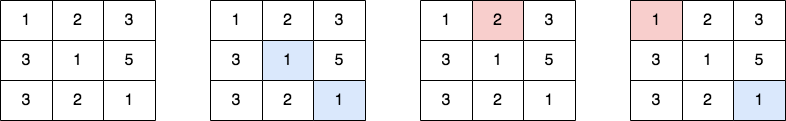
Input: grid = [[1,2,3],[3,1,5],[3,2,1]] Output: [[1,1,0],[1,0,1],[0,1,1]] Explanation: The 1st diagram denotes the initial grid. The 2nd diagram denotes a grid for cell (0,0), where blue-colored cells are cells on its bottom-right diagonal. The 3rd diagram denotes a grid for cell (1,2), where red-colored cells are cells on its top-left diagonal. The 4th diagram denotes a grid for cell (1,1), where blue-colored cells are cells on its bottom-right diagonal and red-colored cells are cells on its top-left diagonal. - The cell (0,0) contains [1,1] on its bottom-right diagonal and [] on its top-left diagonal. The answer is |1 - 0| = 1. - The cell (1,2) contains [] on its bottom-right diagonal and [2] on its top-left diagonal. The answer is |0 - 1| = 1. - The cell (1,1) contains [1] on its bottom-right diagonal and [1] on its top-left diagonal. The answer is |1 - 1| = 0. The answers of other cells are similarly calculated.
Example 2:
Input: grid = [[1]] Output: [[0]] Explanation: - The cell (0,0) contains [] on its bottom-right diagonal and [] on its top-left diagonal. The answer is |0 - 0| = 0.
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n, grid[i][j] <= 50
Solutions
Solution 1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 | |