Union Find
Graph
Minimum Spanning Tree
Sorting
Strongly Connected Component
Description
Given a weighted undirected connected graph with n vertices numbered from 0 to n - 1, and an array edges where edges[i] = [ai , bi , weighti ] represents a bidirectional and weighted edge between nodes ai and bi . A minimum spanning tree (MST) is a subset of the graph's edges that connects all vertices without cycles and with the minimum possible total edge weight.
Find all the critical and pseudo-critical edges in the given graph's minimum spanning tree (MST) . An MST edge whose deletion from the graph would cause the MST weight to increase is called a critical edge . On the other hand, a pseudo-critical edge is that which can appear in some MSTs but not all.
Note that you can return the indices of the edges in any order.
Example 1:
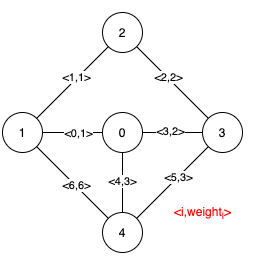
Input: n = 5, edges = [[0,1,1],[1,2,1],[2,3,2],[0,3,2],[0,4,3],[3,4,3],[1,4,6]]
Output: [[0,1],[2,3,4,5]]
Explanation: The figure above describes the graph.
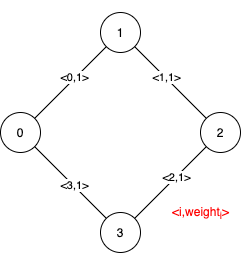
The following figure shows all the possible MSTs:
Example 2:
Input: n = 4, edges = [[0,1,1],[1,2,1],[2,3,1],[0,3,1]]
Output: [[],[0,1,2,3]]
Explanation: We can observe that since all 4 edges have equal weight, choosing any 3 edges from the given 4 will yield an MST. Therefore all 4 edges are pseudo-critical.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 1001 <= edges.length <= min(200, n * (n - 1) / 2)edges[i].length == 30 <= ai < bi < n1 <= weighti <= 1000All pairs (ai , bi ) are distinct .
Solutions
Solution 1
Python3 Java C++ Go
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41 class UnionFind :
def __init__ ( self , n ):
self . p = list ( range ( n ))
self . n = n
def union ( self , a , b ):
if self . find ( a ) == self . find ( b ):
return False
self . p [ self . find ( a )] = self . find ( b )
self . n -= 1
return True
def find ( self , x ):
if self . p [ x ] != x :
self . p [ x ] = self . find ( self . p [ x ])
return self . p [ x ]
class Solution :
def findCriticalAndPseudoCriticalEdges (
self , n : int , edges : List [ List [ int ]]
) -> List [ List [ int ]]:
for i , e in enumerate ( edges ):
e . append ( i )
edges . sort ( key = lambda x : x [ 2 ])
uf = UnionFind ( n )
v = sum ( w for f , t , w , _ in edges if uf . union ( f , t ))
ans = [[], []]
for f , t , w , i in edges :
uf = UnionFind ( n )
k = sum ( z for x , y , z , j in edges if j != i and uf . union ( x , y ))
if uf . n > 1 or ( uf . n == 1 and k > v ):
ans [ 0 ] . append ( i )
continue
uf = UnionFind ( n )
uf . union ( f , t )
k = w + sum ( z for x , y , z , j in edges if j != i and uf . union ( x , y ))
if k == v :
ans [ 1 ] . append ( i )
return ans
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85 class Solution {
public List < List < Integer >> findCriticalAndPseudoCriticalEdges ( int n , int [][] edges ) {
for ( int i = 0 ; i < edges . length ; ++ i ) {
int [] e = edges [ i ] ;
int [] t = new int [ 4 ] ;
System . arraycopy ( e , 0 , t , 0 , 3 );
t [ 3 ] = i ;
edges [ i ] = t ;
}
Arrays . sort ( edges , Comparator . comparingInt ( a -> a [ 2 ] ));
int v = 0 ;
UnionFind uf = new UnionFind ( n );
for ( int [] e : edges ) {
int f = e [ 0 ] , t = e [ 1 ] , w = e [ 2 ] ;
if ( uf . union ( f , t )) {
v += w ;
}
}
List < List < Integer >> ans = new ArrayList <> ();
for ( int i = 0 ; i < 2 ; ++ i ) {
ans . add ( new ArrayList <> ());
}
for ( int [] e : edges ) {
int f = e [ 0 ] , t = e [ 1 ] , w = e [ 2 ] , i = e [ 3 ] ;
uf = new UnionFind ( n );
int k = 0 ;
for ( int [] ne : edges ) {
int x = ne [ 0 ] , y = ne [ 1 ] , z = ne [ 2 ] , j = ne [ 3 ] ;
if ( j != i && uf . union ( x , y )) {
k += z ;
}
}
if ( uf . getN () > 1 || ( uf . getN () == 1 && k > v )) {
ans . get ( 0 ). add ( i );
continue ;
}
uf = new UnionFind ( n );
uf . union ( f , t );
k = w ;
for ( int [] ne : edges ) {
int x = ne [ 0 ] , y = ne [ 1 ] , z = ne [ 2 ] , j = ne [ 3 ] ;
if ( j != i && uf . union ( x , y )) {
k += z ;
}
}
if ( k == v ) {
ans . get ( 1 ). add ( i );
}
}
return ans ;
}
}
class UnionFind {
private int [] p ;
private int n ;
public UnionFind ( int n ) {
p = new int [ n ] ;
this . n = n ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; ++ i ) {
p [ i ] = i ;
}
}
public int getN () {
return n ;
}
public boolean union ( int a , int b ) {
if ( find ( a ) == find ( b )) {
return false ;
}
p [ find ( a ) ] = find ( b );
-- n ;
return true ;
}
public int find ( int x ) {
if ( p [ x ] != x ) {
p [ x ] = find ( p [ x ] );
}
return p [ x ] ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61 class UnionFind {
public :
vector < int > p ;
int n ;
UnionFind ( int _n )
: n ( _n )
, p ( _n ) {
iota ( p . begin (), p . end (), 0 );
}
bool unite ( int a , int b ) {
if ( find ( a ) == find ( b )) return false ;
p [ find ( a )] = find ( b );
-- n ;
return true ;
}
int find ( int x ) {
if ( p [ x ] != x ) p [ x ] = find ( p [ x ]);
return p [ x ];
}
};
class Solution {
public :
vector < vector < int >> findCriticalAndPseudoCriticalEdges ( int n , vector < vector < int >>& edges ) {
for ( int i = 0 ; i < edges . size (); ++ i ) edges [ i ]. push_back ( i );
sort ( edges . begin (), edges . end (), []( auto & a , auto & b ) { return a [ 2 ] < b [ 2 ]; });
int v = 0 ;
UnionFind uf ( n );
for ( auto & e : edges ) {
int f = e [ 0 ], t = e [ 1 ], w = e [ 2 ];
if ( uf . unite ( f , t )) v += w ;
}
vector < vector < int >> ans ( 2 );
for ( auto & e : edges ) {
int f = e [ 0 ], t = e [ 1 ], w = e [ 2 ], i = e [ 3 ];
UnionFind ufa ( n );
int k = 0 ;
for ( auto & ne : edges ) {
int x = ne [ 0 ], y = ne [ 1 ], z = ne [ 2 ], j = ne [ 3 ];
if ( j != i && ufa . unite ( x , y )) k += z ;
}
if ( ufa . n > 1 || ( ufa . n == 1 && k > v )) {
ans [ 0 ]. push_back ( i );
continue ;
}
UnionFind ufb ( n );
ufb . unite ( f , t );
k = w ;
for ( auto & ne : edges ) {
int x = ne [ 0 ], y = ne [ 1 ], z = ne [ 2 ], j = ne [ 3 ];
if ( j != i && ufb . unite ( x , y )) k += z ;
}
if ( k == v ) ans [ 1 ]. push_back ( i );
}
return ans ;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74 type unionFind struct {
p [] int
n int
}
func newUnionFind ( n int ) * unionFind {
p := make ([] int , n )
for i := range p {
p [ i ] = i
}
return & unionFind { p , n }
}
func ( uf * unionFind ) find ( x int ) int {
if uf . p [ x ] != x {
uf . p [ x ] = uf . find ( uf . p [ x ])
}
return uf . p [ x ]
}
func ( uf * unionFind ) union ( a , b int ) bool {
if uf . find ( a ) == uf . find ( b ) {
return false
}
uf . p [ uf . find ( a )] = uf . find ( b )
uf . n --
return true
}
func findCriticalAndPseudoCriticalEdges ( n int , edges [][] int ) [][] int {
for i := range edges {
edges [ i ] = append ( edges [ i ], i )
}
sort . Slice ( edges , func ( i , j int ) bool {
return edges [ i ][ 2 ] < edges [ j ][ 2 ]
})
v := 0
uf := newUnionFind ( n )
for _ , e := range edges {
f , t , w := e [ 0 ], e [ 1 ], e [ 2 ]
if uf . union ( f , t ) {
v += w
}
}
ans := make ([][] int , 2 )
for _ , e := range edges {
f , t , w , i := e [ 0 ], e [ 1 ], e [ 2 ], e [ 3 ]
uf = newUnionFind ( n )
k := 0
for _ , ne := range edges {
x , y , z , j := ne [ 0 ], ne [ 1 ], ne [ 2 ], ne [ 3 ]
if j != i && uf . union ( x , y ) {
k += z
}
}
if uf . n > 1 || ( uf . n == 1 && k > v ) {
ans [ 0 ] = append ( ans [ 0 ], i )
continue
}
uf = newUnionFind ( n )
uf . union ( f , t )
k = w
for _ , ne := range edges {
x , y , z , j := ne [ 0 ], ne [ 1 ], ne [ 2 ], ne [ 3 ]
if j != i && uf . union ( x , y ) {
k += z
}
}
if k == v {
ans [ 1 ] = append ( ans [ 1 ], i )
}
}
return ans
}
GitHub
Notice that the two edges 0 and 1 appear in all MSTs, therefore they are critical edges, so we return them in the first list of the output. The edges 2, 3, 4, and 5 are only part of some MSTs, therefore they are considered pseudo-critical edges. We add them to the second list of the output.