1245. Tree Diameter 🔒
Description
The diameter of a tree is the number of edges in the longest path in that tree.
There is an undirected tree of n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1. You are given a 2D array edges where edges.length == n - 1 and edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an undirected edge between nodes ai and bi in the tree.
Return the diameter of the tree.
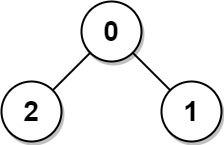
Example 1:
Input: edges = [[0,1],[0,2]] Output: 2 Explanation: The longest path of the tree is the path 1 - 0 - 2.
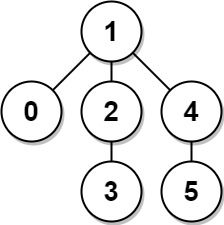
Example 2:
Input: edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[1,4],[4,5]] Output: 4 Explanation: The longest path of the tree is the path 3 - 2 - 1 - 4 - 5.
Constraints:
n == edges.length + 11 <= n <= 1040 <= ai, bi < nai != bi
Solutions
Solution 1: Two DFS
First, perform DFS on any node to find the furthest node, then perform DFS again from this node to reach another furthest node. The node reached by the first DFS can be proven to be one end of the diameter of this graph, and the second DFS will reach the other end. Let's prove this theorem.
Theorem: In a connected undirected acyclic graph, the furthest node that can be reached from any node must be one end of the diameter of the graph.
Proof: Suppose this diameter is $\delta(s, t)$. There are two cases:
- When the starting node $y$ is on $\delta(s, t)$, suppose the furthest node $z$ reached is not any of $s, t$. At this time, connect $\delta(y, z)$ with $\delta(y, s)$ that does not overlap with it (you can also assume that the other direction of the diameter does not overlap), you can get a longer diameter, which contradicts the premise.
-
When the starting node $y$ is not on $\delta(s, t)$, there are two cases:
- When the furthest node $z$ reached by $y$ crosses $\delta(s, t)$, mark the intersecting node as $x$. At this time, $\delta(y, z) = \delta(y, x) + \delta(x, z)$. And at this time $\delta(y, z) > \delta(y, t)$, so $\delta(x, z) > \delta(x, t)$. According to the conclusion of 1, this assumption is not established.
- When the furthest node $z$ reached by $y$ does not intersect with $\delta(s, t)$, define the first node on the simple path from $y$ to $t$ that also exists on the simple path $\delta(s, t)$ as $x$, and the last node on the simple path $\delta(y, z)$ as $x'$. As shown in the figure below. Then according to the assumption, $\delta(y, z) \geq \delta(y, t) \Rightarrow \delta(x', z) \geq \delta(x', x) + \delta(x, t)$. In this case, $\delta(x, z) \geq \delta(x, t)$, which does not match the premise that $\delta(s, t)$ corresponds to the diameter, so the furthest node $z$ of $y$ cannot be outside the path corresponding to the diameter from $s$ to $t$.
Therefore, the theorem holds.
Similar problems:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 | |