Tree
Depth-First Search
Breadth-First Search
Binary Tree
Description
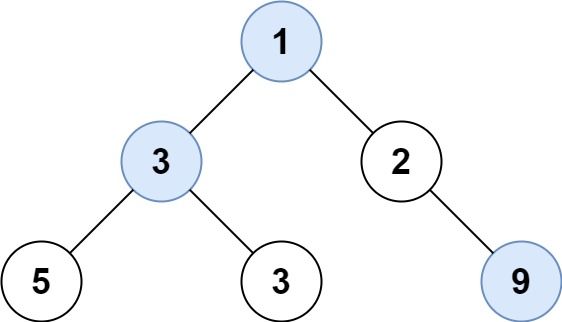
Given the root of a binary tree, return an array of the largest value in each row of the tree (0-indexed) .
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,3,2,5,3,null,9]
Output: [1,3,9]
Example 2:
Input: root = [1,2,3]
Output: [1,3]
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree will be in the range [0, 104 ].
-231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
Solutions
Solution 1
Python3 Java C++ Go TypeScript Rust
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23 # Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution :
def largestValues ( self , root : Optional [ TreeNode ]) -> List [ int ]:
if root is None :
return []
q = deque ([ root ])
ans = []
while q :
t = - inf
for _ in range ( len ( q )):
node = q . popleft ()
t = max ( t , node . val )
if node . left :
q . append ( node . left )
if node . right :
q . append ( node . right )
ans . append ( t )
return ans
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List < Integer > largestValues ( TreeNode root ) {
List < Integer > ans = new ArrayList <> ();
if ( root == null ) {
return ans ;
}
Deque < TreeNode > q = new ArrayDeque <> ();
q . offer ( root );
while ( ! q . isEmpty ()) {
int t = q . peek (). val ;
for ( int i = q . size (); i > 0 ; -- i ) {
TreeNode node = q . poll ();
t = Math . max ( t , node . val );
if ( node . left != null ) {
q . offer ( node . left );
}
if ( node . right != null ) {
q . offer ( node . right );
}
}
ans . add ( t );
}
return ans ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public :
vector < int > largestValues ( TreeNode * root ) {
if ( ! root ) return {};
queue < TreeNode *> q {{ root }};
vector < int > ans ;
while ( ! q . empty ()) {
int t = q . front () -> val ;
for ( int i = q . size (); i ; -- i ) {
TreeNode * node = q . front ();
t = max ( t , node -> val );
q . pop ();
if ( node -> left ) q . push ( node -> left );
if ( node -> right ) q . push ( node -> right );
}
ans . push_back ( t );
}
return ans ;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func largestValues ( root * TreeNode ) [] int {
var ans [] int
if root == nil {
return ans
}
q := [] * TreeNode { root }
for len ( q ) > 0 {
t := q [ 0 ]. Val
for i := len ( q ); i > 0 ; i -- {
node := q [ 0 ]
q = q [ 1 :]
t = max ( t , node . Val )
if node . Left != nil {
q = append ( q , node . Left )
}
if node . Right != nil {
q = append ( q , node . Right )
}
}
ans = append ( ans , t )
}
return ans
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function largestValues ( root : TreeNode | null ) : number [] {
const res : number [] = [];
const queue : TreeNode [] = [];
if ( root ) {
queue . push ( root );
}
while ( queue . length ) {
const n = queue . length ;
let max = - Infinity ;
for ( let i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) {
const { val , left , right } = queue . shift ();
max = Math . max ( max , val );
left && queue . push ( left );
right && queue . push ( right );
}
res . push ( max );
}
return res ;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46 // Definition for a binary tree node.
// #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
// pub struct TreeNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// }
//
// impl TreeNode {
// #[inline]
// pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// TreeNode {
// val,
// left: None,
// right: None
// }
// }
// }
use std :: rc :: Rc ;
use std :: cell :: RefCell ;
use std :: collections :: VecDeque ;
impl Solution {
pub fn largest_values ( root : Option < Rc < RefCell < TreeNode >>> ) -> Vec < i32 > {
let mut res = Vec :: new ();
let mut queue = VecDeque :: new ();
if root . is_some () {
queue . push_back ( root . clone ());
}
while ! queue . is_empty () {
let mut max = i32 :: MIN ;
for _ in 0 .. queue . len () {
let node = queue . pop_front (). unwrap ();
let node = node . as_ref (). unwrap (). borrow ();
max = max . max ( node . val );
if node . left . is_some () {
queue . push_back ( node . left . clone ());
}
if node . right . is_some () {
queue . push_back ( node . right . clone ());
}
}
res . push ( max );
}
res
}
}
Solution 2
Python3 Java C++ Go TypeScript Rust
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21 # Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution :
def largestValues ( self , root : Optional [ TreeNode ]) -> List [ int ]:
def dfs ( root , curr ):
if root is None :
return
if curr == len ( ans ):
ans . append ( root . val )
else :
ans [ curr ] = max ( ans [ curr ], root . val )
dfs ( root . left , curr + 1 )
dfs ( root . right , curr + 1 )
ans = []
dfs ( root , 0 )
return ans
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private List < Integer > ans = new ArrayList <> ();
public List < Integer > largestValues ( TreeNode root ) {
dfs ( root , 0 );
return ans ;
}
private void dfs ( TreeNode root , int curr ) {
if ( root == null ) {
return ;
}
if ( curr == ans . size ()) {
ans . add ( root . val );
} else {
ans . set ( curr , Math . max ( ans . get ( curr ), root . val ));
}
dfs ( root . left , curr + 1 );
dfs ( root . right , curr + 1 );
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public :
vector < int > ans ;
vector < int > largestValues ( TreeNode * root ) {
dfs ( root , 0 );
return ans ;
}
void dfs ( TreeNode * root , int curr ) {
if ( ! root ) return ;
if ( curr == ans . size ())
ans . push_back ( root -> val );
else
ans [ curr ] = max ( ans [ curr ], root -> val );
dfs ( root -> left , curr + 1 );
dfs ( root -> right , curr + 1 );
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func largestValues ( root * TreeNode ) [] int {
var ans [] int
var dfs func ( * TreeNode , int )
dfs = func ( root * TreeNode , curr int ) {
if root == nil {
return
}
if curr == len ( ans ) {
ans = append ( ans , root . Val )
} else {
ans [ curr ] = max ( ans [ curr ], root . Val )
}
dfs ( root . Left , curr + 1 )
dfs ( root . Right , curr + 1 )
}
dfs ( root , 0 )
return ans
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function largestValues ( root : TreeNode | null ) : number [] {
const res = [];
const dfs = ( root : TreeNode | null , depth : number ) => {
if ( root == null ) {
return ;
}
const { val , left , right } = root ;
if ( res . length == depth ) {
res . push ( val );
} else {
res [ depth ] = Math . max ( res [ depth ], val );
}
dfs ( left , depth + 1 );
dfs ( right , depth + 1 );
};
dfs ( root , 0 );
return res ;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41 // Definition for a binary tree node.
// #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
// pub struct TreeNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// }
//
// impl TreeNode {
// #[inline]
// pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// TreeNode {
// val,
// left: None,
// right: None
// }
// }
// }
use std :: rc :: Rc ;
use std :: cell :: RefCell ;
impl Solution {
fn dfs ( root : & Option < Rc < RefCell < TreeNode >>> , depth : usize , res : & mut Vec < i32 > ) {
if root . is_none () {
return ;
}
let node = root . as_ref (). unwrap (). borrow ();
if res . len () == depth {
res . push ( node . val );
} else {
res [ depth ] = res [ depth ]. max ( node . val );
}
Self :: dfs ( & node . left , depth + 1 , res );
Self :: dfs ( & node . right , depth + 1 , res );
}
pub fn largest_values ( root : Option < Rc < RefCell < TreeNode >>> ) -> Vec < i32 > {
let mut res = Vec :: new ();
Self :: dfs ( & root , 0 , & mut res );
res
}
}
GitHub