Union Find
Graph
Topological Sort
Array
Matrix
Sorting
Description
Given an m x n matrix, return a new matrix answer where answer[row][col] is the rank of matrix[row][col].
The rank is an integer that represents how large an element is compared to other elements. It is calculated using the following rules:
The rank is an integer starting from 1.
If two elements p and q are in the same row or column , then:
If p < q then rank(p) < rank(q)
If p == q then rank(p) == rank(q)
If p > q then rank(p) > rank(q)
The rank should be as small as possible.
The test cases are generated so that answer is unique under the given rules.
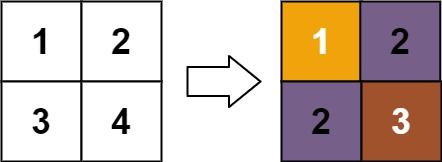
Example 1:
Input: matrix = [[1,2],[3,4]]
Output: [[1,2],[2,3]]
Explanation:
The rank of matrix[0][0] is 1 because it is the smallest integer in its row and column.
The rank of matrix[0][1] is 2 because matrix[0][1] > matrix[0][0] and matrix[0][0] is rank 1.
The rank of matrix[1][0] is 2 because matrix[1][0] > matrix[0][0] and matrix[0][0] is rank 1.
The rank of matrix[1][1] is 3 because matrix[1][1] > matrix[0][1], matrix[1][1] > matrix[1][0], and both matrix[0][1] and matrix[1][0] are rank 2.
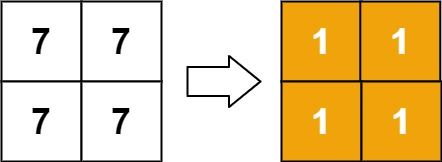
Example 2:
Input: matrix = [[7,7],[7,7]]
Output: [[1,1],[1,1]]
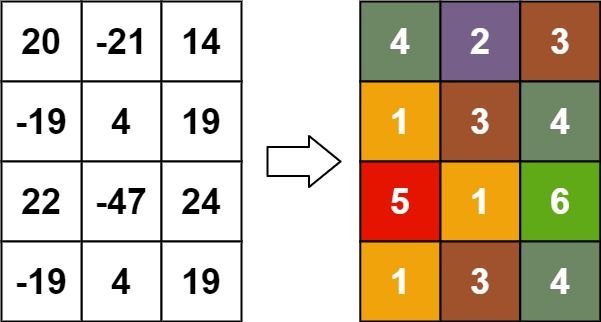
Example 3:
Input: matrix = [[20,-21,14],[-19,4,19],[22,-47,24],[-19,4,19]]
Output: [[4,2,3],[1,3,4],[5,1,6],[1,3,4]]
Constraints:
m == matrix.lengthn == matrix[i].length1 <= m, n <= 500-109 <= matrix[row][col] <= 109
Solutions
Solution 1
Python3 Java C++ Go
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48 class UnionFind :
def __init__ ( self , n ):
self . p = list ( range ( n ))
self . size = [ 1 ] * n
def find ( self , x ):
if self . p [ x ] != x :
self . p [ x ] = self . find ( self . p [ x ])
return self . p [ x ]
def union ( self , a , b ):
pa , pb = self . find ( a ), self . find ( b )
if pa != pb :
if self . size [ pa ] > self . size [ pb ]:
self . p [ pb ] = pa
self . size [ pa ] += self . size [ pb ]
else :
self . p [ pa ] = pb
self . size [ pb ] += self . size [ pa ]
def reset ( self , x ):
self . p [ x ] = x
self . size [ x ] = 1
class Solution :
def matrixRankTransform ( self , matrix : List [ List [ int ]]) -> List [ List [ int ]]:
m , n = len ( matrix ), len ( matrix [ 0 ])
d = defaultdict ( list )
for i , row in enumerate ( matrix ):
for j , v in enumerate ( row ):
d [ v ] . append (( i , j ))
row_max = [ 0 ] * m
col_max = [ 0 ] * n
ans = [[ 0 ] * n for _ in range ( m )]
uf = UnionFind ( m + n )
for v in sorted ( d ):
rank = defaultdict ( int )
for i , j in d [ v ]:
uf . union ( i , j + m )
for i , j in d [ v ]:
rank [ uf . find ( i )] = max ( rank [ uf . find ( i )], row_max [ i ], col_max [ j ])
for i , j in d [ v ]:
ans [ i ][ j ] = row_max [ i ] = col_max [ j ] = 1 + rank [ uf . find ( i )]
for i , j in d [ v ]:
uf . reset ( i )
uf . reset ( j + m )
return ans
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75 class UnionFind {
private int [] p ;
private int [] size ;
public UnionFind ( int n ) {
p = new int [ n ] ;
size = new int [ n ] ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; ++ i ) {
p [ i ] = i ;
size [ i ] = 1 ;
}
}
public int find ( int x ) {
if ( p [ x ] != x ) {
p [ x ] = find ( p [ x ] );
}
return p [ x ] ;
}
public void union ( int a , int b ) {
int pa = find ( a ), pb = find ( b );
if ( pa != pb ) {
if ( size [ pa ] > size [ pb ] ) {
p [ pb ] = pa ;
size [ pa ] += size [ pb ] ;
} else {
p [ pa ] = pb ;
size [ pb ] += size [ pa ] ;
}
}
}
public void reset ( int x ) {
p [ x ] = x ;
size [ x ] = 1 ;
}
}
class Solution {
public int [][] matrixRankTransform ( int [][] matrix ) {
int m = matrix . length , n = matrix [ 0 ] . length ;
TreeMap < Integer , List < int []>> d = new TreeMap <> ();
for ( int i = 0 ; i < m ; ++ i ) {
for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j ) {
d . computeIfAbsent ( matrix [ i ][ j ] , k -> new ArrayList <> ()). add ( new int [] { i , j });
}
}
int [] rowMax = new int [ m ] ;
int [] colMax = new int [ n ] ;
int [][] ans = new int [ m ][ n ] ;
UnionFind uf = new UnionFind ( m + n );
int [] rank = new int [ m + n ] ;
for ( var ps : d . values ()) {
for ( var p : ps ) {
uf . union ( p [ 0 ] , p [ 1 ] + m );
}
for ( var p : ps ) {
int i = p [ 0 ] , j = p [ 1 ] ;
rank [ uf . find ( i ) ] = Math . max ( rank [ uf . find ( i ) ] , Math . max ( rowMax [ i ] , colMax [ j ] ));
}
for ( var p : ps ) {
int i = p [ 0 ] , j = p [ 1 ] ;
ans [ i ][ j ] = 1 + rank [ uf . find ( i ) ] ;
rowMax [ i ] = ans [ i ][ j ] ;
colMax [ j ] = ans [ i ][ j ] ;
}
for ( var p : ps ) {
uf . reset ( p [ 0 ] );
uf . reset ( p [ 1 ] + m );
}
}
return ans ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70 class UnionFind {
public :
UnionFind ( int n ) {
p = vector < int > ( n );
size = vector < int > ( n , 1 );
iota ( p . begin (), p . end (), 0 );
}
void unite ( int a , int b ) {
int pa = find ( a ), pb = find ( b );
if ( pa != pb ) {
if ( size [ pa ] > size [ pb ]) {
p [ pb ] = pa ;
size [ pa ] += size [ pb ];
} else {
p [ pa ] = pb ;
size [ pb ] += size [ pa ];
}
}
}
int find ( int x ) {
if ( p [ x ] != x ) {
p [ x ] = find ( p [ x ]);
}
return p [ x ];
}
void reset ( int x ) {
p [ x ] = x ;
size [ x ] = 1 ;
}
private :
vector < int > p , size ;
};
class Solution {
public :
vector < vector < int >> matrixRankTransform ( vector < vector < int >>& matrix ) {
int m = matrix . size (), n = matrix [ 0 ]. size ();
map < int , vector < pair < int , int >>> d ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < m ; ++ i ) {
for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j ) {
d [ matrix [ i ][ j ]]. push_back ({ i , j });
}
}
vector < int > rowMax ( m );
vector < int > colMax ( n );
vector < vector < int >> ans ( m , vector < int > ( n ));
UnionFind uf ( m + n );
vector < int > rank ( m + n );
for ( auto & [ _ , ps ] : d ) {
for ( auto & [ i , j ] : ps ) {
uf . unite ( i , j + m );
}
for ( auto & [ i , j ] : ps ) {
rank [ uf . find ( i )] = max ({ rank [ uf . find ( i )], rowMax [ i ], colMax [ j ]});
}
for ( auto & [ i , j ] : ps ) {
ans [ i ][ j ] = rowMax [ i ] = colMax [ j ] = 1 + rank [ uf . find ( i )];
}
for ( auto & [ i , j ] : ps ) {
uf . reset ( i );
uf . reset ( j + m );
}
}
return ans ;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82 type unionFind struct {
p , size [] int
}
func newUnionFind ( n int ) * unionFind {
p := make ([] int , n )
size := make ([] int , n )
for i := range p {
p [ i ] = i
size [ i ] = 1
}
return & unionFind { p , size }
}
func ( uf * unionFind ) find ( x int ) int {
if uf . p [ x ] != x {
uf . p [ x ] = uf . find ( uf . p [ x ])
}
return uf . p [ x ]
}
func ( uf * unionFind ) union ( a , b int ) {
pa , pb := uf . find ( a ), uf . find ( b )
if pa != pb {
if uf . size [ pa ] > uf . size [ pb ] {
uf . p [ pb ] = pa
uf . size [ pa ] += uf . size [ pb ]
} else {
uf . p [ pa ] = pb
uf . size [ pb ] += uf . size [ pa ]
}
}
}
func ( uf * unionFind ) reset ( x int ) {
uf . p [ x ] = x
uf . size [ x ] = 1
}
func matrixRankTransform ( matrix [][] int ) [][] int {
m , n := len ( matrix ), len ( matrix [ 0 ])
type pair struct { i , j int }
d := map [ int ][] pair {}
for i , row := range matrix {
for j , v := range row {
d [ v ] = append ( d [ v ], pair { i , j })
}
}
rowMax := make ([] int , m )
colMax := make ([] int , n )
ans := make ([][] int , m )
for i := range ans {
ans [ i ] = make ([] int , n )
}
vs := [] int {}
for v := range d {
vs = append ( vs , v )
}
sort . Ints ( vs )
uf := newUnionFind ( m + n )
rank := make ([] int , m + n )
for _ , v := range vs {
ps := d [ v ]
for _ , p := range ps {
uf . union ( p . i , p . j + m )
}
for _ , p := range ps {
i , j := p . i , p . j
rank [ uf . find ( i )] = max ( rank [ uf . find ( i )], max ( rowMax [ i ], colMax [ j ]))
}
for _ , p := range ps {
i , j := p . i , p . j
ans [ i ][ j ] = 1 + rank [ uf . find ( i )]
rowMax [ i ], colMax [ j ] = ans [ i ][ j ], ans [ i ][ j ]
}
for _ , p := range ps {
uf . reset ( p . i )
uf . reset ( p . j + m )
}
}
return ans
}
GitHub