Array
Matrix
Description
Given an m x n binary matrix mat, return the number of special positions in mat.
A position (i, j) is called special if mat[i][j] == 1 and all other elements in row i and column j are 0 (rows and columns are 0-indexed ).
Example 1:
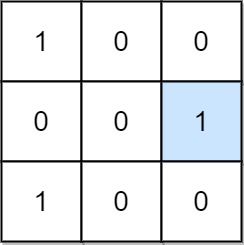
Input: mat = [[1,0,0],[0,0,1],[1,0,0]]
Output: 1
Explanation: (1, 2) is a special position because mat[1][2] == 1 and all other elements in row 1 and column 2 are 0.
Example 2:
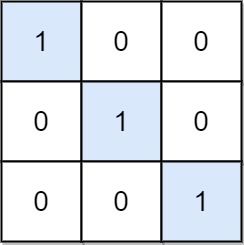
Input: mat = [[1,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,1]]
Output: 3
Explanation: (0, 0), (1, 1) and (2, 2) are special positions.
Constraints:
m == mat.lengthn == mat[i].length1 <= m, n <= 100mat[i][j] is either 0 or 1.
Solutions
Solution 1
Python3 Java C++ Go TypeScript Rust C
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15 class Solution :
def numSpecial ( self , mat : List [ List [ int ]]) -> int :
m , n = len ( mat ), len ( mat [ 0 ])
r = [ 0 ] * m
c = [ 0 ] * n
for i , row in enumerate ( mat ):
for j , v in enumerate ( row ):
r [ i ] += v
c [ j ] += v
ans = 0
for i in range ( m ):
for j in range ( n ):
if mat [ i ][ j ] == 1 and r [ i ] == 1 and c [ j ] == 1 :
ans += 1
return ans
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22 class Solution {
public int numSpecial ( int [][] mat ) {
int m = mat . length , n = mat [ 0 ] . length ;
int [] r = new int [ m ] ;
int [] c = new int [ n ] ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < m ; ++ i ) {
for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j ) {
r [ i ] += mat [ i ][ j ] ;
c [ j ] += mat [ i ][ j ] ;
}
}
int ans = 0 ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < m ; ++ i ) {
for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j ) {
if ( mat [ i ][ j ] == 1 && r [ i ] == 1 && c [ j ] == 1 ) {
++ ans ;
}
}
}
return ans ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22 class Solution {
public :
int numSpecial ( vector < vector < int >>& mat ) {
int m = mat . size (), n = mat [ 0 ]. size ();
vector < int > r ( m ), c ( n );
for ( int i = 0 ; i < m ; ++ i ) {
for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j ) {
r [ i ] += mat [ i ][ j ];
c [ j ] += mat [ i ][ j ];
}
}
int ans = 0 ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < m ; ++ i ) {
for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j ) {
if ( mat [ i ][ j ] == 1 && r [ i ] == 1 && c [ j ] == 1 ) {
++ ans ;
}
}
}
return ans ;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19 func numSpecial ( mat [][] int ) int {
m , n := len ( mat ), len ( mat [ 0 ])
r , c := make ([] int , m ), make ([] int , n )
for i , row := range mat {
for j , v := range row {
r [ i ] += v
c [ j ] += v
}
}
ans := 0
for i , x := range r {
for j , y := range c {
if mat [ i ][ j ] == 1 && x == 1 && y == 1 {
ans ++
}
}
}
return ans
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25 function numSpecial ( mat : number [][]) : number {
const m = mat . length ;
const n = mat [ 0 ]. length ;
const rows = new Array ( m ). fill ( 0 );
const cols = new Array ( n ). fill ( 0 );
for ( let i = 0 ; i < m ; i ++ ) {
for ( let j = 0 ; j < n ; j ++ ) {
if ( mat [ i ][ j ] === 1 ) {
rows [ i ] ++ ;
cols [ j ] ++ ;
}
}
}
let res = 0 ;
for ( let i = 0 ; i < m ; i ++ ) {
for ( let j = 0 ; j < n ; j ++ ) {
if ( mat [ i ][ j ] === 1 && rows [ i ] === 1 && cols [ j ] === 1 ) {
res ++ ;
}
}
}
return res ;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24 impl Solution {
pub fn num_special ( mat : Vec < Vec < i32 >> ) -> i32 {
let m = mat . len ();
let n = mat [ 0 ]. len ();
let mut rows = vec! [ 0 ; m ];
let mut cols = vec! [ 0 ; n ];
for i in 0 .. m {
for j in 0 .. n {
rows [ i ] += mat [ i ][ j ];
cols [ j ] += mat [ i ][ j ];
}
}
let mut res = 0 ;
for i in 0 .. m {
for j in 0 .. n {
if mat [ i ][ j ] == 1 && rows [ i ] == 1 && cols [ j ] == 1 {
res += 1 ;
}
}
}
res
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27 int numSpecial ( int ** mat , int matSize , int * matColSize ) {
int m = matSize ;
int n = * matColSize ;
int * rows = ( int * ) malloc ( sizeof ( int ) * m );
int * cols = ( int * ) malloc ( sizeof ( int ) * n );
memset ( rows , 0 , sizeof ( int ) * m );
memset ( cols , 0 , sizeof ( int ) * n );
for ( int i = 0 ; i < m ; i ++ ) {
for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; j ++ ) {
if ( mat [ i ][ j ] == 1 ) {
rows [ i ] ++ ;
cols [ j ] ++ ;
}
}
}
int res = 0 ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < m ; i ++ ) {
for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; j ++ ) {
if ( mat [ i ][ j ] == 1 && rows [ i ] == 1 && cols [ j ] == 1 ) {
res ++ ;
}
}
}
free ( rows );
free ( cols );
return res ;
}