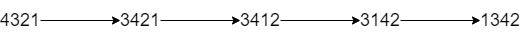Greedy
Binary Indexed Tree
Segment Tree
String
Description
You are given a string num representing the digits of a very large integer and an integer k. You are allowed to swap any two adjacent digits of the integer at most k times.
Return the minimum integer you can obtain also as a string .
Example 1:
Input: num = "4321", k = 4
Output: "1342"
Explanation: The steps to obtain the minimum integer from 4321 with 4 adjacent swaps are shown.
Example 2:
Input: num = "100", k = 1
Output: "010"
Explanation: It's ok for the output to have leading zeros, but the input is guaranteed not to have any leading zeros.
Example 3:
Input: num = "36789", k = 1000
Output: "36789"
Explanation: We can keep the number without any swaps.
Constraints:
1 <= num.length <= 3 * 104 num consists of only digits and does not contain leading zeros .1 <= k <= 109
Solutions
Solution 1
Python3 Java C++ Go
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43 class BinaryIndexedTree :
def __init__ ( self , n ):
self . n = n
self . c = [ 0 ] * ( n + 1 )
@staticmethod
def lowbit ( x ):
return x & - x
def update ( self , x , delta ):
while x <= self . n :
self . c [ x ] += delta
x += BinaryIndexedTree . lowbit ( x )
def query ( self , x ):
s = 0
while x :
s += self . c [ x ]
x -= BinaryIndexedTree . lowbit ( x )
return s
class Solution :
def minInteger ( self , num : str , k : int ) -> str :
pos = defaultdict ( deque )
for i , v in enumerate ( num , 1 ):
pos [ int ( v )] . append ( i )
ans = []
n = len ( num )
tree = BinaryIndexedTree ( n )
for i in range ( 1 , n + 1 ):
for v in range ( 10 ):
q = pos [ v ]
if q :
j = q [ 0 ]
dist = tree . query ( n ) - tree . query ( j ) + j - i
if dist <= k :
k -= dist
q . popleft ()
ans . append ( str ( v ))
tree . update ( j , 1 )
break
return '' . join ( ans )
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61 class Solution {
public String minInteger ( String num , int k ) {
Queue < Integer >[] pos = new Queue [ 10 ] ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; ++ i ) {
pos [ i ] = new ArrayDeque <> ();
}
int n = num . length ();
for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; ++ i ) {
pos [ num . charAt ( i ) - '0' ] . offer ( i + 1 );
}
StringBuilder ans = new StringBuilder ();
BinaryIndexedTree tree = new BinaryIndexedTree ( n );
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++ i ) {
for ( int v = 0 ; v < 10 ; ++ v ) {
if ( ! pos [ v ] . isEmpty ()) {
Queue < Integer > q = pos [ v ] ;
int j = q . peek ();
int dist = tree . query ( n ) - tree . query ( j ) + j - i ;
if ( dist <= k ) {
k -= dist ;
q . poll ();
ans . append ( v );
tree . update ( j , 1 );
break ;
}
}
}
}
return ans . toString ();
}
}
class BinaryIndexedTree {
private int n ;
private int [] c ;
public BinaryIndexedTree ( int n ) {
this . n = n ;
c = new int [ n + 1 ] ;
}
public void update ( int x , int delta ) {
while ( x <= n ) {
c [ x ] += delta ;
x += lowbit ( x );
}
}
public int query ( int x ) {
int s = 0 ;
while ( x > 0 ) {
s += c [ x ] ;
x -= lowbit ( x );
}
return s ;
}
public static int lowbit ( int x ) {
return x & - x ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57 class BinaryIndexedTree {
public :
int n ;
vector < int > c ;
BinaryIndexedTree ( int _n )
: n ( _n )
, c ( _n + 1 ) {}
void update ( int x , int delta ) {
while ( x <= n ) {
c [ x ] += delta ;
x += lowbit ( x );
}
}
int query ( int x ) {
int s = 0 ;
while ( x > 0 ) {
s += c [ x ];
x -= lowbit ( x );
}
return s ;
}
int lowbit ( int x ) {
return x & - x ;
}
};
class Solution {
public :
string minInteger ( string num , int k ) {
vector < queue < int >> pos ( 10 );
int n = num . size ();
for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; ++ i ) pos [ num [ i ] - '0' ]. push ( i + 1 );
BinaryIndexedTree * tree = new BinaryIndexedTree ( n );
string ans = "" ;
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++ i ) {
for ( int v = 0 ; v < 10 ; ++ v ) {
auto & q = pos [ v ];
if ( ! q . empty ()) {
int j = q . front ();
int dist = tree -> query ( n ) - tree -> query ( j ) + j - i ;
if ( dist <= k ) {
k -= dist ;
q . pop ();
ans += ( v + '0' );
tree -> update ( j , 1 );
break ;
}
}
}
}
return ans ;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55 type BinaryIndexedTree struct {
n int
c [] int
}
func newBinaryIndexedTree ( n int ) * BinaryIndexedTree {
c := make ([] int , n + 1 )
return & BinaryIndexedTree { n , c }
}
func ( this * BinaryIndexedTree ) lowbit ( x int ) int {
return x & - x
}
func ( this * BinaryIndexedTree ) update ( x , delta int ) {
for x <= this . n {
this . c [ x ] += delta
x += this . lowbit ( x )
}
}
func ( this * BinaryIndexedTree ) query ( x int ) int {
s := 0
for x > 0 {
s += this . c [ x ]
x -= this . lowbit ( x )
}
return s
}
func minInteger ( num string , k int ) string {
pos := make ([][] int , 10 )
for i , c := range num {
pos [ c - '0' ] = append ( pos [ c - '0' ], i + 1 )
}
n := len ( num )
tree := newBinaryIndexedTree ( n )
var ans strings . Builder
for i := 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ {
for v := 0 ; v < 10 ; v ++ {
if len ( pos [ v ]) > 0 {
j := pos [ v ][ 0 ]
dist := tree . query ( n ) - tree . query ( j ) + j - i
if dist <= k {
k -= dist
pos [ v ] = pos [ v ][ 1 :]
ans . WriteByte ( byte ( v + '0' ))
tree . update ( j , 1 )
break
}
}
}
}
return ans . String ()
}
GitHub