2090. K Radius Subarray Averages
Description
You are given a 0-indexed array nums of n integers, and an integer k.
The k-radius average for a subarray of nums centered at some index i with the radius k is the average of all elements in nums between the indices i - k and i + k (inclusive). If there are less than k elements before or after the index i, then the k-radius average is -1.
Build and return an array avgs of length n where avgs[i] is the k-radius average for the subarray centered at index i.
The average of x elements is the sum of the x elements divided by x, using integer division. The integer division truncates toward zero, which means losing its fractional part.
- For example, the average of four elements
2,3,1, and5is(2 + 3 + 1 + 5) / 4 = 11 / 4 = 2.75, which truncates to2.
Example 1:
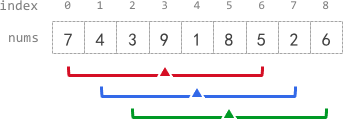
Input: nums = [7,4,3,9,1,8,5,2,6], k = 3 Output: [-1,-1,-1,5,4,4,-1,-1,-1] Explanation: - avg[0], avg[1], and avg[2] are -1 because there are less than k elements before each index. - The sum of the subarray centered at index 3 with radius 3 is: 7 + 4 + 3 + 9 + 1 + 8 + 5 = 37. Using integer division, avg[3] = 37 / 7 = 5. - For the subarray centered at index 4, avg[4] = (4 + 3 + 9 + 1 + 8 + 5 + 2) / 7 = 4. - For the subarray centered at index 5, avg[5] = (3 + 9 + 1 + 8 + 5 + 2 + 6) / 7 = 4. - avg[6], avg[7], and avg[8] are -1 because there are less than k elements after each index.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [100000], k = 0 Output: [100000] Explanation: - The sum of the subarray centered at index 0 with radius 0 is: 100000. avg[0] = 100000 / 1 = 100000.
Example 3:
Input: nums = [8], k = 100000 Output: [-1] Explanation: - avg[0] is -1 because there are less than k elements before and after index 0.
Constraints:
n == nums.length1 <= n <= 1050 <= nums[i], k <= 105
Solutions
Solution 1: Sliding Window
The number of elements in a subarray with radius $k$ is $k \times 2 + 1$. Therefore, we can redefine $k$ as $k \times 2 + 1$.
We create an answer array $ans$ of length $n$, initially each element is $-1$.
Next, we first check whether $k$ is greater than the length $n$ of the array nums. If it is, we directly return the answer array.
Otherwise, we calculate the sum $s$ of the first $k$ elements of the array nums, and assign the quotient of $s$ divided by $k$ to the $j$-th element of the answer array $ans$, where $j = k / 2$.
Then, we start traversing the array nums from $k$. For each iteration, we add the value of $nums[i]$ to $s$ and subtract the value of $nums[i - k]$, and update $j = j + 1$. Then we get the sum $s$ of the subarray with the $j$-th element as the center and radius $k$, and assign the quotient of $s$ divided by $k$ to the $j$-th element of the answer array $ans$.
Finally, we return the answer array.
The time complexity is $O(n)$, where $n$ is the length of the array nums. Ignoring the space consumption of the answer, the space complexity is $O(1)$.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | |
Solution 2: Another Way of Sliding Window
We maintain a window of size $k \times 2 + 1$, and let the sum of all elements in the window be $s$.
Like Solution 1, we create an answer array $ans$ of length $n$, initially each element is $-1$.
Next, we traverse the array nums, add the value of $nums[i]$ to the sum $s$. If $i \geq k \times 2$, it means the window size is $k \times 2 + 1$ now, so we set $ans[i-k] = \frac{s}{k \times 2 + 1}$, then we subtract the value of $nums[i - k \times 2]$ from the sum $s$. Continue to the next element.
Finally, we return the answer array.
The time complexity is $O(n)$, where $n$ is the length of the array nums. Ignoring the space consumption of the answer, the space complexity is $O(1)$.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | |