Backtracking
Breadth-First Search
Depth-First Search
Graph
Description
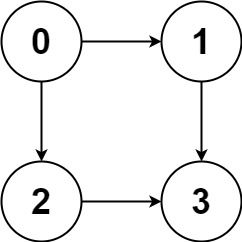
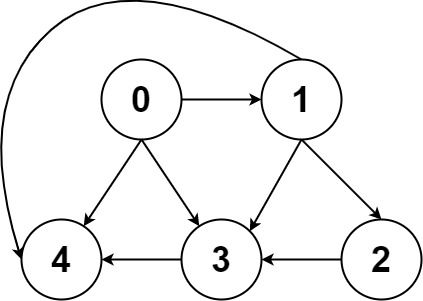
Given a directed acyclic graph (DAG ) of n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1, find all possible paths from node 0 to node n - 1 and return them in any order .
The graph is given as follows: graph[i] is a list of all nodes you can visit from node i (i.e., there is a directed edge from node i to node graph[i][j]).
Example 1:
Input: graph = [[1,2],[3],[3],[]]
Output: [[0,1,3],[0,2,3]]
Explanation: There are two paths: 0 -> 1 -> 3 and 0 -> 2 -> 3.
Example 2:
Input: graph = [[4,3,1],[3,2,4],[3],[4],[]]
Output: [[0,4],[0,3,4],[0,1,3,4],[0,1,2,3,4],[0,1,4]]
Constraints:
n == graph.length2 <= n <= 150 <= graph[i][j] < ngraph[i][j] != i (i.e., there will be no self-loops).All the elements of graph[i] are unique .
The input graph is guaranteed to be a DAG .
Solutions
Solution 1
Python3 Java C++ Go Rust JavaScript TypeScript
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14 class Solution :
def allPathsSourceTarget ( self , graph : List [ List [ int ]]) -> List [ List [ int ]]:
n = len ( graph )
q = deque ([[ 0 ]])
ans = []
while q :
path = q . popleft ()
u = path [ - 1 ]
if u == n - 1 :
ans . append ( path )
continue
for v in graph [ u ]:
q . append ( path + [ v ])
return ans
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22 class Solution {
public List < List < Integer >> allPathsSourceTarget ( int [][] graph ) {
int n = graph . length ;
Queue < List < Integer >> queue = new ArrayDeque <> ();
queue . offer ( Arrays . asList ( 0 ));
List < List < Integer >> ans = new ArrayList <> ();
while ( ! queue . isEmpty ()) {
List < Integer > path = queue . poll ();
int u = path . get ( path . size () - 1 );
if ( u == n - 1 ) {
ans . add ( path );
continue ;
}
for ( int v : graph [ u ] ) {
List < Integer > next = new ArrayList <> ( path );
next . add ( v );
queue . offer ( next );
}
}
return ans ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25 class Solution {
public :
vector < vector < int >> graph ;
vector < vector < int >> ans ;
vector < vector < int >> allPathsSourceTarget ( vector < vector < int >>& graph ) {
this -> graph = graph ;
vector < int > path ;
path . push_back ( 0 );
dfs ( 0 , path );
return ans ;
}
void dfs ( int i , vector < int > path ) {
if ( i == graph . size () - 1 ) {
ans . push_back ( path );
return ;
}
for ( int j : graph [ i ]) {
path . push_back ( j );
dfs ( j , path );
path . pop_back ();
}
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21 func allPathsSourceTarget ( graph [][] int ) [][] int {
var path [] int
path = append ( path , 0 )
var ans [][] int
var dfs func ( i int )
dfs = func ( i int ) {
if i == len ( graph ) - 1 {
ans = append ( ans , append ([] int ( nil ), path ... ))
return
}
for _ , j := range graph [ i ] {
path = append ( path , j )
dfs ( j )
path = path [: len ( path ) - 1 ]
}
}
dfs ( 0 )
return ans
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18 impl Solution {
fn dfs ( i : usize , path : & mut Vec < i32 > , res : & mut Vec < Vec < i32 >> , graph : & Vec < Vec < i32 >> ) {
path . push ( i as i32 );
if i == graph . len () - 1 {
res . push ( path . clone ());
}
for j in graph [ i ]. iter () {
Self :: dfs ( * j as usize , path , res , graph );
}
path . pop ();
}
pub fn all_paths_source_target ( graph : Vec < Vec < i32 >> ) -> Vec < Vec < i32 >> {
let mut res = Vec :: new ();
Self :: dfs ( 0 , & mut vec! [], & mut res , & graph );
res
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24 /**
* @param {number[][]} graph
* @return {number[][]}
*/
var allPathsSourceTarget = function ( graph ) {
const ans = [];
const t = [ 0 ];
const dfs = t => {
const cur = t [ t . length - 1 ];
if ( cur == graph . length - 1 ) {
ans . push ([... t ]);
return ;
}
for ( const v of graph [ cur ]) {
t . push ( v );
dfs ( t );
t . pop ();
}
};
dfs ( t );
return ans ;
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21 function allPathsSourceTarget ( graph : number [][]) : number [][] {
const ans : number [][] = [];
const dfs = ( path : number []) => {
const curr = path . at ( - 1 ) ! ;
if ( curr === graph . length - 1 ) {
ans . push ([... path ]);
return ;
}
for ( const v of graph [ curr ]) {
path . push ( v );
dfs ( path );
path . pop ();
}
};
dfs ([ 0 ]);
return ans ;
}
Solution 2