Depth-First Search
Dynamic Programming
Math
Number Theory
Tree
Description
There is an undirected tree with n nodes labeled from 1 to n. You are given the integer n and a 2D integer array edges of length n - 1, where edges[i] = [ui , vi ] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ui and vi in the tree.
Return the number of valid paths in the tree .
A path (a, b) is valid if there exists exactly one prime number among the node labels in the path from a to b.
Note that:
The path (a, b) is a sequence of distinct nodes starting with node a and ending with node b such that every two adjacent nodes in the sequence share an edge in the tree.
Path (a, b) and path (b, a) are considered the same and counted only once .
Example 1:
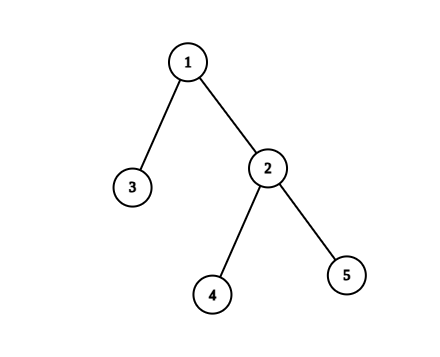
Input: n = 5, edges = [[1,2],[1,3],[2,4],[2,5]]
Output: 4
Explanation: The pairs with exactly one prime number on the path between them are:
- (1, 2) since the path from 1 to 2 contains prime number 2.
- (1, 3) since the path from 1 to 3 contains prime number 3.
- (1, 4) since the path from 1 to 4 contains prime number 2.
- (2, 4) since the path from 2 to 4 contains prime number 2.
It can be shown that there are only 4 valid paths.
Example 2:
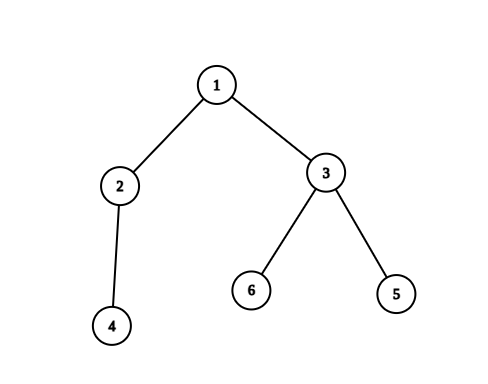
Input: n = 6, edges = [[1,2],[1,3],[2,4],[3,5],[3,6]]
Output: 6
Explanation: The pairs with exactly one prime number on the path between them are:
- (1, 2) since the path from 1 to 2 contains prime number 2.
- (1, 3) since the path from 1 to 3 contains prime number 3.
- (1, 4) since the path from 1 to 4 contains prime number 2.
- (1, 6) since the path from 1 to 6 contains prime number 3.
- (2, 4) since the path from 2 to 4 contains prime number 2.
- (3, 6) since the path from 3 to 6 contains prime number 3.
It can be shown that there are only 6 valid paths.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 105 edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 21 <= ui , vi <= nThe input is generated such that edges represent a valid tree.
Solutions
Solution 1: Preprocessing + Union-Find + Enumeration
We can preprocess to get all the prime numbers in \([1, n]\) , where \(prime[i]\) indicates whether \(i\) is a prime number.
Next, we build a graph \(g\) based on the two-dimensional integer array, where \(g[i]\) represents all the neighbor nodes of node \(i\) . If both nodes of an edge are not prime numbers, we merge these two nodes into the same connected component.
Then, we enumerate all prime numbers \(i\) in the range of \([1, n]\) , considering all paths that include \(i\) .
Since \(i\) is already a prime number, if \(i\) is an endpoint of the path, we only need to accumulate the sizes of all connected components adjacent to node \(i\) . If \(i\) is a middle point on the path, we need to accumulate the product of the sizes of any two adjacent connected components.
The time complexity is \(O(n \times \alpha(n))\) , and the space complexity is \(O(n)\) . Here, \(n\) is the number of nodes, and \(\alpha\) is the inverse function of the Ackermann function.
Python3 Java C++ Go TypeScript
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53 class UnionFind :
def __init__ ( self , n ):
self . p = list ( range ( n ))
self . size = [ 1 ] * n
def find ( self , x ):
if self . p [ x ] != x :
self . p [ x ] = self . find ( self . p [ x ])
return self . p [ x ]
def union ( self , a , b ):
pa , pb = self . find ( a ), self . find ( b )
if pa == pb :
return False
if self . size [ pa ] > self . size [ pb ]:
self . p [ pb ] = pa
self . size [ pa ] += self . size [ pb ]
else :
self . p [ pa ] = pb
self . size [ pb ] += self . size [ pa ]
return True
mx = 10 ** 5 + 10
prime = [ True ] * ( mx + 1 )
prime [ 0 ] = prime [ 1 ] = False
for i in range ( 2 , mx + 1 ):
if prime [ i ]:
for j in range ( i * i , mx + 1 , i ):
prime [ j ] = False
class Solution :
def countPaths ( self , n : int , edges : List [ List [ int ]]) -> int :
g = [[] for _ in range ( n + 1 )]
uf = UnionFind ( n + 1 )
for u , v in edges :
g [ u ] . append ( v )
g [ v ] . append ( u )
if prime [ u ] + prime [ v ] == 0 :
uf . union ( u , v )
ans = 0
for i in range ( 1 , n + 1 ):
if prime [ i ]:
t = 0
for j in g [ i ]:
if not prime [ j ]:
cnt = uf . size [ uf . find ( j )]
ans += cnt
ans += t * cnt
t += cnt
return ans
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94 class PrimeTable {
private final boolean [] prime ;
public PrimeTable ( int n ) {
prime = new boolean [ n + 1 ] ;
Arrays . fill ( prime , true );
prime [ 0 ] = false ;
prime [ 1 ] = false ;
for ( int i = 2 ; i <= n ; ++ i ) {
if ( prime [ i ] ) {
for ( int j = i + i ; j <= n ; j += i ) {
prime [ j ] = false ;
}
}
}
}
public boolean isPrime ( int x ) {
return prime [ x ] ;
}
}
class UnionFind {
private final int [] p ;
private final int [] size ;
public UnionFind ( int n ) {
p = new int [ n ] ;
size = new int [ n ] ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; ++ i ) {
p [ i ] = i ;
size [ i ] = 1 ;
}
}
public int find ( int x ) {
if ( p [ x ] != x ) {
p [ x ] = find ( p [ x ] );
}
return p [ x ] ;
}
public boolean union ( int a , int b ) {
int pa = find ( a ), pb = find ( b );
if ( pa == pb ) {
return false ;
}
if ( size [ pa ] > size [ pb ] ) {
p [ pb ] = pa ;
size [ pa ] += size [ pb ] ;
} else {
p [ pa ] = pb ;
size [ pb ] += size [ pa ] ;
}
return true ;
}
public int size ( int x ) {
return size [ find ( x ) ] ;
}
}
class Solution {
private static final PrimeTable PT = new PrimeTable ( 100010 );
public long countPaths ( int n , int [][] edges ) {
List < Integer >[] g = new List [ n + 1 ] ;
Arrays . setAll ( g , i -> new ArrayList <> ());
UnionFind uf = new UnionFind ( n + 1 );
for ( int [] e : edges ) {
int u = e [ 0 ] , v = e [ 1 ] ;
g [ u ] . add ( v );
g [ v ] . add ( u );
if ( ! PT . isPrime ( u ) && ! PT . isPrime ( v )) {
uf . union ( u , v );
}
}
long ans = 0 ;
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++ i ) {
if ( PT . isPrime ( i )) {
long t = 0 ;
for ( int j : g [ i ] ) {
if ( ! PT . isPrime ( j )) {
long cnt = uf . size ( j );
ans += cnt ;
ans += cnt * t ;
t += cnt ;
}
}
}
}
return ans ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82 const int mx = 1e5 + 10 ;
bool prime [ mx + 1 ];
int init = []() {
for ( int i = 2 ; i <= mx ; ++ i ) prime [ i ] = true ;
for ( int i = 2 ; i <= mx ; ++ i ) {
if ( prime [ i ]) {
for ( int j = i + i ; j <= mx ; j += i ) {
prime [ j ] = false ;
}
}
}
return 0 ;
}();
class UnionFind {
public :
UnionFind ( int n ) {
p = vector < int > ( n );
size = vector < int > ( n , 1 );
iota ( p . begin (), p . end (), 0 );
}
bool unite ( int a , int b ) {
int pa = find ( a ), pb = find ( b );
if ( pa == pb ) {
return false ;
}
if ( size [ pa ] > size [ pb ]) {
p [ pb ] = pa ;
size [ pa ] += size [ pb ];
} else {
p [ pa ] = pb ;
size [ pb ] += size [ pa ];
}
return true ;
}
int find ( int x ) {
if ( p [ x ] != x ) {
p [ x ] = find ( p [ x ]);
}
return p [ x ];
}
int getSize ( int x ) {
return size [ find ( x )];
}
private :
vector < int > p , size ;
};
class Solution {
public :
long long countPaths ( int n , vector < vector < int >>& edges ) {
vector < int > g [ n + 1 ];
UnionFind uf ( n + 1 );
for ( auto & e : edges ) {
int u = e [ 0 ], v = e [ 1 ];
g [ u ]. push_back ( v );
g [ v ]. push_back ( u );
if ( ! prime [ u ] && ! prime [ v ]) {
uf . unite ( u , v );
}
}
long long ans = 0 ;
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++ i ) {
if ( prime [ i ]) {
long long t = 0 ;
for ( int j : g [ i ]) {
if ( ! prime [ j ]) {
long long cnt = uf . getSize ( j );
ans += cnt ;
ans += cnt * t ;
t += cnt ;
}
}
}
}
return ans ;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82 const mx int = 1e5 + 10
var prime [ mx ] bool
func init () {
for i := 2 ; i < mx ; i ++ {
prime [ i ] = true
}
for i := 2 ; i < mx ; i ++ {
if prime [ i ] {
for j := i + i ; j < mx ; j += i {
prime [ j ] = false
}
}
}
}
type unionFind struct {
p , size [] int
}
func newUnionFind ( n int ) * unionFind {
p := make ([] int , n )
size := make ([] int , n )
for i := range p {
p [ i ] = i
size [ i ] = 1
}
return & unionFind { p , size }
}
func ( uf * unionFind ) find ( x int ) int {
if uf . p [ x ] != x {
uf . p [ x ] = uf . find ( uf . p [ x ])
}
return uf . p [ x ]
}
func ( uf * unionFind ) union ( a , b int ) bool {
pa , pb := uf . find ( a ), uf . find ( b )
if pa == pb {
return false
}
if uf . size [ pa ] > uf . size [ pb ] {
uf . p [ pb ] = pa
uf . size [ pa ] += uf . size [ pb ]
} else {
uf . p [ pa ] = pb
uf . size [ pb ] += uf . size [ pa ]
}
return true
}
func ( uf * unionFind ) getSize ( x int ) int {
return uf . size [ uf . find ( x )]
}
func countPaths ( n int , edges [][] int ) ( ans int64 ) {
uf := newUnionFind ( n + 1 )
g := make ([][] int , n + 1 )
for _ , e := range edges {
u , v := e [ 0 ], e [ 1 ]
g [ u ] = append ( g [ u ], v )
g [ v ] = append ( g [ v ], u )
if ! prime [ u ] && ! prime [ v ] {
uf . union ( u , v )
}
}
for i := 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ {
if prime [ i ] {
t := 0
for _ , j := range g [ i ] {
if ! prime [ j ] {
cnt := uf . getSize ( j )
ans += int64 ( cnt + cnt * t )
t += cnt
}
}
}
}
return
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75 const mx = 100010 ;
const prime = Array ( mx ). fill ( true );
prime [ 0 ] = prime [ 1 ] = false ;
for ( let i = 2 ; i <= mx ; ++ i ) {
if ( prime [ i ]) {
for ( let j = i + i ; j <= mx ; j += i ) {
prime [ j ] = false ;
}
}
}
class UnionFind {
p : number [];
size : number [];
constructor ( n : number ) {
this . p = Array ( n )
. fill ( 0 )
. map (( _ , i ) => i );
this . size = Array ( n ). fill ( 1 );
}
find ( x : number ) : number {
if ( this . p [ x ] !== x ) {
this . p [ x ] = this . find ( this . p [ x ]);
}
return this . p [ x ];
}
union ( a : number , b : number ) : boolean {
const [ pa , pb ] = [ this . find ( a ), this . find ( b )];
if ( pa === pb ) {
return false ;
}
if ( this . size [ pa ] > this . size [ pb ]) {
this . p [ pb ] = pa ;
this . size [ pa ] += this . size [ pb ];
} else {
this . p [ pa ] = pb ;
this . size [ pb ] += this . size [ pa ];
}
return true ;
}
getSize ( x : number ) : number {
return this . size [ this . find ( x )];
}
}
function countPaths ( n : number , edges : number [][]) : number {
const uf = new UnionFind ( n + 1 );
const g : number [][] = Array ( n + 1 )
. fill ( 0 )
. map (() => []);
for ( const [ u , v ] of edges ) {
g [ u ]. push ( v );
g [ v ]. push ( u );
if ( ! prime [ u ] && ! prime [ v ]) {
uf . union ( u , v );
}
}
let ans = 0 ;
for ( let i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++ i ) {
if ( prime [ i ]) {
let t = 0 ;
for ( let j of g [ i ]) {
if ( ! prime [ j ]) {
const cnt = uf . getSize ( j );
ans += cnt + t * cnt ;
t += cnt ;
}
}
}
}
return ans ;
}
Solution 2
Python3 Java C++
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42 class Solution :
def countPaths ( self , n : int , edges : List [ List [ int ]]) -> int :
def mul ( x , y ):
return x * y
def dfs ( x , f , con , prime , r ):
v = [ 1 - prime [ x ], prime [ x ]]
for y in con [ x ]:
if y == f :
continue
p = dfs ( y , x , con , prime , r )
r [ 0 ] += mul ( p [ 0 ], v [ 1 ]) + mul ( p [ 1 ], v [ 0 ])
if prime [ x ]:
v [ 1 ] += p [ 0 ]
else :
v [ 0 ] += p [ 0 ]
v [ 1 ] += p [ 1 ]
return v
prime = [ True ] * ( n + 1 )
prime [ 1 ] = False
all_primes = []
for i in range ( 2 , n + 1 ):
if prime [ i ]:
all_primes . append ( i )
for x in all_primes :
temp = i * x
if temp > n :
break
prime [ temp ] = False
if i % x == 0 :
break
con = [[] for _ in range ( n + 1 )]
for e in edges :
con [ e [ 0 ]] . append ( e [ 1 ])
con [ e [ 1 ]] . append ( e [ 0 ])
r = [ 0 ]
dfs ( 1 , 0 , con , prime , r )
return r [ 0 ]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69 class Solution {
public long countPaths ( int n , int [][] edges ) {
List < Boolean > prime = new ArrayList <> ( n + 1 );
for ( int i = 0 ; i <= n ; ++ i ) {
prime . add ( true );
}
prime . set ( 1 , false );
List < Integer > all = new ArrayList <> ();
for ( int i = 2 ; i <= n ; ++ i ) {
if ( prime . get ( i )) {
all . add ( i );
}
for ( int x : all ) {
int temp = i * x ;
if ( temp > n ) {
break ;
}
prime . set ( temp , false );
if ( i % x == 0 ) {
break ;
}
}
}
List < List < Integer >> con = new ArrayList <> ( n + 1 );
for ( int i = 0 ; i <= n ; ++ i ) {
con . add ( new ArrayList <> ());
}
for ( int [] e : edges ) {
con . get ( e [ 0 ] ). add ( e [ 1 ] );
con . get ( e [ 1 ] ). add ( e [ 0 ] );
}
long [] r = { 0 };
dfs ( 1 , 0 , con , prime , r );
return r [ 0 ] ;
}
private long mul ( long x , long y ) {
return x * y ;
}
private class Pair {
int first ;
int second ;
Pair ( int first , int second ) {
this . first = first ;
this . second = second ;
}
}
private Pair dfs ( int x , int f , List < List < Integer >> con , List < Boolean > prime , long [] r ) {
Pair v = new Pair ( ! prime . get ( x ) ? 1 : 0 , prime . get ( x ) ? 1 : 0 );
for ( int y : con . get ( x )) {
if ( y == f ) continue ;
Pair p = dfs ( y , x , con , prime , r );
r [ 0 ] += mul ( p . first , v . second ) + mul ( p . second , v . first );
if ( prime . get ( x )) {
v . second += p . first ;
} else {
v . first += p . first ;
v . second += p . second ;
}
}
return v ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51 class Solution {
long long mul ( long long x , long long y ) {
return x * y ;
}
pair < int , int > dfs ( int x , int f , const vector < vector < int >>& con , const vector < bool >& prime , long long & r ) {
pair < int , int > v = { ! prime [ x ], prime [ x ]};
for ( int y : con [ x ]) {
if ( y == f ) continue ;
const auto & p = dfs ( y , x , con , prime , r );
r += mul ( p . first , v . second ) + mul ( p . second , v . first );
if ( prime [ x ]) {
v . second += p . first ;
} else {
v . first += p . first ;
v . second += p . second ;
}
}
return v ;
}
public :
long long countPaths ( int n , vector < vector < int >>& edges ) {
vector < bool > prime ( n + 1 , true );
prime [ 1 ] = false ;
vector < int > all ;
for ( int i = 2 ; i <= n ; ++ i ) {
if ( prime [ i ]) {
all . push_back ( i );
}
for ( int x : all ) {
const int temp = i * x ;
if ( temp > n ) {
break ;
}
prime [ temp ] = false ;
if ( i % x == 0 ) {
break ;
}
}
}
vector < vector < int >> con ( n + 1 );
for ( const auto & e : edges ) {
con [ e [ 0 ]]. push_back ( e [ 1 ]);
con [ e [ 1 ]]. push_back ( e [ 0 ]);
}
long long r = 0 ;
dfs ( 1 , 0 , con , prime , r );
return r ;
}
};
GitHub