Linked List
Math
Two Pointers
Description
A polynomial linked list is a special type of linked list where every node represents a term in a polynomial expression.
Each node has three attributes:
coefficient: an integer representing the number multiplier of the term. The coefficient of the term 9 x4 9.power: an integer representing the exponent. The power of the term 9x4 is 4.next: a pointer to the next node in the list, or null if it is the last node of the list.
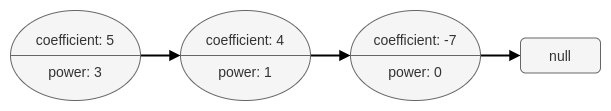
For example, the polynomial 5x3 + 4x - 7 is represented by the polynomial linked list illustrated below:
The polynomial linked list must be in its standard form: the polynomial must be in strictly descending order by its power value. Also, terms with a coefficient of 0 are omitted.
Given two polynomial linked list heads, poly1 and poly2, add the polynomials together and return the head of the sum of the polynomials .
PolyNode format:
The input/output format is as a list of n nodes, where each node is represented as its [coefficient, power]. For example, the polynomial 5x3 + 4x - 7 would be represented as: [[5,3],[4,1],[-7,0]].
Example 1:
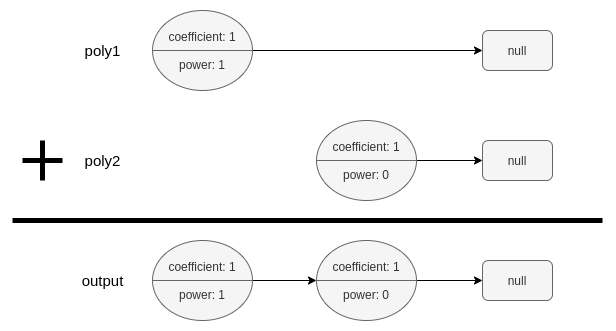
Input: poly1 = [[1,1]], poly2 = [[1,0]]
Output: [[1,1],[1,0]]
Explanation: poly1 = x. poly2 = 1. The sum is x + 1.
Example 2:
Input: poly1 = [[2,2],[4,1],[3,0]], poly2 = [[3,2],[-4,1],[-1,0]]
Output: [[5,2],[2,0]]
Explanation: poly1 = 2x2 + 4x + 3. poly2 = 3x2 - 4x - 1. The sum is 5x2 + 2. Notice that we omit the "0x" term.
Example 3:
Input: poly1 = [[1,2]], poly2 = [[-1,2]]
Output: []
Explanation: The sum is 0. We return an empty list.
Constraints:
0 <= n <= 104 -109 <= PolyNode.coefficient <= 109 PolyNode.coefficient != 00 <= PolyNode.power <= 109 PolyNode.power > PolyNode.next.power
Solutions
Solution 1
Python3 Java C++ JavaScript C#
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28 # Definition for polynomial singly-linked list.
# class PolyNode:
# def __init__(self, x=0, y=0, next=None):
# self.coefficient = x
# self.power = y
# self.next = next
class Solution :
def addPoly ( self , poly1 : "PolyNode" , poly2 : "PolyNode" ) -> "PolyNode" :
dummy = curr = PolyNode ()
while poly1 and poly2 :
if poly1 . power > poly2 . power :
curr . next = poly1
poly1 = poly1 . next
curr = curr . next
elif poly1 . power < poly2 . power :
curr . next = poly2
poly2 = poly2 . next
curr = curr . next
else :
if c := poly1 . coefficient + poly2 . coefficient :
curr . next = PolyNode ( c , poly1 . power )
curr = curr . next
poly1 = poly1 . next
poly2 = poly2 . next
curr . next = poly1 or poly2
return dummy . next
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45 /**
* Definition for polynomial singly-linked list.
* class PolyNode {
* int coefficient, power;
* PolyNode next = null;
* PolyNode() {}
* PolyNode(int x, int y) { this.coefficient = x; this.power = y; }
* PolyNode(int x, int y, PolyNode next) { this.coefficient = x; this.power = y; this.next =
next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public PolyNode addPoly ( PolyNode poly1 , PolyNode poly2 ) {
PolyNode dummy = new PolyNode ();
PolyNode curr = dummy ;
while ( poly1 != null && poly2 != null ) {
if ( poly1 . power > poly2 . power ) {
curr . next = poly1 ;
poly1 = poly1 . next ;
curr = curr . next ;
} else if ( poly1 . power < poly2 . power ) {
curr . next = poly2 ;
poly2 = poly2 . next ;
curr = curr . next ;
} else {
int c = poly1 . coefficient + poly2 . coefficient ;
if ( c != 0 ) {
curr . next = new PolyNode ( c , poly1 . power );
curr = curr . next ;
}
poly1 = poly1 . next ;
poly2 = poly2 . next ;
}
}
if ( poly1 == null ) {
curr . next = poly2 ;
}
if ( poly2 == null ) {
curr . next = poly1 ;
}
return dummy . next ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44 /**
* Definition for polynomial singly-linked list->
* struct PolyNode {
* int coefficient, power;
* PolyNode *next;
* PolyNode(): coefficient(0), power(0), next(nullptr) {};
* PolyNode(int x, int y): coefficient(x), power(y), next(nullptr) {};
* PolyNode(int x, int y, PolyNode* next): coefficient(x), power(y), next(next) {};
* };
*/
class Solution {
public :
PolyNode * addPoly ( PolyNode * poly1 , PolyNode * poly2 ) {
PolyNode * dummy = new PolyNode ();
PolyNode * curr = dummy ;
while ( poly1 && poly2 ) {
if ( poly1 -> power > poly2 -> power ) {
curr -> next = poly1 ;
poly1 = poly1 -> next ;
curr = curr -> next ;
} else if ( poly1 -> power < poly2 -> power ) {
curr -> next = poly2 ;
poly2 = poly2 -> next ;
curr = curr -> next ;
} else {
int c = poly1 -> coefficient + poly2 -> coefficient ;
if ( c != 0 ) {
curr -> next = new PolyNode ( c , poly1 -> power );
curr = curr -> next ;
}
poly1 = poly1 -> next ;
poly2 = poly2 -> next ;
}
}
if ( ! poly1 ) {
curr -> next = poly2 ;
}
if ( ! poly2 ) {
curr -> next = poly1 ;
}
return dummy -> next ;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39 /**
* Definition for polynomial singly-linked list.
* function PolyNode(x=0, y=0, next=null) {
* this.coefficient = x;
* this.power = y;
* this.next = next;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {PolyNode} poly1
* @param {PolyNode} poly2
* @return {PolyNode}
*/
var addPoly = function ( poly1 , poly2 ) {
const dummy = new PolyNode ();
let curr = dummy ;
while ( poly1 && poly2 ) {
if ( poly1 . power > poly2 . power ) {
curr . next = poly1 ;
poly1 = poly1 . next ;
curr = curr . next ;
} else if ( poly1 . power < poly2 . power ) {
curr . next = poly2 ;
poly2 = poly2 . next ;
curr = curr . next ;
} else {
const c = poly1 . coefficient + poly2 . coefficient ;
if ( c != 0 ) {
curr . next = new PolyNode ( c , poly1 . power );
curr = curr . next ;
}
poly1 = poly1 . next ;
poly2 = poly2 . next ;
}
}
curr . next = poly1 || poly2 ;
return dummy . next ;
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46 /**
* Definition for polynomial singly-linked list.
* public class PolyNode {
* public int coefficient, power;
* public PolyNode next;
*
* public PolyNode(int x=0, int y=0, PolyNode next=null) {
* this.coefficient = x;
* this.power = y;
* this.next = next;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public PolyNode AddPoly ( PolyNode poly1 , PolyNode poly2 ) {
PolyNode dummy = new PolyNode ();
PolyNode curr = dummy ;
while ( poly1 != null && poly2 != null ) {
if ( poly1 . power > poly2 . power ) {
curr . next = poly1 ;
poly1 = poly1 . next ;
curr = curr . next ;
} else if ( poly1 . power < poly2 . power ) {
curr . next = poly2 ;
poly2 = poly2 . next ;
curr = curr . next ;
} else {
int c = poly1 . coefficient + poly2 . coefficient ;
if ( c != 0 ) {
curr . next = new PolyNode ( c , poly1 . power );
curr = curr . next ;
}
poly1 = poly1 . next ;
poly2 = poly2 . next ;
}
}
if ( poly1 == null ) {
curr . next = poly2 ;
}
if ( poly2 == null ) {
curr . next = poly1 ;
}
return dummy . next ;
}
}
GitHub