999. Available Captures for Rook
Description
You are given an 8 x 8 matrix representing a chessboard. There is exactly one white rook represented by 'R', some number of white bishops 'B', and some number of black pawns 'p'. Empty squares are represented by '.'.
A rook can move any number of squares horizontally or vertically (up, down, left, right) until it reaches another piece or the edge of the board. A rook is attacking a pawn if it can move to the pawn's square in one move.
Note: A rook cannot move through other pieces, such as bishops or pawns. This means a rook cannot attack a pawn if there is another piece blocking the path.
Return the number of pawns the white rook is attacking.
Example 1:
Input: board = [[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".","p",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".","R",".",".",".","p"],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".","p",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."]]
Output: 3
Explanation:
In this example, the rook is attacking all the pawns.
Example 2:
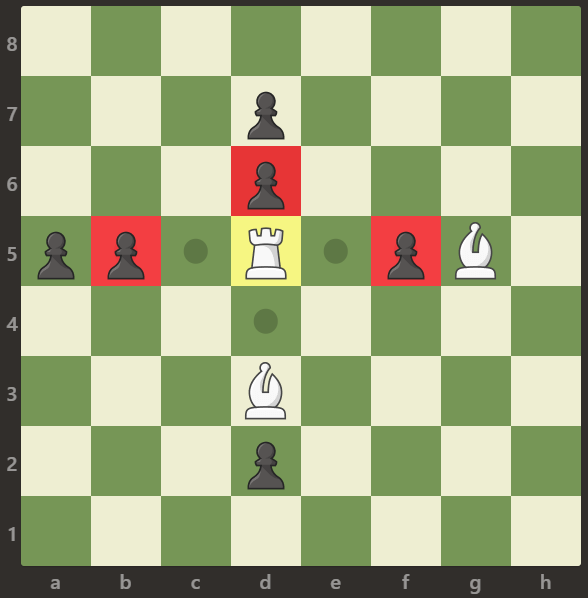
Input: board = [[".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".","p","p","p","p","p",".","."],[".","p","p","B","p","p",".","."],[".","p","B","R","B","p",".","."],[".","p","p","B","p","p",".","."],[".","p","p","p","p","p",".","."],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."]]
Output: 0
Explanation:
The bishops are blocking the rook from attacking any of the pawns.
Example 3:
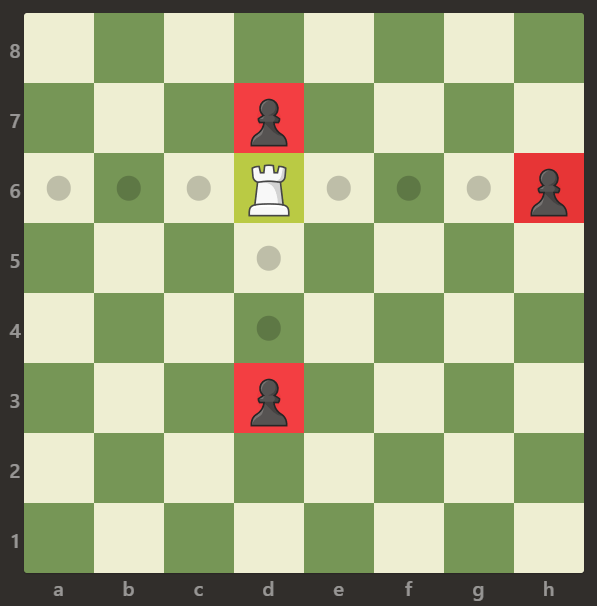
Input: board = [[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".","p",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".","p",".",".",".","."],["p","p",".","R",".","p","B","."],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".","B",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".","p",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."]]
Output: 3
Explanation:
The rook is attacking the pawns at positions b5, d6, and f5.
Constraints:
board.length == 8board[i].length == 8board[i][j]is either'R','.','B', or'p'- There is exactly one cell with
board[i][j] == 'R'
Solutions
Solution 1: Simulation
We first traverse the board to find the position of the rook $(i, j)$. Then, starting from $(i, j)$, we traverse in four directions: up, down, left, and right.
- If it is not the boundary and not a bishop, continue moving forward.
- If it is a pawn, increment the answer by one and stop traversing in that direction.
After traversing in all four directions, we get the answer.
The time complexity is $O(m \times n)$, where $m$ and $n$ are the number of rows and columns of the board, respectively. In this problem, $m = n = 8$. The space complexity is $O(1)$.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 | |