Array
Line Sweep
Two Pointers
Description
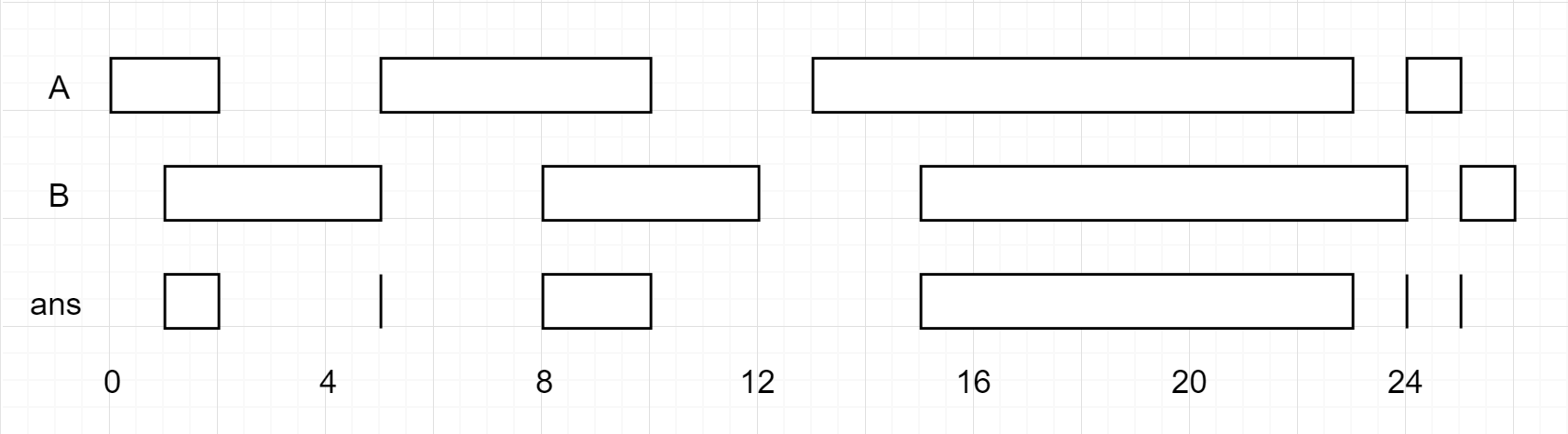
You are given two lists of closed intervals, firstList and secondList, where firstList[i] = [starti , endi ] and secondList[j] = [startj , endj ]. Each list of intervals is pairwise disjoint and in sorted order .
Return the intersection of these two interval lists .
A closed interval [a, b] (with a <= b) denotes the set of real numbers x with a <= x <= b.
The intersection of two closed intervals is a set of real numbers that are either empty or represented as a closed interval. For example, the intersection of [1, 3] and [2, 4] is [2, 3].
Example 1:
Input: firstList = [[0,2],[5,10],[13,23],[24,25]], secondList = [[1,5],[8,12],[15,24],[25,26]]
Output: [[1,2],[5,5],[8,10],[15,23],[24,24],[25,25]]
Example 2:
Input: firstList = [[1,3],[5,9]], secondList = []
Output: []
Constraints:
0 <= firstList.length, secondList.length <= 1000firstList.length + secondList.length >= 10 <= starti < endi <= 109 endi < starti+1 0 <= startj < endj <= 109 endj < startj+1
Solutions
Solution 1
Python3 Java C++ Go TypeScript Rust
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16 class Solution :
def intervalIntersection (
self , firstList : List [ List [ int ]], secondList : List [ List [ int ]]
) -> List [ List [ int ]]:
i = j = 0
ans = []
while i < len ( firstList ) and j < len ( secondList ):
s1 , e1 , s2 , e2 = * firstList [ i ], * secondList [ j ]
l , r = max ( s1 , s2 ), min ( e1 , e2 )
if l <= r :
ans . append ([ l , r ])
if e1 < e2 :
i += 1
else :
j += 1
return ans
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19 class Solution {
public int [][] intervalIntersection ( int [][] firstList , int [][] secondList ) {
List < int []> ans = new ArrayList <> ();
int m = firstList . length , n = secondList . length ;
for ( int i = 0 , j = 0 ; i < m && j < n ;) {
int l = Math . max ( firstList [ i ][ 0 ] , secondList [ j ][ 0 ] );
int r = Math . min ( firstList [ i ][ 1 ] , secondList [ j ][ 1 ] );
if ( l <= r ) {
ans . add ( new int [] { l , r });
}
if ( firstList [ i ][ 1 ] < secondList [ j ][ 1 ] ) {
++ i ;
} else {
++ j ;
}
}
return ans . toArray ( new int [ ans . size () ][] );
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17 class Solution {
public :
vector < vector < int >> intervalIntersection ( vector < vector < int >>& firstList , vector < vector < int >>& secondList ) {
vector < vector < int >> ans ;
int m = firstList . size (), n = secondList . size ();
for ( int i = 0 , j = 0 ; i < m && j < n ;) {
int l = max ( firstList [ i ][ 0 ], secondList [ j ][ 0 ]);
int r = min ( firstList [ i ][ 1 ], secondList [ j ][ 1 ]);
if ( l <= r ) ans . push_back ({ l , r });
if ( firstList [ i ][ 1 ] < secondList [ j ][ 1 ])
++ i ;
else
++ j ;
}
return ans ;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17 func intervalIntersection ( firstList [][] int , secondList [][] int ) [][] int {
m , n := len ( firstList ), len ( secondList )
var ans [][] int
for i , j := 0 , 0 ; i < m && j < n ; {
l := max ( firstList [ i ][ 0 ], secondList [ j ][ 0 ])
r := min ( firstList [ i ][ 1 ], secondList [ j ][ 1 ])
if l <= r {
ans = append ( ans , [] int { l , r })
}
if firstList [ i ][ 1 ] < secondList [ j ][ 1 ] {
i ++
} else {
j ++
}
}
return ans
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20 function intervalIntersection ( firstList : number [][], secondList : number [][]) : number [][] {
const n = firstList . length ;
const m = secondList . length ;
const res = [];
let i = 0 ;
let j = 0 ;
while ( i < n && j < m ) {
const start = Math . max ( firstList [ i ][ 0 ], secondList [ j ][ 0 ]);
const end = Math . min ( firstList [ i ][ 1 ], secondList [ j ][ 1 ]);
if ( start <= end ) {
res . push ([ start , end ]);
}
if ( firstList [ i ][ 1 ] < secondList [ j ][ 1 ]) {
i ++ ;
} else {
j ++ ;
}
}
return res ;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24 impl Solution {
pub fn interval_intersection (
first_list : Vec < Vec < i32 >> ,
second_list : Vec < Vec < i32 >> ,
) -> Vec < Vec < i32 >> {
let n = first_list . len ();
let m = second_list . len ();
let mut res = Vec :: new ();
let ( mut i , mut j ) = ( 0 , 0 );
while i < n && j < m {
let start = first_list [ i ][ 0 ]. max ( second_list [ j ][ 0 ]);
let end = first_list [ i ][ 1 ]. min ( second_list [ j ][ 1 ]);
if start <= end {
res . push ( vec! [ start , end ]);
}
if first_list [ i ][ 1 ] < second_list [ j ][ 1 ] {
i += 1 ;
} else {
j += 1 ;
}
}
res
}
}