Dynamic Programming
Description
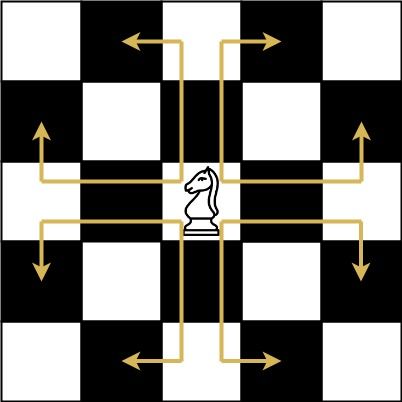
The chess knight has a unique movement , it may move two squares vertically and one square horizontally, or two squares horizontally and one square vertically (with both forming the shape of an L ). The possible movements of chess knight are shown in this diagram:
A chess knight can move as indicated in the chess diagram below:
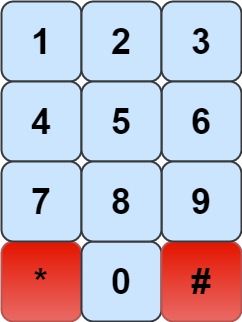
We have a chess knight and a phone pad as shown below, the knight can only stand on a numeric cell (i.e. blue cell).
Given an integer n, return how many distinct phone numbers of length n we can dial.
You are allowed to place the knight on any numeric cell initially and then you should perform n - 1 jumps to dial a number of length n. All jumps should be valid knight jumps.
As the answer may be very large, return the answer modulo 109 + 7.
Example 1:
Input: n = 1
Output: 10
Explanation: We need to dial a number of length 1, so placing the knight over any numeric cell of the 10 cells is sufficient.
Example 2:
Input: n = 2
Output: 20
Explanation: All the valid number we can dial are [04, 06, 16, 18, 27, 29, 34, 38, 40, 43, 49, 60, 61, 67, 72, 76, 81, 83, 92, 94]
Example 3:
Input: n = 3131
Output: 136006598
Explanation: Please take care of the mod.
Constraints:
Solutions
Solution 1: Recurrence
According to the problem description, we need to calculate the number of different phone numbers of length \(n\) . Each digit can only follow certain fixed digits, which we can list as follows:
Current Digit
Previous Digits
0
4, 6
1
6, 8
2
7, 9
3
4, 8
4
0, 3, 9
5
6
0, 1, 7
7
2, 6
8
1, 3
9
2, 4
We can use a recurrence approach to calculate the number of different phone numbers of length \(n\) . Let \(f[i]\) represent the number of different phone numbers of length \(i\) . Initially, \(f[1] = 1\) . For phone numbers of length \(i\) , we can calculate them based on phone numbers of length \(i - 1\) . Therefore, we can derive the recurrence relations:
\[
\begin{aligned}
g[0] & = f[4] + f[6] \\
g[1] & = f[6] + f[8] \\
g[2] & = f[7] + f[9] \\
g[3] & = f[4] + f[8] \\
g[4] & = f[0] + f[3] + f[9] \\
g[6] & = f[0] + f[1] + f[7] \\
g[7] & = f[2] + f[6] \\
g[8] & = f[1] + f[3] \\
g[9] & = f[2] + f[4]
\end{aligned}
\]
Then, we update \(f\) to \(g\) and continue calculating the phone numbers of the next length until we calculate the number of phone numbers of length \(n\) .
Finally, we sum all the elements in \(f\) and take the result modulo \(10^9 + 7\) to get the answer.
The time complexity is \(O(n)\) , where \(n\) is the length of the phone number. The space complexity is \(O(|\Sigma|)\) , where \(\Sigma\) is the set of digits, and in this problem \(|\Sigma| = 10\) .
Python3 Java C++ Go TypeScript C#
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16 class Solution :
def knightDialer ( self , n : int ) -> int :
f = [ 1 ] * 10
for _ in range ( n - 1 ):
g = [ 0 ] * 10
g [ 0 ] = f [ 4 ] + f [ 6 ]
g [ 1 ] = f [ 6 ] + f [ 8 ]
g [ 2 ] = f [ 7 ] + f [ 9 ]
g [ 3 ] = f [ 4 ] + f [ 8 ]
g [ 4 ] = f [ 0 ] + f [ 3 ] + f [ 9 ]
g [ 6 ] = f [ 0 ] + f [ 1 ] + f [ 7 ]
g [ 7 ] = f [ 2 ] + f [ 6 ]
g [ 8 ] = f [ 1 ] + f [ 3 ]
g [ 9 ] = f [ 2 ] + f [ 4 ]
f = g
return sum ( f ) % ( 10 ** 9 + 7 )
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21 class Solution {
public int knightDialer ( int n ) {
final int mod = ( int ) 1e9 + 7 ;
long [] f = new long [ 10 ] ;
Arrays . fill ( f , 1 );
while ( -- n > 0 ) {
long [] g = new long [ 10 ] ;
g [ 0 ] = ( f [ 4 ] + f [ 6 ] ) % mod ;
g [ 1 ] = ( f [ 6 ] + f [ 8 ] ) % mod ;
g [ 2 ] = ( f [ 7 ] + f [ 9 ] ) % mod ;
g [ 3 ] = ( f [ 4 ] + f [ 8 ] ) % mod ;
g [ 4 ] = ( f [ 0 ] + f [ 3 ] + f [ 9 ] ) % mod ;
g [ 6 ] = ( f [ 0 ] + f [ 1 ] + f [ 7 ] ) % mod ;
g [ 7 ] = ( f [ 2 ] + f [ 6 ] ) % mod ;
g [ 8 ] = ( f [ 1 ] + f [ 3 ] ) % mod ;
g [ 9 ] = ( f [ 2 ] + f [ 4 ] ) % mod ;
f = g ;
}
return ( int ) ( Arrays . stream ( f ). sum () % mod );
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21 class Solution {
public :
int knightDialer ( int n ) {
const int mod = 1e9 + 7 ;
vector < long long > f ( 10 , 1 );
while ( -- n ) {
vector < long long > g ( 10 );
g [ 0 ] = ( f [ 4 ] + f [ 6 ]) % mod ;
g [ 1 ] = ( f [ 6 ] + f [ 8 ]) % mod ;
g [ 2 ] = ( f [ 7 ] + f [ 9 ]) % mod ;
g [ 3 ] = ( f [ 4 ] + f [ 8 ]) % mod ;
g [ 4 ] = ( f [ 0 ] + f [ 3 ] + f [ 9 ]) % mod ;
g [ 6 ] = ( f [ 0 ] + f [ 1 ] + f [ 7 ]) % mod ;
g [ 7 ] = ( f [ 2 ] + f [ 6 ]) % mod ;
g [ 8 ] = ( f [ 1 ] + f [ 3 ]) % mod ;
g [ 9 ] = ( f [ 2 ] + f [ 4 ]) % mod ;
f = g ;
}
return accumulate ( f . begin (), f . end (), 0L L ) % mod ;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24 func knightDialer ( n int ) ( ans int ) {
f := make ([] int , 10 )
for i := range f {
f [ i ] = 1
}
const mod int = 1e9 + 7
for i := 1 ; i < n ; i ++ {
g := make ([] int , 10 )
g [ 0 ] = ( f [ 4 ] + f [ 6 ]) % mod
g [ 1 ] = ( f [ 6 ] + f [ 8 ]) % mod
g [ 2 ] = ( f [ 7 ] + f [ 9 ]) % mod
g [ 3 ] = ( f [ 4 ] + f [ 8 ]) % mod
g [ 4 ] = ( f [ 0 ] + f [ 3 ] + f [ 9 ]) % mod
g [ 6 ] = ( f [ 0 ] + f [ 1 ] + f [ 7 ]) % mod
g [ 7 ] = ( f [ 2 ] + f [ 6 ]) % mod
g [ 8 ] = ( f [ 1 ] + f [ 3 ]) % mod
g [ 9 ] = ( f [ 2 ] + f [ 4 ]) % mod
f = g
}
for _ , x := range f {
ans = ( ans + x ) % mod
}
return
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18 function knightDialer ( n : number ) : number {
const mod = 1e9 + 7 ;
const f : number [] = Array ( 10 ). fill ( 1 );
while ( -- n ) {
const g : number [] = Array ( 10 ). fill ( 0 );
g [ 0 ] = ( f [ 4 ] + f [ 6 ]) % mod ;
g [ 1 ] = ( f [ 6 ] + f [ 8 ]) % mod ;
g [ 2 ] = ( f [ 7 ] + f [ 9 ]) % mod ;
g [ 3 ] = ( f [ 4 ] + f [ 8 ]) % mod ;
g [ 4 ] = ( f [ 0 ] + f [ 3 ] + f [ 9 ]) % mod ;
g [ 6 ] = ( f [ 0 ] + f [ 1 ] + f [ 7 ]) % mod ;
g [ 7 ] = ( f [ 2 ] + f [ 6 ]) % mod ;
g [ 8 ] = ( f [ 1 ] + f [ 3 ]) % mod ;
g [ 9 ] = ( f [ 2 ] + f [ 4 ]) % mod ;
f . splice ( 0 , 10 , ... g );
}
return f . reduce (( a , b ) => ( a + b ) % mod );
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25 public class Solution {
public int KnightDialer ( int n ) {
const int mod = 1000000007 ;
long [] f = new long [ 10 ];
for ( int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i ++ ) {
f [ i ] = 1 ;
}
while ( -- n > 0 ) {
long [] g = new long [ 10 ];
g [ 0 ] = ( f [ 4 ] + f [ 6 ]) % mod ;
g [ 1 ] = ( f [ 6 ] + f [ 8 ]) % mod ;
g [ 2 ] = ( f [ 7 ] + f [ 9 ]) % mod ;
g [ 3 ] = ( f [ 4 ] + f [ 8 ]) % mod ;
g [ 4 ] = ( f [ 0 ] + f [ 3 ] + f [ 9 ]) % mod ;
g [ 6 ] = ( f [ 0 ] + f [ 1 ] + f [ 7 ]) % mod ;
g [ 7 ] = ( f [ 2 ] + f [ 6 ]) % mod ;
g [ 8 ] = ( f [ 1 ] + f [ 3 ]) % mod ;
g [ 9 ] = ( f [ 2 ] + f [ 4 ]) % mod ;
f = g ;
}
return ( int )( f . Sum () % mod );
}
}
Solution 2: Matrix Exponentiation to Accelerate Recurrence
Let's denote \(T(n)\) as a \(1 \times 10\) matrix \(\begin{bmatrix} F_0 & F_1 & F_2 \cdots F_9 \end{bmatrix}\) , where \(F_i\) represents the number of phone numbers ending with digit \(i\) . We want to derive \(T(n)\) from \(T(n - 1)\) . In other words, we need a matrix \(\textit{base}\) such that \(T(n - 1) \times \textit{base} = T(n)\) , i.e.:
\[
\begin{bmatrix}
F_0 & F_1 & F_2 \cdots F_9
\end{bmatrix} \times \textit{base} = \begin{bmatrix} F_0' & F_1' & F_2' \cdots F_9' \end{bmatrix}
\]
Since \(F_i' = \sum_{j} F_j\) , where \(j\) is the previous digit of \(i\) , the first column of the matrix \(\textit{base}\) is:
\[
\begin{bmatrix}
0 \\
0 \\
0 \\
0 \\
1 \\
0 \\
1 \\
0 \\
0 \\
0
\end{bmatrix}
\]
Similarly, we can derive the entire matrix \(\textit{base}\) as follows:
\[
\begin{bmatrix}
0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\
0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\
0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 1 \\
0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\
1 & 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \\
0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\
1 & 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 \\
0 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\
0 & 1 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\
0 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0
\end{bmatrix}
\]
We define the initial matrix \(res = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 1 & 1 \cdots 1 \end{bmatrix}\) , and multiply it by the matrix \(\textit{base}\) raised to the power of \(n - 1\) to obtain \(T(n)\) . Finally, we sum all elements in \(T(n)\) and take the result modulo \(10^9 + 7\) to get the answer. The matrix \(\textit{base}^{n - 1}\) can be computed using matrix exponentiation, which has a time complexity of \(O(\log n)\) .
The time complexity is \(O(\log n)\) , and the space complexity is \(O(|\Sigma|^2)\) , where \(\Sigma\) is the set of digits, and in this problem \(|\Sigma| = 10\) .
Python3 Java C++ Go TypeScript C#
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28 import numpy as np
base = [
( 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 ),
( 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 1 , 0 ),
( 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 1 ),
( 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 ),
( 1 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 ),
( 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 ),
( 1 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 ),
( 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 ),
( 0 , 1 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 ),
( 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 ),
]
class Solution :
def knightDialer ( self , n : int ) -> int :
factor = np . asmatrix ( base , np . dtype ( "O" ))
res = np . asmatrix ([[ 1 ] * 10 ], np . dtype ( "O" ))
n -= 1
mod = 10 ** 9 + 7
while n :
if n & 1 :
res = res * factor % mod
factor = factor * factor % mod
n >>= 1
return res . sum () % mod
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43 class Solution {
private final int mod = ( int ) 1e9 + 7 ;
private final int [][] base = {{ 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 }, { 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 1 , 0 },
{ 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 1 }, { 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 },
{ 1 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 }, { 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 },
{ 1 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 }, { 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 },
{ 0 , 1 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 }, { 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 }};
public int knightDialer ( int n ) {
int [][] res = pow ( base , n - 1 );
int ans = 0 ;
for ( int x : res [ 0 ] ) {
ans = ( ans + x ) % mod ;
}
return ans ;
}
private int [][] mul ( int [][] a , int [][] b ) {
int m = a . length , n = b [ 0 ] . length ;
int [][] c = new int [ m ][ n ] ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < m ; ++ i ) {
for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j ) {
for ( int k = 0 ; k < b . length ; ++ k ) {
c [ i ][ j ] = ( int ) (( c [ i ][ j ] + 1L * a [ i ][ k ] * b [ k ][ j ] % mod ) % mod );
}
}
}
return c ;
}
private int [][] pow ( int [][] a , int n ) {
int [][] res = new int [ 1 ][ a . length ] ;
Arrays . fill ( res [ 0 ] , 1 );
while ( n > 0 ) {
if (( n & 1 ) == 1 ) {
res = mul ( res , a );
}
a = mul ( a , a );
n >>= 1 ;
}
return res ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46 class Solution {
public :
int knightDialer ( int n ) {
const int mod = 1e9 + 7 ;
vector < vector < int >> base = {
{ 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 },
{ 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 1 , 0 },
{ 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 1 },
{ 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 },
{ 1 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 },
{ 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 },
{ 1 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 },
{ 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 },
{ 0 , 1 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 },
{ 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 }};
vector < vector < int >> res = pow ( base , n - 1 , mod );
return accumulate ( res [ 0 ]. begin (), res [ 0 ]. end (), 0L L ) % mod ;
}
private :
vector < vector < int >> mul ( const vector < vector < int >>& a , const vector < vector < int >>& b , int mod ) {
int m = a . size (), n = b [ 0 ]. size ();
vector < vector < int >> c ( m , vector < int > ( n , 0 ));
for ( int i = 0 ; i < m ; ++ i ) {
for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j ) {
for ( int k = 0 ; k < b . size (); ++ k ) {
c [ i ][ j ] = ( c [ i ][ j ] + ( 1L L * a [ i ][ k ] * b [ k ][ j ]) % mod ) % mod ;
}
}
}
return c ;
}
vector < vector < int >> pow ( vector < vector < int >>& a , int n , int mod ) {
int size = a . size ();
vector < vector < int >> res ( 1 , vector < int > ( size , 1 ));
while ( n > 0 ) {
if ( n % 2 == 1 ) {
res = mul ( res , a , mod );
}
a = mul ( a , a , mod );
n /= 2 ;
}
return res ;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59 const mod = 1e9 + 7
func knightDialer ( n int ) int {
base := [][] int {
{ 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 },
{ 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 1 , 0 },
{ 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 1 },
{ 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 },
{ 1 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 },
{ 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 },
{ 1 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 },
{ 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 },
{ 0 , 1 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 },
{ 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 },
}
res := pow ( base , n - 1 )
ans := 0
for _ , x := range res [ 0 ] {
ans = ( ans + x ) % mod
}
return ans
}
func mul ( a , b [][] int ) [][] int {
m := len ( a )
n := len ( b [ 0 ])
c := make ([][] int , m )
for i := range c {
c [ i ] = make ([] int , n )
}
for i := 0 ; i < m ; i ++ {
for j := 0 ; j < n ; j ++ {
for k := 0 ; k < len ( b ); k ++ {
c [ i ][ j ] = ( c [ i ][ j ] + a [ i ][ k ] * b [ k ][ j ]) % mod
}
}
}
return c
}
func pow ( a [][] int , n int ) [][] int {
size := len ( a )
res := make ([][] int , 1 )
res [ 0 ] = make ([] int , size )
for i := 0 ; i < size ; i ++ {
res [ 0 ][ i ] = 1
}
for n > 0 {
if n % 2 == 1 {
res = mul ( res , a )
}
a = mul ( a , a )
n /= 2
}
return res
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54 const mod = 1e9 + 7 ;
function knightDialer ( n : number ) : number {
const base : number [][] = [
[ 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 ],
[ 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 1 , 0 ],
[ 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 1 ],
[ 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 ],
[ 1 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 ],
[ 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 ],
[ 1 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 ],
[ 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 ],
[ 0 , 1 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 ],
[ 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 ],
];
const res = pow ( base , n - 1 );
let ans = 0 ;
for ( const x of res [ 0 ]) {
ans = ( ans + x ) % mod ;
}
return ans ;
}
function mul ( a : number [][], b : number [][]) : number [][] {
const m = a . length ;
const n = b [ 0 ]. length ;
const c : number [][] = Array . from ({ length : m }, () => Array ( n ). fill ( 0 ));
for ( let i = 0 ; i < m ; i ++ ) {
for ( let j = 0 ; j < n ; j ++ ) {
for ( let k = 0 ; k < b . length ; k ++ ) {
c [ i ][ j ] =
( c [ i ][ j ] + Number (( BigInt ( a [ i ][ k ]) * BigInt ( b [ k ][ j ])) % BigInt ( mod ))) % mod ;
}
}
}
return c ;
}
function pow ( a : number [][], n : number ) : number [][] {
const size = a . length ;
let res : number [][] = Array . from ({ length : 1 }, () => Array ( size ). fill ( 1 ));
while ( n > 0 ) {
if ( n % 2 === 1 ) {
res = mul ( res , a );
}
a = mul ( a , a );
n = Math . floor ( n / 2 );
}
return res ;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60 public class Solution {
private const int mod = 1000000007 ;
private readonly int [][] baseMatrix = {
new int [] { 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 },
new int [] { 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 1 , 0 },
new int [] { 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 1 },
new int [] { 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 },
new int [] { 1 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 },
new int [] { 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 },
new int [] { 1 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 },
new int [] { 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 },
new int [] { 0 , 1 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 },
new int [] { 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 }
};
public int KnightDialer ( int n ) {
int [][] res = Pow ( baseMatrix , n - 1 );
int ans = 0 ;
foreach ( var x in res [ 0 ]) {
ans = ( ans + x ) % mod ;
}
return ans ;
}
private int [][] Mul ( int [][] a , int [][] b ) {
int m = a . Length , n = b [ 0 ]. Length ;
int [][] c = new int [ m ][];
for ( int i = 0 ; i < m ; i ++ ) {
c [ i ] = new int [ n ];
}
for ( int i = 0 ; i < m ; i ++ ) {
for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; j ++ ) {
for ( int k = 0 ; k < b . Length ; k ++ ) {
c [ i ][ j ] = ( int )(( c [ i ][ j ] + ( long ) a [ i ][ k ] * b [ k ][ j ]) % mod );
}
}
}
return c ;
}
private int [][] Pow ( int [][] a , int n ) {
int size = a . Length ;
int [][] res = new int [ 1 ][];
res [ 0 ] = new int [ size ];
for ( int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++ ) {
res [ 0 ][ i ] = 1 ;
}
while ( n > 0 ) {
if ( n % 2 == 1 ) {
res = Mul ( res , a );
}
a = Mul ( a , a );
n /= 2 ;
}
return res ;
}
}