Array
Hash Table
Matrix
Description
Given two sparse matrices mat1 of size m x k and mat2 of size k x n, return the result of mat1 x mat2. You may assume that multiplication is always possible.
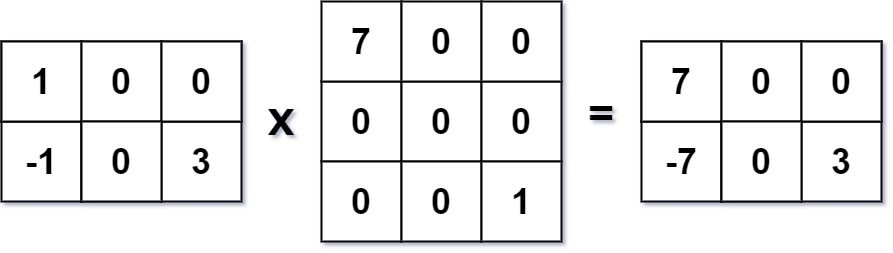
Example 1:
Input: mat1 = [[1,0,0],[-1,0,3]], mat2 = [[7,0,0],[0,0,0],[0,0,1]]
Output: [[7,0,0],[-7,0,3]]
Example 2:
Input: mat1 = [[0]], mat2 = [[0]]
Output: [[0]]
Constraints:
m == mat1.lengthk == mat1[i].length == mat2.lengthn == mat2[i].length1 <= m, n, k <= 100-100 <= mat1[i][j], mat2[i][j] <= 100
Solutions
Solution 1: Direct Multiplication
We can directly calculate each element in the result matrix according to the definition of matrix multiplication.
The time complexity is \(O(m \times n \times k)\) , and the space complexity is \(O(m \times n)\) . Where \(m\) and \(n\) are the number of rows of matrix \(mat1\) and the number of columns of matrix \(mat2\) respectively, and \(k\) is the number of columns of matrix \(mat1\) or the number of rows of matrix \(mat2\) .
Python3 Java C++ Go TypeScript
class Solution :
def multiply ( self , mat1 : List [ List [ int ]], mat2 : List [ List [ int ]]) -> List [ List [ int ]]:
m , n = len ( mat1 ), len ( mat2 [ 0 ])
ans = [[ 0 ] * n for _ in range ( m )]
for i in range ( m ):
for j in range ( n ):
for k in range ( len ( mat2 )):
ans [ i ][ j ] += mat1 [ i ][ k ] * mat2 [ k ][ j ]
return ans
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14 class Solution {
public int [][] multiply ( int [][] mat1 , int [][] mat2 ) {
int m = mat1 . length , n = mat2 [ 0 ] . length ;
int [][] ans = new int [ m ][ n ] ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < m ; ++ i ) {
for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j ) {
for ( int k = 0 ; k < mat2 . length ; ++ k ) {
ans [ i ][ j ] += mat1 [ i ][ k ] * mat2 [ k ][ j ] ;
}
}
}
return ans ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15 class Solution {
public :
vector < vector < int >> multiply ( vector < vector < int >>& mat1 , vector < vector < int >>& mat2 ) {
int m = mat1 . size (), n = mat2 [ 0 ]. size ();
vector < vector < int >> ans ( m , vector < int > ( n ));
for ( int i = 0 ; i < m ; ++ i ) {
for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j ) {
for ( int k = 0 ; k < mat2 . size (); ++ k ) {
ans [ i ][ j ] += mat1 [ i ][ k ] * mat2 [ k ][ j ];
}
}
}
return ans ;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15 func multiply ( mat1 [][] int , mat2 [][] int ) [][] int {
m , n := len ( mat1 ), len ( mat2 [ 0 ])
ans := make ([][] int , m )
for i := range ans {
ans [ i ] = make ([] int , n )
}
for i := 0 ; i < m ; i ++ {
for j := 0 ; j < n ; j ++ {
for k := 0 ; k < len ( mat2 ); k ++ {
ans [ i ][ j ] += mat1 [ i ][ k ] * mat2 [ k ][ j ]
}
}
}
return ans
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12 function multiply ( mat1 : number [][], mat2 : number [][]) : number [][] {
const [ m , n ] = [ mat1 . length , mat2 [ 0 ]. length ];
const ans : number [][] = Array . from ({ length : m }, () => Array . from ({ length : n }, () => 0 ));
for ( let i = 0 ; i < m ; ++ i ) {
for ( let j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j ) {
for ( let k = 0 ; k < mat2 . length ; ++ k ) {
ans [ i ][ j ] += mat1 [ i ][ k ] * mat2 [ k ][ j ];
}
}
}
return ans ;
}
Solution 2: Preprocessing
We can preprocess the sparse representation of the two matrices, i.e., \(g1[i]\) represents the column index and value of all non-zero elements in the \(i\) th row of matrix \(mat1\) , and \(g2[i]\) represents the column index and value of all non-zero elements in the \(i\) th row of matrix \(mat2\) .
Next, we traverse each row \(i\) , traverse each element \((k, x)\) in \(g1[i]\) , traverse each element \((j, y)\) in \(g2[k]\) , then \(mat1[i][k] \times mat2[k][j]\) will correspond to \(ans[i][j]\) in the result matrix, and we can accumulate all the results.
The time complexity is \(O(m \times n \times k)\) , and the space complexity is \(O(m \times n)\) . Where \(m\) and \(n\) are the number of rows of matrix \(mat1\) and the number of columns of matrix \(mat2\) respectively, and \(k\) is the number of columns of matrix \(mat1\) or the number of rows of matrix \(mat2\) .
Python3 Java C++ Go TypeScript
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19 class Solution :
def multiply ( self , mat1 : List [ List [ int ]], mat2 : List [ List [ int ]]) -> List [ List [ int ]]:
def f ( mat : List [ List [ int ]]) -> List [ List [ int ]]:
g = [[] for _ in range ( len ( mat ))]
for i , row in enumerate ( mat ):
for j , x in enumerate ( row ):
if x :
g [ i ] . append (( j , x ))
return g
g1 = f ( mat1 )
g2 = f ( mat2 )
m , n = len ( mat1 ), len ( mat2 [ 0 ])
ans = [[ 0 ] * n for _ in range ( m )]
for i in range ( m ):
for k , x in g1 [ i ]:
for j , y in g2 [ k ]:
ans [ i ][ j ] += x * y
return ans
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32 class Solution {
public int [][] multiply ( int [][] mat1 , int [][] mat2 ) {
int m = mat1 . length , n = mat2 [ 0 ] . length ;
int [][] ans = new int [ m ][ n ] ;
var g1 = f ( mat1 );
var g2 = f ( mat2 );
for ( int i = 0 ; i < m ; ++ i ) {
for ( int [] p : g1 [ i ] ) {
int k = p [ 0 ] , x = p [ 1 ] ;
for ( int [] q : g2 [ k ] ) {
int j = q [ 0 ] , y = q [ 1 ] ;
ans [ i ][ j ] += x * y ;
}
}
}
return ans ;
}
private List < int []>[] f ( int [][] mat ) {
int m = mat . length , n = mat [ 0 ] . length ;
List < int []>[] g = new List [ m ] ;
Arrays . setAll ( g , i -> new ArrayList <> ());
for ( int i = 0 ; i < m ; ++ i ) {
for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j ) {
if ( mat [ i ][ j ] != 0 ) {
g [ i ] . add ( new int [] { j , mat [ i ][ j ] });
}
}
}
return g ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29 class Solution {
public :
vector < vector < int >> multiply ( vector < vector < int >>& mat1 , vector < vector < int >>& mat2 ) {
int m = mat1 . size (), n = mat2 [ 0 ]. size ();
vector < vector < int >> ans ( m , vector < int > ( n ));
auto g1 = f ( mat1 ), g2 = f ( mat2 );
for ( int i = 0 ; i < m ; ++ i ) {
for ( auto & [ k , x ] : g1 [ i ]) {
for ( auto & [ j , y ] : g2 [ k ]) {
ans [ i ][ j ] += x * y ;
}
}
}
return ans ;
}
vector < vector < pair < int , int >>> f ( vector < vector < int >>& mat ) {
int m = mat . size (), n = mat [ 0 ]. size ();
vector < vector < pair < int , int >>> g ( m );
for ( int i = 0 ; i < m ; ++ i ) {
for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j ) {
if ( mat [ i ][ j ]) {
g [ i ]. emplace_back ( j , mat [ i ][ j ]);
}
}
}
return g ;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31 func multiply ( mat1 [][] int , mat2 [][] int ) [][] int {
m , n := len ( mat1 ), len ( mat2 [ 0 ])
ans := make ([][] int , m )
for i := range ans {
ans [ i ] = make ([] int , n )
}
f := func ( mat [][] int ) [][][ 2 ] int {
m , n := len ( mat ), len ( mat [ 0 ])
g := make ([][][ 2 ] int , m )
for i := range g {
g [ i ] = make ([][ 2 ] int , 0 , n )
for j := range mat [ i ] {
if mat [ i ][ j ] != 0 {
g [ i ] = append ( g [ i ], [ 2 ] int { j , mat [ i ][ j ]})
}
}
}
return g
}
g1 , g2 := f ( mat1 ), f ( mat2 )
for i := range g1 {
for _ , p := range g1 [ i ] {
k , x := p [ 0 ], p [ 1 ]
for _ , q := range g2 [ k ] {
j , y := q [ 0 ], q [ 1 ]
ans [ i ][ j ] += x * y
}
}
}
return ans
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26 function multiply ( mat1 : number [][], mat2 : number [][]) : number [][] {
const [ m , n ] = [ mat1 . length , mat2 [ 0 ]. length ];
const ans : number [][] = Array . from ({ length : m }, () => Array . from ({ length : n }, () => 0 ));
const f = ( mat : number [][]) : number [][][] => {
const [ m , n ] = [ mat . length , mat [ 0 ]. length ];
const ans : number [][][] = Array . from ({ length : m }, () => []);
for ( let i = 0 ; i < m ; ++ i ) {
for ( let j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j ) {
if ( mat [ i ][ j ] !== 0 ) {
ans [ i ]. push ([ j , mat [ i ][ j ]]);
}
}
}
return ans ;
};
const g1 = f ( mat1 );
const g2 = f ( mat2 );
for ( let i = 0 ; i < m ; ++ i ) {
for ( const [ k , x ] of g1 [ i ]) {
for ( const [ j , y ] of g2 [ k ]) {
ans [ i ][ j ] += x * y ;
}
}
}
return ans ;
}
GitHub