3004. Maximum Subtree of the Same Color 🔒
Description
You are given a 2D integer array edges representing a tree with n nodes, numbered from 0 to n - 1, rooted at node 0, where edges[i] = [ui, vi] means there is an edge between the nodes vi and ui.
You are also given a 0-indexed integer array colors of size n, where colors[i] is the color assigned to node i.
We want to find a node v such that every node in the subtree of v has the same color.
Return the size of such subtree with the maximum number of nodes possible.
Example 1:
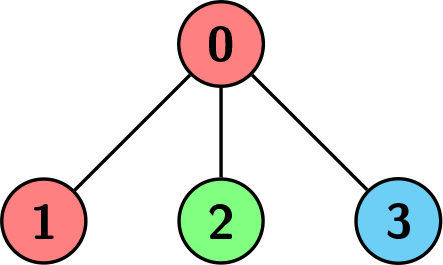
Input: edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3]], colors = [1,1,2,3] Output: 1 Explanation: Each color is represented as: 1 -> Red, 2 -> Green, 3 -> Blue. We can see that the subtree rooted at node 0 has children with different colors. Any other subtree is of the same color and has a size of 1. Hence, we return 1.
Example 2:
Input: edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3]], colors = [1,1,1,1] Output: 4 Explanation: The whole tree has the same color, and the subtree rooted at node 0 has the most number of nodes which is 4. Hence, we return 4.
Example 3:
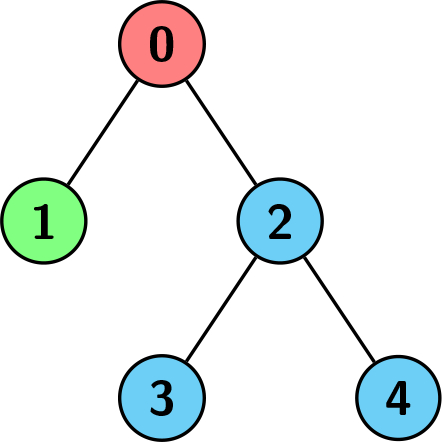
Input: edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[2,3],[2,4]], colors = [1,2,3,3,3] Output: 3 Explanation: Each color is represented as: 1 -> Red, 2 -> Green, 3 -> Blue. We can see that the subtree rooted at node 0 has children with different colors. Any other subtree is of the same color, but the subtree rooted at node 2 has a size of 3 which is the maximum. Hence, we return 3.
Constraints:
n == edges.length + 11 <= n <= 5 * 104edges[i] == [ui, vi]0 <= ui, vi < ncolors.length == n1 <= colors[i] <= 105- The input is generated such that the graph represented by
edgesis a tree.
Solutions
Solution 1: DFS
First, according to the edge information given in the problem, we construct an adjacency list \(g\), where \(g[a]\) represents all adjacent nodes of node \(a\). Then we create an array \(size\) of length \(n\), where \(size[a]\) represents the number of nodes in the subtree with node \(a\) as the root.
Next, we design a function \(dfs(a, fa)\), which will return whether the subtree with node \(a\) as the root meets the requirements of the problem. The execution process of the function \(dfs(a, fa)\) is as follows:
- First, we use a variable \(ok\) to record whether the subtree with node \(a\) as the root meets the requirements of the problem, and initially \(ok\) is \(true\).
- Then, we traverse all adjacent nodes \(b\) of node \(a\). If \(b\) is not the parent node \(fa\) of \(a\), then we recursively call \(dfs(b, a)\), save the return value into the variable \(t\), and update \(ok\) to the value of \(ok\) and \(colors[a] = colors[b] \land t\), where \(\land\) represents logical AND operation. Then, we update \(size[a] = size[a] + size[b]\).
- After that, we judge the value of \(ok\). If \(ok\) is \(true\), then we update the answer \(ans = \max(ans, size[a])\).
- Finally, we return the value of \(ok\).
We call \(dfs(0, -1)\), where \(0\) represents the root node number, and \(-1\) represents that the root node has no parent node. The final answer is \(ans\).
The time complexity is \(O(n)\), and the space complexity is \(O(n)\). Where \(n\) is the number of nodes.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 | |