Breadth-First Search
Depth-First Search
Graph
Union Find
Description
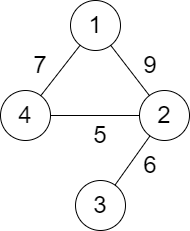
You are given a positive integer n representing n cities numbered from 1 to n. You are also given a 2D array roads where roads[i] = [ai , bi , distancei ] indicates that there is a bidirectional road between cities ai and bi with a distance equal to distancei . The cities graph is not necessarily connected.
The score of a path between two cities is defined as the minimum distance of a road in this path.
Return the minimum possible score of a path between cities 1 and n.
Note :
A path is a sequence of roads between two cities.
It is allowed for a path to contain the same road multiple times, and you can visit cities 1 and n multiple times along the path.
The test cases are generated such that there is at least one path between 1 and n.
Example 1:
Input: n = 4, roads = [[1,2,9],[2,3,6],[2,4,5],[1,4,7]]
Output: 5
Explanation: The path from city 1 to 4 with the minimum score is: 1 -> 2 -> 4. The score of this path is min(9,5) = 5.
It can be shown that no other path has less score.
Example 2:
Input: n = 4, roads = [[1,2,2],[1,3,4],[3,4,7]]
Output: 2
Explanation: The path from city 1 to 4 with the minimum score is: 1 -> 2 -> 1 -> 3 -> 4. The score of this path is min(2,2,4,7) = 2.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 105 1 <= roads.length <= 105 roads[i].length == 31 <= ai , bi <= nai != bi 1 <= distancei <= 104 There are no repeated edges.
There is at least one path between 1 and n.
Solutions
Solution 1: DFS
According to the problem description, each edge can be passed multiple times, and it is guaranteed that node \(1\) and node \(n\) are in the same connected component. Therefore, the problem is actually looking for the smallest edge in the connected component where node \(1\) is located. We can use DFS, start searching from node \(1\) , and find the smallest edge.
The time complexity is \(O(n + m)\) , where \(n\) and \(m\) are the number of nodes and edges, respectively.
Python3 Java C++ Go TypeScript Rust JavaScript
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18 class Solution :
def minScore ( self , n : int , roads : List [ List [ int ]]) -> int :
def dfs ( i ):
nonlocal ans
for j , d in g [ i ]:
ans = min ( ans , d )
if not vis [ j ]:
vis [ j ] = True
dfs ( j )
g = defaultdict ( list )
for a , b , d in roads :
g [ a ] . append (( b , d ))
g [ b ] . append (( a , d ))
vis = [ False ] * ( n + 1 )
ans = inf
dfs ( 1 )
return ans
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29 class Solution {
private List < int []>[] g ;
private boolean [] vis ;
private int ans = 1 << 30 ;
public int minScore ( int n , int [][] roads ) {
g = new List [ n ] ;
vis = new boolean [ n ] ;
Arrays . setAll ( g , k -> new ArrayList <> ());
for ( var e : roads ) {
int a = e [ 0 ] - 1 , b = e [ 1 ] - 1 , d = e [ 2 ] ;
g [ a ] . add ( new int [] { b , d });
g [ b ] . add ( new int [] { a , d });
}
dfs ( 0 );
return ans ;
}
private void dfs ( int i ) {
for ( var nxt : g [ i ] ) {
int j = nxt [ 0 ] , d = nxt [ 1 ] ;
ans = Math . min ( ans , d );
if ( ! vis [ j ] ) {
vis [ j ] = true ;
dfs ( j );
}
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25 class Solution {
public :
int minScore ( int n , vector < vector < int >>& roads ) {
vector < vector < pair < int , int >>> g ( n );
bool vis [ n ];
memset ( vis , 0 , sizeof vis );
for ( auto & e : roads ) {
int a = e [ 0 ] - 1 , b = e [ 1 ] - 1 , d = e [ 2 ];
g [ a ]. emplace_back ( b , d );
g [ b ]. emplace_back ( a , d );
}
int ans = INT_MAX ;
function < void ( int ) > dfs = [ & ]( int i ) {
for ( auto [ j , d ] : g [ i ]) {
ans = min ( ans , d );
if ( ! vis [ j ]) {
vis [ j ] = true ;
dfs ( j );
}
}
};
dfs ( 0 );
return ans ;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24 func minScore ( n int , roads [][] int ) int {
type pair struct { i , v int }
g := make ([][] pair , n )
for _ , e := range roads {
a , b , d := e [ 0 ] - 1 , e [ 1 ] - 1 , e [ 2 ]
g [ a ] = append ( g [ a ], pair { b , d })
g [ b ] = append ( g [ b ], pair { a , d })
}
vis := make ([] bool , n )
ans := 1 << 30
var dfs func ( int )
dfs = func ( i int ) {
for _ , nxt := range g [ i ] {
j , d := nxt . i , nxt . v
ans = min ( ans , d )
if ! vis [ j ] {
vis [ j ] = true
dfs ( j )
}
}
}
dfs ( 0 )
return ans
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21 function minScore ( n : number , roads : number [][]) : number {
const vis = new Array ( n + 1 ). fill ( false );
const g = Array . from ({ length : n + 1 }, () => []);
for ( const [ a , b , v ] of roads ) {
g [ a ]. push ([ b , v ]);
g [ b ]. push ([ a , v ]);
}
let ans = Infinity ;
const dfs = ( i : number ) => {
if ( vis [ i ]) {
return ;
}
vis [ i ] = true ;
for ( const [ j , v ] of g [ i ]) {
ans = Math . min ( ans , v );
dfs ( j );
}
};
dfs ( 1 );
return ans ;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26 impl Solution {
fn dfs ( i : usize , mut ans : i32 , g : & Vec < Vec < ( usize , i32 ) >> , vis : & mut Vec < bool > ) -> i32 {
if vis [ i ] {
return ans ;
}
vis [ i ] = true ;
for ( j , v ) in g [ i ]. iter () {
ans = ans . min ( * v . min ( & Self :: dfs ( * j , ans , g , vis )));
}
ans
}
pub fn min_score ( n : i32 , roads : Vec < Vec < i32 >> ) -> i32 {
let n = n as usize ;
let mut vis = vec! [ false ; n + 1 ];
let mut g = vec! [ Vec :: new (); n + 1 ];
for road in roads . iter () {
let a = road [ 0 ] as usize ;
let b = road [ 1 ] as usize ;
let v = road [ 2 ];
g [ a ]. push (( b , v ));
g [ b ]. push (( a , v ));
}
Self :: dfs ( 1 , i32 :: MAX , & g , & mut vis )
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22 var minScore = function ( n , roads ) {
// 构建点到点的映射表
const graph = Array . from ({ length : n + 1 }, () => new Map ());
for ( let [ u , v , w ] of roads ) {
graph [ u ]. set ( v , w );
graph [ v ]. set ( u , w );
}
// DFS
const vis = new Array ( n ). fill ( false );
let ans = Infinity ;
var dfs = function ( u ) {
vis [ u ] = true ;
for ( const [ v , w ] of graph [ u ]) {
ans = Math . min ( ans , w );
if ( ! vis [ v ]) dfs ( v );
}
};
dfs ( 1 );
return ans ;
};
Solution 2: BFS
We can also use BFS to solve this problem.
The time complexity is \(O(n + m)\) , where \(n\) and \(m\) are the number of nodes and edges, respectively.
Python3 Java C++ Go
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19 class Solution :
def minScore ( self , n : int , roads : List [ List [ int ]]) -> int :
g = defaultdict ( list )
for a , b , d in roads :
g [ a ] . append (( b , d ))
g [ b ] . append (( a , d ))
vis = [ False ] * ( n + 1 )
vis [ 1 ] = True
ans = inf
q = deque ([ 1 ])
while q :
for _ in range ( len ( q )):
i = q . popleft ()
for j , d in g [ i ]:
ans = min ( ans , d )
if not vis [ j ]:
vis [ j ] = True
q . append ( j )
return ans
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30 class Solution {
public int minScore ( int n , int [][] roads ) {
List < int []>[] g = new List [ n ] ;
boolean [] vis = new boolean [ n ] ;
Arrays . setAll ( g , k -> new ArrayList <> ());
for ( var e : roads ) {
int a = e [ 0 ] - 1 , b = e [ 1 ] - 1 , d = e [ 2 ] ;
g [ a ] . add ( new int [] { b , d });
g [ b ] . add ( new int [] { a , d });
}
Deque < Integer > q = new ArrayDeque <> ();
q . offer ( 0 );
vis [ 0 ] = true ;
int ans = 1 << 30 ;
while ( ! q . isEmpty ()) {
for ( int k = q . size (); k > 0 ; -- k ) {
int i = q . pollFirst ();
for ( var nxt : g [ i ] ) {
int j = nxt [ 0 ] , d = nxt [ 1 ] ;
ans = Math . min ( ans , d );
if ( ! vis [ j ] ) {
vis [ j ] = true ;
q . offer ( j );
}
}
}
}
return ans ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30 class Solution {
public :
int minScore ( int n , vector < vector < int >>& roads ) {
vector < vector < pair < int , int >>> g ( n );
bool vis [ n ];
memset ( vis , 0 , sizeof vis );
for ( auto & e : roads ) {
int a = e [ 0 ] - 1 , b = e [ 1 ] - 1 , d = e [ 2 ];
g [ a ]. emplace_back ( b , d );
g [ b ]. emplace_back ( a , d );
}
int ans = INT_MAX ;
queue < int > q {{ 0 }};
vis [ 0 ] = true ;
while ( ! q . empty ()) {
for ( int k = q . size (); k ; -- k ) {
int i = q . front ();
q . pop ();
for ( auto [ j , d ] : g [ i ]) {
ans = min ( ans , d );
if ( ! vis [ j ]) {
vis [ j ] = true ;
q . push ( j );
}
}
}
}
return ans ;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28 func minScore ( n int , roads [][] int ) int {
type pair struct { i , v int }
g := make ([][] pair , n )
for _ , e := range roads {
a , b , d := e [ 0 ] - 1 , e [ 1 ] - 1 , e [ 2 ]
g [ a ] = append ( g [ a ], pair { b , d })
g [ b ] = append ( g [ b ], pair { a , d })
}
vis := make ([] bool , n )
ans := 1 << 30
q := [] int { 0 }
vis [ 0 ] = true
for len ( q ) > 0 {
for k := len ( q ); k > 0 ; k -- {
i := q [ 0 ]
q = q [ 1 :]
for _ , nxt := range g [ i ] {
j , d := nxt . i , nxt . v
ans = min ( ans , d )
if ! vis [ j ] {
vis [ j ] = true
q = append ( q , j )
}
}
}
}
return ans
}