2378. Choose Edges to Maximize Score in a Tree 🔒
Description
You are given a weighted tree consisting of n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1.
The tree is rooted at node 0 and represented with a 2D array edges of size n where edges[i] = [pari, weighti] indicates that node pari is the parent of node i, and the edge between them has a weight equal to weighti. Since the root does not have a parent, you have edges[0] = [-1, -1].
Choose some edges from the tree such that no two chosen edges are adjacent and the sum of the weights of the chosen edges is maximized.
Return the maximum sum of the chosen edges.
Note:
- You are allowed to not choose any edges in the tree, the sum of weights in this case will be
0. - Two edges
Edge1andEdge2in the tree are adjacent if they have a common node.- In other words, they are adjacent if
Edge1connects nodesaandbandEdge2connects nodesbandc.
- In other words, they are adjacent if
Example 1:
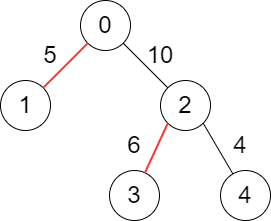
Input: edges = [[-1,-1],[0,5],[0,10],[2,6],[2,4]] Output: 11 Explanation: The above diagram shows the edges that we have to choose colored in red. The total score is 5 + 6 = 11. It can be shown that no better score can be obtained.
Example 2:
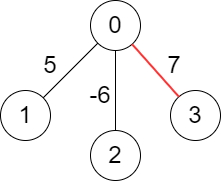
Input: edges = [[-1,-1],[0,5],[0,-6],[0,7]] Output: 7 Explanation: We choose the edge with weight 7. Note that we cannot choose more than one edge because all edges are adjacent to each other.
Constraints:
n == edges.length1 <= n <= 105edges[i].length == 2par0 == weight0 == -10 <= pari <= n - 1for alli >= 1.pari != i-106 <= weighti <= 106for alli >= 1.edgesrepresents a valid tree.
Solutions
Solution 1: Tree DP
We design a function \(dfs(i)\), which represents the maximum sum of the weights of selected edges in the subtree rooted at node \(i\), such that no two selected edges are adjacent. This function returns two values \((a, b)\). The first value \(a\) represents the sum of the weights of selected edges when the edge between the current node \(i\) and its parent node is selected. The second value \(b\) represents the sum of the weights of selected edges when the edge between the current node \(i\) and its parent node is not selected.
We can observe the following for the current node \(i\):
- If the edge between \(i\) and its parent node is selected, then none of the edges between \(i\) and its child nodes can be selected. In this case, the value of \(a\) for the current node is the sum of the \(b\) values of all its child nodes.
- If the edge between \(i\) and its parent node is not selected, then we can select at most one edge between \(i\) and its child nodes. In this case, the value of \(b\) for the current node is the sum of the \(a\) values of the selected child nodes and the \(b\) values of the unselected child nodes, plus the weight of the edge between \(i\) and the selected child node.
We call the function \(dfs(0)\), and the second value returned is the answer, which is the sum of the weights of selected edges when the edge between the root node and its parent node is not selected.
The time complexity is \(O(n)\), and the space complexity is \(O(n)\). Here, \(n\) is the number of nodes.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 | |