Binary Tree
Breadth-First Search
Depth-First Search
Tree
Description
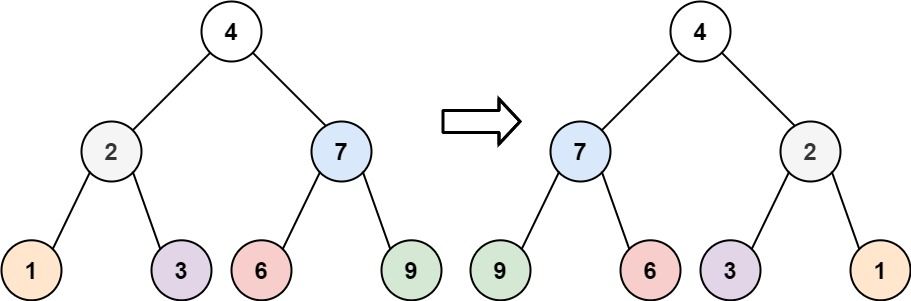
Given the root of a binary tree, invert the tree, and return its root .
Example 1:
Input: root = [4,2,7,1,3,6,9]
Output: [4,7,2,9,6,3,1]
Example 2:
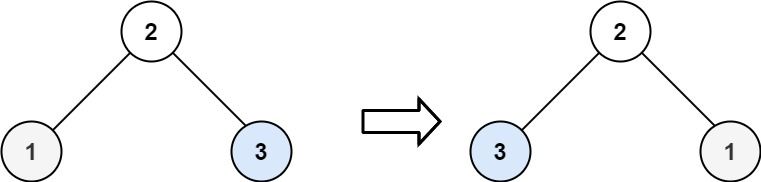
Input: root = [2,1,3]
Output: [2,3,1]
Example 3:
Input: root = []
Output: []
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 100].
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
Solutions
Solution 1: Recursion
First, we check if \(\textit{root}\) is null. If it is, we return \(\text{null}\) . Then, we recursively invert the left and right subtrees, set the inverted right subtree as the new left subtree, and set the inverted left subtree as the new right subtree. Finally, we return \(\textit{root}\) .
The time complexity is \(O(n)\) , and the space complexity is \(O(n)\) . Here, \(n\) is the number of nodes in the binary tree.
Python3 Java C++ Go TypeScript Rust JavaScript C#
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13 # Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution :
def invertTree ( self , root : Optional [ TreeNode ]) -> Optional [ TreeNode ]:
if root is None :
return None
l , r = self . invertTree ( root . left ), self . invertTree ( root . right )
root . left , root . right = r , l
return root
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree ( TreeNode root ) {
if ( root == null ) {
return null ;
}
TreeNode l = invertTree ( root . left );
TreeNode r = invertTree ( root . right );
root . left = r ;
root . right = l ;
return root ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public :
TreeNode * invertTree ( TreeNode * root ) {
if ( ! root ) {
return root ;
}
TreeNode * l = invertTree ( root -> left );
TreeNode * r = invertTree ( root -> right );
root -> left = r ;
root -> right = l ;
return root ;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func invertTree ( root * TreeNode ) * TreeNode {
if root == nil {
return root
}
l , r := invertTree ( root . Left ), invertTree ( root . Right )
root . Left , root . Right = r , l
return root
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function invertTree ( root : TreeNode | null ) : TreeNode | null {
if ( ! root ) {
return root ;
}
const l = invertTree ( root . left );
const r = invertTree ( root . right );
root . left = r ;
root . right = l ;
return root ;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32 // Definition for a binary tree node.
// #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
// pub struct TreeNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// }
//
// impl TreeNode {
// #[inline]
// pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// TreeNode {
// val,
// left: None,
// right: None
// }
// }
// }
use std :: rc :: Rc ;
use std :: cell :: RefCell ;
impl Solution {
pub fn invert_tree ( root : Option < Rc < RefCell < TreeNode >>> ) -> Option < Rc < RefCell < TreeNode >>> {
if let Some ( node ) = root . clone () {
let mut node = node . borrow_mut ();
let left = node . left . take ();
let right = node . right . take ();
node . left = Self :: invert_tree ( right );
node . right = Self :: invert_tree ( left );
}
root
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var invertTree = function ( root ) {
if ( ! root ) {
return root ;
}
const l = invertTree ( root . left );
const r = invertTree ( root . right );
root . left = r ;
root . right = l ;
return root ;
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* public int val;
* public TreeNode left;
* public TreeNode right;
* public TreeNode(int val=0, TreeNode left=null, TreeNode right=null) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public TreeNode InvertTree ( TreeNode root ) {
if ( root == null ) {
return null ;
}
TreeNode l = InvertTree ( root . left );
TreeNode r = InvertTree ( root . right );
root . left = r ;
root . right = l ;
return root ;
}
}