2194. Cells in a Range on an Excel Sheet
Description
A cell (r, c) of an excel sheet is represented as a string "<col><row>" where:
<col>denotes the column numbercof the cell. It is represented by alphabetical letters.- For example, the
1stcolumn is denoted by'A', the2ndby'B', the3rdby'C', and so on.
- For example, the
<row>is the row numberrof the cell. Therthrow is represented by the integerr.
You are given a string s in the format "<col1><row1>:<col2><row2>", where <col1> represents the column c1, <row1> represents the row r1, <col2> represents the column c2, and <row2> represents the row r2, such that r1 <= r2 and c1 <= c2.
Return the list of cells (x, y) such that r1 <= x <= r2 and c1 <= y <= c2. The cells should be represented as strings in the format mentioned above and be sorted in non-decreasing order first by columns and then by rows.
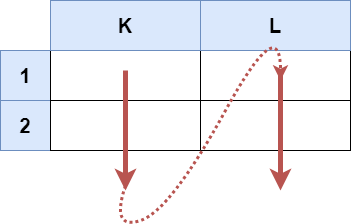
Example 1:
Input: s = "K1:L2" Output: ["K1","K2","L1","L2"] Explanation: The above diagram shows the cells which should be present in the list. The red arrows denote the order in which the cells should be presented.
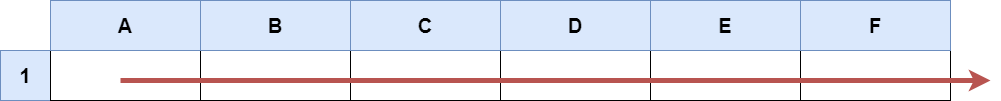
Example 2:
Input: s = "A1:F1" Output: ["A1","B1","C1","D1","E1","F1"] Explanation: The above diagram shows the cells which should be present in the list. The red arrow denotes the order in which the cells should be presented.
Constraints:
s.length == 5'A' <= s[0] <= s[3] <= 'Z''1' <= s[1] <= s[4] <= '9'sconsists of uppercase English letters, digits and':'.
Solutions
Solution 1: Simulation
We directly traverse all the cells within the range and add them to the answer array.
The time complexity is \(O(m \times n)\), and the space complexity is \(O(m \times n)\), where \(m\) and \(n\) are the range of rows and columns, respectively.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | |