2003. Smallest Missing Genetic Value in Each Subtree
Description
There is a family tree rooted at 0 consisting of n nodes numbered 0 to n - 1. You are given a 0-indexed integer array parents, where parents[i] is the parent for node i. Since node 0 is the root, parents[0] == -1.
There are 105 genetic values, each represented by an integer in the inclusive range [1, 105]. You are given a 0-indexed integer array nums, where nums[i] is a distinct genetic value for node i.
Return an array ans of length n where ans[i] is the smallest genetic value that is missing from the subtree rooted at node i.
The subtree rooted at a node x contains node x and all of its descendant nodes.
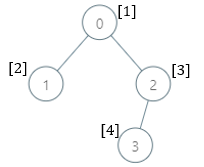
Example 1:
Input: parents = [-1,0,0,2], nums = [1,2,3,4] Output: [5,1,1,1] Explanation: The answer for each subtree is calculated as follows: - 0: The subtree contains nodes [0,1,2,3] with values [1,2,3,4]. 5 is the smallest missing value. - 1: The subtree contains only node 1 with value 2. 1 is the smallest missing value. - 2: The subtree contains nodes [2,3] with values [3,4]. 1 is the smallest missing value. - 3: The subtree contains only node 3 with value 4. 1 is the smallest missing value.
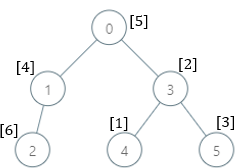
Example 2:
Input: parents = [-1,0,1,0,3,3], nums = [5,4,6,2,1,3] Output: [7,1,1,4,2,1] Explanation: The answer for each subtree is calculated as follows: - 0: The subtree contains nodes [0,1,2,3,4,5] with values [5,4,6,2,1,3]. 7 is the smallest missing value. - 1: The subtree contains nodes [1,2] with values [4,6]. 1 is the smallest missing value. - 2: The subtree contains only node 2 with value 6. 1 is the smallest missing value. - 3: The subtree contains nodes [3,4,5] with values [2,1,3]. 4 is the smallest missing value. - 4: The subtree contains only node 4 with value 1. 2 is the smallest missing value. - 5: The subtree contains only node 5 with value 3. 1 is the smallest missing value.
Example 3:
Input: parents = [-1,2,3,0,2,4,1], nums = [2,3,4,5,6,7,8] Output: [1,1,1,1,1,1,1] Explanation: The value 1 is missing from all the subtrees.
Constraints:
n == parents.length == nums.length2 <= n <= 1050 <= parents[i] <= n - 1fori != 0parents[0] == -1parentsrepresents a valid tree.1 <= nums[i] <= 105- Each
nums[i]is distinct.
Solutions
Solution 1: DFS
We notice that each node has a unique gene value, so we only need to find the node \(idx\) with gene value \(1\), and all nodes except for those on the path from node \(idx\) to the root node \(0\) have an answer of \(1\).
Therefore, we initialize the answer array \(ans\) to \([1,1,...,1]\), and our focus is on finding the answer for each node on the path from node \(idx\) to the root node \(0\).
We can start from node \(idx\) and use depth-first search to mark the gene values that appear in the subtree rooted at \(idx\), and record them in the array \(has\). During the search process, we use an array \(vis\) to mark the visited nodes to prevent repeated visits.
Next, we start from \(i=2\) and keep looking for the first gene value that has not appeared, which is the answer for node \(idx\). Here, \(i\) is strictly increasing, because the gene values are unique, so we can always find a gene value that has not appeared in \([1,..n+1]\).
Then, we update the answer for node \(idx\), i.e., \(ans[idx]=i\), and update \(idx\) to its parent node to continue the above process until \(idx=-1\), which means we have reached the root node \(0\).
Finally, we return the answer array \(ans\).
The time complexity is \(O(n)\), and the space complexity is \(O(n)\). Here, \(n\) is the number of nodes.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 | |