Breadth-First Search
Depth-First Search
Graph
Union Find
Description
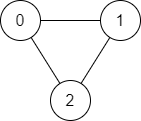
There is a bi-directional graph with n vertices, where each vertex is labeled from 0 to n - 1 (inclusive ). The edges in the graph are represented as a 2D integer array edges, where each edges[i] = [ui , vi ] denotes a bi-directional edge between vertex ui and vertex vi . Every vertex pair is connected by at most one edge, and no vertex has an edge to itself.
You want to determine if there is a valid path that exists from vertex source to vertex destination.
Given edges and the integers n, source, and destination, return true if there is a valid path from source to destination, or false otherwise .
Example 1:
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,0]], source = 0, destination = 2
Output: true
Explanation: There are two paths from vertex 0 to vertex 2:
- 0 → 1 → 2
- 0 → 2
Example 2:
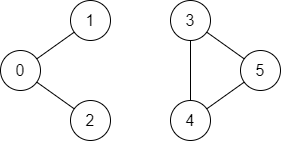
Input: n = 6, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[3,5],[5,4],[4,3]], source = 0, destination = 5
Output: false
Explanation: There is no path from vertex 0 to vertex 5.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 2 * 105 0 <= edges.length <= 2 * 105 edges[i].length == 20 <= ui , vi <= n - 1ui != vi 0 <= source, destination <= n - 1There are no duplicate edges.
There are no self edges.
Solutions
Solution 1: DFS
We first convert \(\textit{edges}\) into an adjacency list \(g\) , then use DFS to determine whether there is a path from \(\textit{source}\) to \(\textit{destination}\) .
During the process, we use an array \(\textit{vis}\) to record the vertices that have already been visited to avoid revisiting them.
The time complexity is \(O(n + m)\) , and the space complexity is \(O(n + m)\) . Here, \(n\) and \(m\) are the number of nodes and edges, respectively.
Python3 Java C++ Go TypeScript Rust
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19 class Solution :
def validPath (
self , n : int , edges : List [ List [ int ]], source : int , destination : int
) -> bool :
def dfs ( i : int ) -> bool :
if i == destination :
return True
vis . add ( i )
for j in g [ i ]:
if j not in vis and dfs ( j ):
return True
return False
g = [[] for _ in range ( n )]
for u , v in edges :
g [ u ] . append ( v )
g [ v ] . append ( u )
vis = set ()
return dfs ( source )
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31 class Solution {
private int destination ;
private boolean [] vis ;
private List < Integer >[] g ;
public boolean validPath ( int n , int [][] edges , int source , int destination ) {
this . destination = destination ;
vis = new boolean [ n ] ;
g = new List [ n ] ;
Arrays . setAll ( g , i -> new ArrayList <> ());
for ( var e : edges ) {
int u = e [ 0 ] , v = e [ 1 ] ;
g [ u ] . add ( v );
g [ v ] . add ( u );
}
return dfs ( source );
}
private boolean dfs ( int i ) {
if ( i == destination ) {
return true ;
}
vis [ i ] = true ;
for ( var j : g [ i ] ) {
if ( ! vis [ j ] && dfs ( j )) {
return true ;
}
}
return false ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25 class Solution {
public :
bool validPath ( int n , vector < vector < int >>& edges , int source , int destination ) {
vector < int > g [ n ];
vector < bool > vis ( n );
for ( const auto & e : edges ) {
int u = e [ 0 ], v = e [ 1 ];
g [ u ]. push_back ( v );
g [ v ]. push_back ( u );
}
function < bool ( int ) > dfs = [ & ]( int i ) -> bool {
if ( i == destination ) {
return true ;
}
vis [ i ] = true ;
for ( int j : g [ i ]) {
if ( ! vis [ j ] && dfs ( j )) {
return true ;
}
}
return false ;
};
return dfs ( source );
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23 func validPath ( n int , edges [][] int , source int , destination int ) bool {
vis := make ([] bool , n )
g := make ([][] int , n )
for _ , e := range edges {
u , v := e [ 0 ], e [ 1 ]
g [ u ] = append ( g [ u ], v )
g [ v ] = append ( g [ v ], u )
}
var dfs func ( int ) bool
dfs = func ( i int ) bool {
if i == destination {
return true
}
vis [ i ] = true
for _ , j := range g [ i ] {
if ! vis [ j ] && dfs ( j ) {
return true
}
}
return false
}
return dfs ( source )
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19 function validPath ( n : number , edges : number [][], source : number , destination : number ) : boolean {
const g : number [][] = Array . from ({ length : n }, () => []);
for ( const [ u , v ] of edges ) {
g [ u ]. push ( v );
g [ v ]. push ( u );
}
const vis = new Set < number > ();
const dfs = ( i : number ) => {
if ( i === destination ) {
return true ;
}
if ( vis . has ( i )) {
return false ;
}
vis . add ( i );
return g [ i ]. some ( dfs );
};
return dfs ( source );
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32 impl Solution {
pub fn valid_path ( n : i32 , edges : Vec < Vec < i32 >> , source : i32 , destination : i32 ) -> bool {
let n = n as usize ;
let source = source as usize ;
let destination = destination as usize ;
let mut g = vec! [ Vec :: new (); n ];
let mut vis = vec! [ false ; n ];
for e in edges {
let u = e [ 0 ] as usize ;
let v = e [ 1 ] as usize ;
g [ u ]. push ( v );
g [ v ]. push ( u );
}
fn dfs ( g : & Vec < Vec < usize >> , vis : & mut Vec < bool > , i : usize , destination : usize ) -> bool {
if i == destination {
return true ;
}
vis [ i ] = true ;
for & j in & g [ i ] {
if ! vis [ j ] && dfs ( g , vis , j , destination ) {
return true ;
}
}
false
}
dfs ( & g , & mut vis , source , destination )
}
}
Solution 2: BFS
We can also use BFS to determine whether there is a path from \(\textit{source}\) to \(\textit{destination}\) .
Specifically, we define a queue \(q\) , initially adding \(\textit{source}\) to the queue. Additionally, we use a set \(\textit{vis}\) to record the vertices that have already been visited to avoid revisiting them.
Next, we continuously take vertices \(i\) from the queue. If \(i = \textit{destination}\) , it means there is a path from \(\textit{source}\) to \(\textit{destination}\) , and we return \(\textit{true}\) . Otherwise, we traverse all adjacent vertices \(j\) of \(i\) . If \(j\) has not been visited, we add \(j\) to the queue \(q\) and mark \(j\) as visited.
Finally, if the queue is empty, it means there is no path from \(\textit{source}\) to \(\textit{destination}\) , and we return \(\textit{false}\) .
The time complexity is \(O(n + m)\) , and the space complexity is \(O(n + m)\) . Here, \(n\) and \(m\) are the number of nodes and edges, respectively.
Python3 Java C++ Go TypeScript Rust
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19 class Solution :
def validPath (
self , n : int , edges : List [ List [ int ]], source : int , destination : int
) -> bool :
g = [[] for _ in range ( n )]
for u , v in edges :
g [ u ] . append ( v )
g [ v ] . append ( u )
q = deque ([ source ])
vis = { source }
while q :
i = q . popleft ()
if i == destination :
return True
for j in g [ i ]:
if j not in vis :
vis . add ( j )
q . append ( j )
return False
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28 class Solution {
public boolean validPath ( int n , int [][] edges , int source , int destination ) {
List < Integer >[] g = new List [ n ] ;
Arrays . setAll ( g , k -> new ArrayList <> ());
for ( var e : edges ) {
int u = e [ 0 ] , v = e [ 1 ] ;
g [ u ] . add ( v );
g [ v ] . add ( u );
}
Deque < Integer > q = new ArrayDeque <> ();
q . offer ( source );
boolean [] vis = new boolean [ n ] ;
vis [ source ] = true ;
while ( ! q . isEmpty ()) {
int i = q . poll ();
if ( i == destination ) {
return true ;
}
for ( int j : g [ i ] ) {
if ( ! vis [ j ] ) {
vis [ j ] = true ;
q . offer ( j );
}
}
}
return false ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28 class Solution {
public :
bool validPath ( int n , vector < vector < int >>& edges , int source , int destination ) {
vector < vector < int >> g ( n );
for ( const auto & e : edges ) {
int u = e [ 0 ], v = e [ 1 ];
g [ u ]. push_back ( v );
g [ v ]. push_back ( u );
}
queue < int > q {{ source }};
vector < bool > vis ( n );
vis [ source ] = true ;
while ( q . size ()) {
int i = q . front ();
q . pop ();
if ( i == destination ) {
return true ;
}
for ( int j : g [ i ]) {
if ( ! vis [ j ]) {
vis [ j ] = true ;
q . push ( j );
}
}
}
return false ;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25 func validPath ( n int , edges [][] int , source int , destination int ) bool {
g := make ([][] int , n )
for _ , e := range edges {
u , v := e [ 0 ], e [ 1 ]
g [ u ] = append ( g [ u ], v )
g [ v ] = append ( g [ v ], u )
}
q := [] int { source }
vis := make ([] bool , n )
vis [ source ] = true
for len ( q ) > 0 {
i := q [ 0 ]
q = q [ 1 :]
if i == destination {
return true
}
for _ , j := range g [ i ] {
if ! vis [ j ] {
vis [ j ] = true
q = append ( q , j )
}
}
}
return false
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22 function validPath ( n : number , edges : number [][], source : number , destination : number ) : boolean {
const g : number [][] = Array . from ({ length : n }, () => []);
for ( const [ u , v ] of edges ) {
g [ u ]. push ( v );
g [ v ]. push ( u );
}
const vis = new Set < number > ([ source ]);
const q = [ source ];
while ( q . length ) {
const i = q . pop () ! ;
if ( i === destination ) {
return true ;
}
for ( const j of g [ i ]) {
if ( ! vis . has ( j )) {
vis . add ( j );
q . push ( j );
}
}
}
return false ;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36 use std :: collections ::{ HashSet , VecDeque };
impl Solution {
pub fn valid_path ( n : i32 , edges : Vec < Vec < i32 >> , source : i32 , destination : i32 ) -> bool {
let n = n as usize ;
let source = source as usize ;
let destination = destination as usize ;
let mut g = vec! [ Vec :: new (); n ];
for edge in edges {
let u = edge [ 0 ] as usize ;
let v = edge [ 1 ] as usize ;
g [ u ]. push ( v );
g [ v ]. push ( u );
}
let mut q = VecDeque :: new ();
let mut vis = HashSet :: new ();
q . push_back ( source );
vis . insert ( source );
while let Some ( i ) = q . pop_front () {
if i == destination {
return true ;
}
for & j in & g [ i ] {
if ! vis . contains ( & j ) {
vis . insert ( j );
q . push_back ( j );
}
}
}
false
}
}
Solution 3: Union-Find
Union-Find is a tree-like data structure that, as the name suggests, is used to handle some disjoint set merge and query problems. It supports two operations:
Find: Determine which subset an element belongs to. The time complexity of a single operation is \(O(\alpha(n))\) .
Union: Merge two subsets into one set. The time complexity of a single operation is \(O(\alpha(n))\) .
For this problem, we can use the Union-Find set to merge the edges in edges, and then determine whether source and destination are in the same set.
The time complexity is \(O(n \log n + m)\) or \(O(n \alpha(n) + m)\) , and the space complexity is \(O(n)\) . Where \(n\) and \(m\) are the number of nodes and edges, respectively.
Python3 Java C++ Go TypeScript Rust
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31 class UnionFind :
def __init__ ( self , n ):
self . p = list ( range ( n ))
self . size = [ 1 ] * n
def find ( self , x ):
if self . p [ x ] != x :
self . p [ x ] = self . find ( self . p [ x ])
return self . p [ x ]
def union ( self , a , b ):
pa , pb = self . find ( a ), self . find ( b )
if pa == pb :
return False
if self . size [ pa ] > self . size [ pb ]:
self . p [ pb ] = pa
self . size [ pa ] += self . size [ pb ]
else :
self . p [ pa ] = pb
self . size [ pb ] += self . size [ pa ]
return True
class Solution :
def validPath (
self , n : int , edges : List [ List [ int ]], source : int , destination : int
) -> bool :
uf = UnionFind ( n )
for u , v in edges :
uf . union ( u , v )
return uf . find ( source ) == uf . find ( destination )
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43 class UnionFind {
private int [] p ;
private int [] size ;
public UnionFind ( int n ) {
p = new int [ n ] ;
size = new int [ n ] ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; ++ i ) {
p [ i ] = i ;
size [ i ] = 1 ;
}
}
public int find ( int x ) {
if ( p [ x ] != x ) {
p [ x ] = find ( p [ x ] );
}
return p [ x ] ;
}
public void union ( int a , int b ) {
int pa = find ( a ), pb = find ( b );
if ( pa != pb ) {
if ( size [ pa ] > size [ pb ] ) {
p [ pb ] = pa ;
size [ pa ] += size [ pb ] ;
} else {
p [ pa ] = pb ;
size [ pb ] += size [ pa ] ;
}
}
}
}
class Solution {
public boolean validPath ( int n , int [][] edges , int source , int destination ) {
UnionFind uf = new UnionFind ( n );
for ( var e : edges ) {
uf . union ( e [ 0 ] , e [ 1 ] );
}
return uf . find ( source ) == uf . find ( destination );
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42 class UnionFind {
public :
UnionFind ( int n ) {
p = vector < int > ( n );
size = vector < int > ( n , 1 );
iota ( p . begin (), p . end (), 0 );
}
void unite ( int a , int b ) {
int pa = find ( a ), pb = find ( b );
if ( pa != pb ) {
if ( size [ pa ] > size [ pb ]) {
p [ pb ] = pa ;
size [ pa ] += size [ pb ];
} else {
p [ pa ] = pb ;
size [ pb ] += size [ pa ];
}
}
}
int find ( int x ) {
if ( p [ x ] != x ) {
p [ x ] = find ( p [ x ]);
}
return p [ x ];
}
private :
vector < int > p , size ;
};
class Solution {
public :
bool validPath ( int n , vector < vector < int >>& edges , int source , int destination ) {
UnionFind uf ( n );
for ( const auto & e : edges ) {
uf . unite ( e [ 0 ], e [ 1 ]);
}
return uf . find ( source ) == uf . find ( destination );
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43 type unionFind struct {
p , size [] int
}
func newUnionFind ( n int ) * unionFind {
p := make ([] int , n )
size := make ([] int , n )
for i := range p {
p [ i ] = i
size [ i ] = 1
}
return & unionFind { p , size }
}
func ( uf * unionFind ) find ( x int ) int {
if uf . p [ x ] != x {
uf . p [ x ] = uf . find ( uf . p [ x ])
}
return uf . p [ x ]
}
func ( uf * unionFind ) union ( a , b int ) bool {
pa , pb := uf . find ( a ), uf . find ( b )
if pa == pb {
return false
}
if uf . size [ pa ] > uf . size [ pb ] {
uf . p [ pb ] = pa
uf . size [ pa ] += uf . size [ pb ]
} else {
uf . p [ pa ] = pb
uf . size [ pb ] += uf . size [ pa ]
}
return true
}
func validPath ( n int , edges [][] int , source int , destination int ) bool {
uf := newUnionFind ( n )
for _ , e := range edges {
uf . union ( e [ 0 ], e [ 1 ])
}
return uf . find ( source ) == uf . find ( destination )
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38 class UnionFind {
p : number [];
size : number [];
constructor ( n : number ) {
this . p = Array ( n )
. fill ( 0 )
. map (( _ , i ) => i );
this . size = Array ( n ). fill ( 1 );
}
find ( x : number ) : number {
if ( this . p [ x ] !== x ) {
this . p [ x ] = this . find ( this . p [ x ]);
}
return this . p [ x ];
}
union ( a : number , b : number ) : boolean {
const [ pa , pb ] = [ this . find ( a ), this . find ( b )];
if ( pa === pb ) {
return false ;
}
if ( this . size [ pa ] > this . size [ pb ]) {
this . p [ pb ] = pa ;
this . size [ pa ] += this . size [ pb ];
} else {
this . p [ pa ] = pb ;
this . size [ pb ] += this . size [ pa ];
}
return true ;
}
}
function validPath ( n : number , edges : number [][], source : number , destination : number ) : boolean {
const uf = new UnionFind ( n );
edges . forEach (([ u , v ]) => uf . union ( u , v ));
return uf . find ( source ) === uf . find ( destination );
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48 struct UnionFind {
p : Vec < usize > ,
size : Vec < usize > ,
}
impl UnionFind {
fn new ( n : usize ) -> Self {
let p = ( 0 .. n ). collect ();
let size = vec! [ 1 ; n ];
UnionFind { p , size }
}
fn find ( & mut self , x : usize ) -> usize {
if self . p [ x ] != x {
self . p [ x ] = self . find ( self . p [ x ]);
}
self . p [ x ]
}
fn union ( & mut self , a : usize , b : usize ) {
let pa = self . find ( a );
let pb = self . find ( b );
if pa != pb {
if self . size [ pa ] > self . size [ pb ] {
self . p [ pb ] = pa ;
self . size [ pa ] += self . size [ pb ];
} else {
self . p [ pa ] = pb ;
self . size [ pb ] += self . size [ pa ];
}
}
}
}
impl Solution {
pub fn valid_path ( n : i32 , edges : Vec < Vec < i32 >> , source : i32 , destination : i32 ) -> bool {
let n = n as usize ;
let mut uf = UnionFind :: new ( n );
for e in edges {
let u = e [ 0 ] as usize ;
let v = e [ 1 ] as usize ;
uf . union ( u , v );
}
uf . find ( source as usize ) == uf . find ( destination as usize )
}
}