Linked List
Two Pointers
Description
Given the head of a linked list, remove the nth node from the end of the list and return its head.
Example 1:
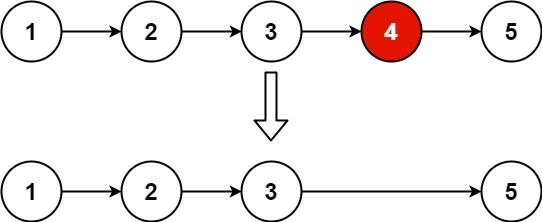
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2
Output: [1,2,3,5]
Example 2:
Input: head = [1], n = 1
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: head = [1,2], n = 1
Output: [1]
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the list is sz.
1 <= sz <= 300 <= Node.val <= 1001 <= n <= sz
Follow up: Could you do this in one pass?
Solutions
Solution 1: Fast and Slow Pointers
We define two pointers fast and slow, both initially pointing to the dummy head node of the linked list.
Next, the fast pointer moves forward \(n\) steps first, then fast and slow pointers move forward together until the fast pointer reaches the end of the linked list. At this point, the node pointed to by slow.next is the predecessor of the \(n\) -th node from the end, and we can delete it.
The time complexity is \(O(n)\) , where \(n\) is the length of the linked list. The space complexity is \(O(1)\) .
Python3 Java C++ Go TypeScript Rust JavaScript Swift Ruby C# PHP
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15 # Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution :
def removeNthFromEnd ( self , head : Optional [ ListNode ], n : int ) -> Optional [ ListNode ]:
dummy = ListNode ( next = head )
fast = slow = dummy
for _ in range ( n ):
fast = fast . next
while fast . next :
slow , fast = slow . next , fast . next
slow . next = slow . next . next
return dummy . next
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25 /**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd ( ListNode head , int n ) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode ( 0 , head );
ListNode fast = dummy , slow = dummy ;
while ( n -- > 0 ) {
fast = fast . next ;
}
while ( fast . next != null ) {
slow = slow . next ;
fast = fast . next ;
}
slow . next = slow . next . next ;
return dummy . next ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27 /**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public :
ListNode * removeNthFromEnd ( ListNode * head , int n ) {
ListNode * dummy = new ListNode ( 0 , head );
ListNode * fast = dummy ;
ListNode * slow = dummy ;
while ( n -- ) {
fast = fast -> next ;
}
while ( fast -> next ) {
slow = slow -> next ;
fast = fast -> next ;
}
slow -> next = slow -> next -> next ;
return dummy -> next ;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19 /**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func removeNthFromEnd ( head * ListNode , n int ) * ListNode {
dummy := & ListNode { 0 , head }
fast , slow := dummy , dummy
for ; n > 0 ; n -- {
fast = fast . Next
}
for fast . Next != nil {
slow , fast = slow . Next , fast . Next
}
slow . Next = slow . Next . Next
return dummy . Next
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26 /**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* val: number
* next: ListNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
* }
*/
function removeNthFromEnd ( head : ListNode | null , n : number ) : ListNode | null {
const dummy = new ListNode ( 0 , head );
let fast = dummy ;
let slow = dummy ;
while ( n -- ) {
fast = fast . next ;
}
while ( fast . next ) {
slow = slow . next ;
fast = fast . next ;
}
slow . next = slow . next . next ;
return dummy . next ;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32 // Definition for singly-linked list.
// #[derive(PartialEq, Eq, Clone, Debug)]
// pub struct ListNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub next: Option<Box<ListNode>>
// }
//
// impl ListNode {
// #[inline]
// fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// ListNode {
// next: None,
// val
// }
// }
// }
impl Solution {
pub fn remove_nth_from_end ( head : Option < Box < ListNode >> , n : i32 ) -> Option < Box < ListNode >> {
let mut dummy = Some ( Box :: new ( ListNode { val : 0 , next : head }));
let mut slow = & mut dummy ;
let mut fast = & slow . clone ();
for _ in 0 ..= n {
fast = & fast . as_ref (). unwrap (). next ;
}
while fast . is_some () {
fast = & fast . as_ref (). unwrap (). next ;
slow = & mut slow . as_mut (). unwrap (). next ;
}
slow . as_mut (). unwrap (). next = slow . as_mut (). unwrap (). next . as_mut (). unwrap (). next . take ();
dummy . unwrap (). next
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26 /**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} n
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var removeNthFromEnd = function ( head , n ) {
const dummy = new ListNode ( 0 , head );
let fast = dummy ,
slow = dummy ;
while ( n -- ) {
fast = fast . next ;
}
while ( fast . next ) {
slow = slow . next ;
fast = fast . next ;
}
slow . next = slow . next . next ;
return dummy . next ;
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27 /**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* public var val: Int
* public var next: ListNode?
* public init() { self.val = 0; self.next = nil; }
* public init(_ val: Int) { self.val = val; self.next = nil; }
* public init(_ val: Int, _ next: ListNode?) { self.val = val; self.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
func removeNthFromEnd ( _ head : ListNode ?, _ n : Int ) -> ListNode ? {
let dummy = ListNode ( 0 )
dummy . next = head
var fast : ListNode ? = dummy
var slow : ListNode ? = dummy
for _ in 0. .< n {
fast = fast ?. next
}
while fast ?. next != nil {
fast = fast ?. next
slow = slow ?. next
}
slow ?. next = slow ?. next ?. next
return dummy . next
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25 # Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode
# attr_accessor :val, :next
# def initialize(val = 0, _next = nil)
# @val = val
# @next = _next
# end
# end
# @param {ListNode} head
# @param {Integer} n
# @return {ListNode}
def remove_nth_from_end ( head , n )
dummy = ListNode . new ( 0 , head )
fast = slow = dummy
while n > 0
fast = fast . next
n -= 1
end
while fast . next
slow = slow . next
fast = fast . next
end
slow . next = slow . next . next
return dummy . next
end
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26 /**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* public int val;
* public ListNode next;
* public ListNode(int val=0, ListNode next=null) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = next;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode RemoveNthFromEnd ( ListNode head , int n ) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode ( 0 , head );
ListNode fast = dummy , slow = dummy ;
while ( n -- > 0 ) {
fast = fast . next ;
}
while ( fast . next != null ) {
slow = slow . next ;
fast = fast . next ;
}
slow . next = slow . next . next ;
return dummy . next ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31 /**
* Definition for a singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* public $val = 0;
* public $next = null;
* function __construct($val = 0, $next = null) {
* $this->val = $val;
* $this->next = $next;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
/**
* @param ListNode $head
* @param Integer $n
* @return ListNode
*/
function removeNthFromEnd($head, $n) {
$dummy = new ListNode(0, $head);
$fast = $slow = $dummy;
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++) {
$fast = $fast->next;
}
while ($fast->next !== null) {
$fast = $fast->next;
$slow = $slow->next;
}
$slow->next = $slow->next->next;
return $dummy->next;
}
}