1812. Determine Color of a Chessboard Square
Description
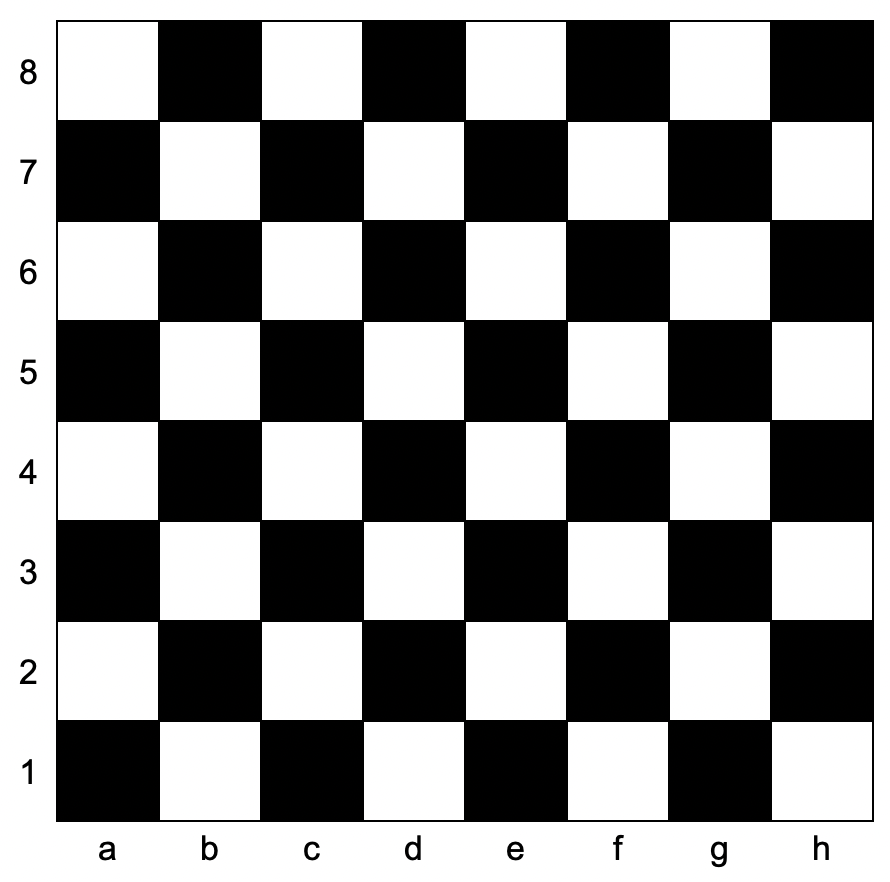
You are given coordinates, a string that represents the coordinates of a square of the chessboard. Below is a chessboard for your reference.
Return true if the square is white, and false if the square is black.
The coordinate will always represent a valid chessboard square. The coordinate will always have the letter first, and the number second.
Example 1:
Input: coordinates = "a1" Output: false Explanation: From the chessboard above, the square with coordinates "a1" is black, so return false.
Example 2:
Input: coordinates = "h3" Output: true Explanation: From the chessboard above, the square with coordinates "h3" is white, so return true.
Example 3:
Input: coordinates = "c7" Output: false
Constraints:
coordinates.length == 2'a' <= coordinates[0] <= 'h''1' <= coordinates[1] <= '8'
Solutions
Solution 1: Pattern Recognition
Observing the chessboard, we find that two squares \((x_1, y_1)\) and \((x_2, y_2)\) with the same color satisfy that both \(x_1 + y_1\) and \(x_2 + y_2\) are either odd or even.
Therefore, we can get the corresponding coordinates \((x, y)\) from \(\textit{coordinates}\). If \(x + y\) is odd, the square is white, and we return \(\textit{true}\); otherwise, we return \(\textit{false}\).
The time complexity is \(O(1)\), and the space complexity is \(O(1)\).
1 2 3 | |
1 2 3 4 5 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 | |
1 2 3 | |
1 2 3 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | |
1 2 3 | |