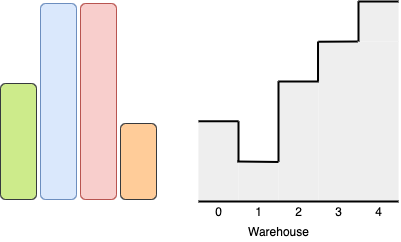1580. Put Boxes Into the Warehouse II 🔒
Description
You are given two arrays of positive integers, boxes and warehouse, representing the heights of some boxes of unit width and the heights of n rooms in a warehouse respectively. The warehouse's rooms are labeled from 0 to n - 1 from left to right where warehouse[i] (0-indexed) is the height of the ith room.
Boxes are put into the warehouse by the following rules:
- Boxes cannot be stacked.
- You can rearrange the insertion order of the boxes.
- Boxes can be pushed into the warehouse from either side (left or right)
- If the height of some room in the warehouse is less than the height of a box, then that box and all other boxes behind it will be stopped before that room.
Return the maximum number of boxes you can put into the warehouse.
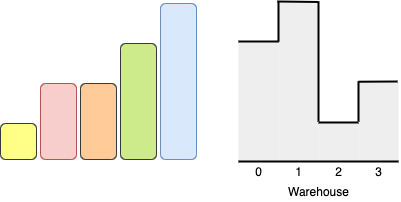
Example 1:
Input: boxes = [1,2,2,3,4], warehouse = [3,4,1,2] Output: 4 Explanation:We can store the boxes in the following order: 1- Put the yellow box in room 2 from either the left or right side. 2- Put the orange box in room 3 from the right side. 3- Put the green box in room 1 from the left side. 4- Put the red box in room 0 from the left side. Notice that there are other valid ways to put 4 boxes such as swapping the red and green boxes or the red and orange boxes.
Example 2:
Input: boxes = [3,5,5,2], warehouse = [2,1,3,4,5] Output: 3 Explanation:It is not possible to put the two boxes of height 5 in the warehouse since there's only 1 room of height >= 5. Other valid solutions are to put the green box in room 2 or to put the orange box first in room 2 before putting the green and red boxes.
Constraints:
n == warehouse.length1 <= boxes.length, warehouse.length <= 1051 <= boxes[i], warehouse[i] <= 109
Solutions
Solution 1: Preprocessing + Sorting + Greedy
First, we preprocess the warehouse to get the maximum height of each room. Then, we sort both the boxes and the warehouse. Starting with the smallest box and the smallest room, if the current room's height is greater than or equal to the current box's height, we can place the current box in the current room; otherwise, we continue to the next room.
Finally, we return the number of boxes that can be placed.
The time complexity is \(O(n \times \log n)\), and the space complexity is \(O(n)\). Here, \(n\) is the length of the warehouse.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 | |