Array
Heap (Priority Queue)
Sorting
Description
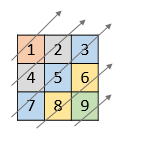
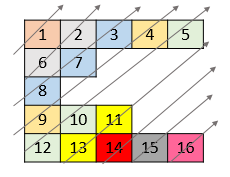
Given a 2D integer array nums, return all elements of nums in diagonal order as shown in the below images .
Example 1:
Input: nums = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
Output: [1,4,2,7,5,3,8,6,9]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [[1,2,3,4,5],[6,7],[8],[9,10,11],[12,13,14,15,16]]
Output: [1,6,2,8,7,3,9,4,12,10,5,13,11,14,15,16]
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 105 1 <= nums[i].length <= 105 1 <= sum(nums[i].length) <= 105 1 <= nums[i][j] <= 105
Solutions
Solution 1: Sorting
We observe that:
The value of \(i + j\) is the same for each diagonal;
The value of \(i + j\) for the next diagonal is greater than that of the previous diagonal;
Within the same diagonal, the value of \(i + j\) is the same, and the value of \(j\) increases from small to large.
Therefore, we store all numbers in the form of \((i, j, \textit{nums}[i][j])\) into \(\textit{arr}\) , and then sort according to the first two items. Finally, return the array composed of the values at index 2 of all elements in \(\textit{arr}\) .
The time complexity is \(O(n \times \log n)\) , where \(n\) is the number of elements in the array \(\textit{nums}\) . The space complexity is \(O(n)\) .
Python3 Java C++ Go TypeScript C#
class Solution :
def findDiagonalOrder ( self , nums : List [ List [ int ]]) -> List [ int ]:
arr = []
for i , row in enumerate ( nums ):
for j , v in enumerate ( row ):
arr . append (( i + j , j , v ))
arr . sort ()
return [ v [ 2 ] for v in arr ]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16 class Solution {
public int [] findDiagonalOrder ( List < List < Integer >> nums ) {
List < int []> arr = new ArrayList <> ();
for ( int i = 0 ; i < nums . size (); ++ i ) {
for ( int j = 0 ; j < nums . get ( i ). size (); ++ j ) {
arr . add ( new int [] { i + j , j , nums . get ( i ). get ( j )});
}
}
arr . sort (( a , b ) -> a [ 0 ] == b [ 0 ] ? a [ 1 ] - b [ 1 ] : a [ 0 ] - b [ 0 ] );
int [] ans = new int [ arr . size () ] ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < arr . size (); ++ i ) {
ans [ i ] = arr . get ( i ) [ 2 ] ;
}
return ans ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17 class Solution {
public :
vector < int > findDiagonalOrder ( vector < vector < int >>& nums ) {
vector < tuple < int , int , int >> arr ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < nums . size (); ++ i ) {
for ( int j = 0 ; j < nums [ i ]. size (); ++ j ) {
arr . push_back ({ i + j , j , nums [ i ][ j ]});
}
}
sort ( arr . begin (), arr . end ());
vector < int > ans ;
for ( auto & e : arr ) {
ans . push_back ( get < 2 > ( e ));
}
return ans ;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19 func findDiagonalOrder ( nums [][] int ) [] int {
arr := [][] int {}
for i , row := range nums {
for j , v := range row {
arr = append ( arr , [] int { i + j , j , v })
}
}
sort . Slice ( arr , func ( i , j int ) bool {
if arr [ i ][ 0 ] == arr [ j ][ 0 ] {
return arr [ i ][ 1 ] < arr [ j ][ 1 ]
}
return arr [ i ][ 0 ] < arr [ j ][ 0 ]
})
ans := [] int {}
for _ , v := range arr {
ans = append ( ans , v [ 2 ])
}
return ans
}
function findDiagonalOrder ( nums : number [][]) : number [] {
const arr : number [][] = [];
for ( let i = 0 ; i < nums . length ; ++ i ) {
for ( let j = 0 ; j < nums [ i ]. length ; ++ j ) {
arr . push ([ i + j , j , nums [ i ][ j ]]);
}
}
arr . sort (( a , b ) => ( a [ 0 ] === b [ 0 ] ? a [ 1 ] - b [ 1 ] : a [ 0 ] - b [ 0 ]));
return arr . map ( x => x [ 2 ]);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16 public class Solution {
public int [] FindDiagonalOrder ( IList < IList < int >> nums ) {
List < int [] > arr = new List < int [] > ();
for ( int i = 0 ; i < nums . Count ; ++ i ) {
for ( int j = 0 ; j < nums [ i ]. Count ; ++ j ) {
arr . Add ( new int [] { i + j , j , nums [ i ][ j ] });
}
}
arr . Sort (( a , b ) => a [ 0 ] == b [ 0 ] ? a [ 1 ] - b [ 1 ] : a [ 0 ] - b [ 0 ]);
int [] ans = new int [ arr . Count ];
for ( int i = 0 ; i < arr . Count ; ++ i ) {
ans [ i ] = arr [ i ][ 2 ];
}
return ans ;
}
}
GitHub