Binary Search Tree
Binary Tree
Depth-First Search
Sorting
Tree
Description
Given two binary search trees root1 and root2, return a list containing all the integers from both trees sorted in ascending order .
Example 1:
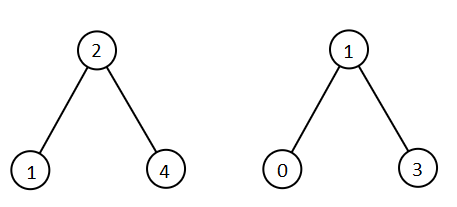
Input: root1 = [2,1,4], root2 = [1,0,3]
Output: [0,1,1,2,3,4]
Example 2:
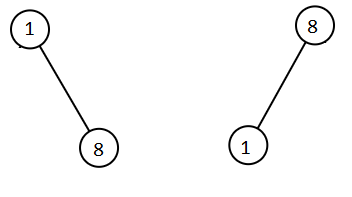
Input: root1 = [1,null,8], root2 = [8,1]
Output: [1,1,8,8]
Constraints:
The number of nodes in each tree is in the range [0, 5000].
-105 <= Node.val <= 105
Solutions
Solution 1: DFS + Merge
Since both trees are binary search trees, we can obtain the node value sequences \(\textit{a}\) and \(\textit{b}\) of the two trees through in-order traversal. Then, we use two pointers to merge the two sorted arrays to get the final answer.
The time complexity is \(O(n+m)\) , and the space complexity is \(O(n+m)\) . Here, \(n\) and \(m\) are the number of nodes in the two trees, respectively.
Python3 Java C++ Go TypeScript Rust
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37 # Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution :
def getAllElements (
self , root1 : Optional [ TreeNode ], root2 : Optional [ TreeNode ]
) -> List [ int ]:
def dfs ( root : Optional [ TreeNode ], nums : List [ int ]) -> int :
if root is None :
return
dfs ( root . left , nums )
nums . append ( root . val )
dfs ( root . right , nums )
a , b = [], []
dfs ( root1 , a )
dfs ( root2 , b )
m , n = len ( a ), len ( b )
i = j = 0
ans = []
while i < m and j < n :
if a [ i ] <= b [ j ]:
ans . append ( a [ i ])
i += 1
else :
ans . append ( b [ j ])
j += 1
while i < m :
ans . append ( a [ i ])
i += 1
while j < n :
ans . append ( b [ j ])
j += 1
return ans
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List < Integer > getAllElements ( TreeNode root1 , TreeNode root2 ) {
List < Integer > a = new ArrayList <> ();
List < Integer > b = new ArrayList <> ();
dfs ( root1 , a );
dfs ( root2 , b );
int m = a . size (), n = b . size ();
int i = 0 , j = 0 ;
List < Integer > ans = new ArrayList <> ();
while ( i < m && j < n ) {
if ( a . get ( i ) <= b . get ( j )) {
ans . add ( a . get ( i ++ ));
} else {
ans . add ( b . get ( j ++ ));
}
}
while ( i < m ) {
ans . add ( a . get ( i ++ ));
}
while ( j < n ) {
ans . add ( b . get ( j ++ ));
}
return ans ;
}
private void dfs ( TreeNode root , List < Integer > nums ) {
if ( root == null ) {
return ;
}
dfs ( root . left , nums );
nums . add ( root . val );
dfs ( root . right , nums );
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public :
vector < int > getAllElements ( TreeNode * root1 , TreeNode * root2 ) {
vector < int > a , b , ans ;
dfs ( root1 , a );
dfs ( root2 , b );
int i = 0 , j = 0 ;
while ( i < a . size () && j < b . size ()) {
if ( a [ i ] <= b [ j ]) {
ans . push_back ( a [ i ++ ]);
} else {
ans . push_back ( b [ j ++ ]);
}
}
while ( i < a . size ()) {
ans . push_back ( a [ i ++ ]);
}
while ( j < b . size ()) {
ans . push_back ( b [ j ++ ]);
}
return ans ;
}
private :
void dfs ( TreeNode * root , vector < int >& nums ) {
if ( root == nullptr ) {
return ;
}
dfs ( root -> left , nums );
nums . push_back ( root -> val );
dfs ( root -> right , nums );
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func getAllElements ( root1 * TreeNode , root2 * TreeNode ) ( ans [] int ) {
var dfs func ( * TreeNode , * [] int )
dfs = func ( root * TreeNode , nums * [] int ) {
if root == nil {
return
}
dfs ( root . Left , nums )
* nums = append ( * nums , root . Val )
dfs ( root . Right , nums )
}
a , b := [] int {}, [] int {}
dfs ( root1 , & a )
dfs ( root2 , & b )
i , j := 0 , 0
m , n := len ( a ), len ( b )
for i < m && j < n {
if a [ i ] < b [ j ] {
ans = append ( ans , a [ i ])
i ++
} else {
ans = append ( ans , b [ j ])
j ++
}
}
for ; i < m ; i ++ {
ans = append ( ans , a [ i ])
}
for ; j < n ; j ++ {
ans = append ( ans , b [ j ])
}
return
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function getAllElements ( root1 : TreeNode | null , root2 : TreeNode | null ) : number [] {
const dfs = ( root : TreeNode | null , nums : number []) => {
if ( ! root ) {
return ;
}
dfs ( root . left , nums );
nums . push ( root . val );
dfs ( root . right , nums );
};
const a : number [] = [];
const b : number [] = [];
dfs ( root1 , a );
dfs ( root2 , b );
const [ m , n ] = [ a . length , b . length ];
const ans : number [] = [];
let [ i , j ] = [ 0 , 0 ];
while ( i < m && j < n ) {
if ( a [ i ] < b [ j ]) {
ans . push ( a [ i ++ ]);
} else {
ans . push ( b [ j ++ ]);
}
}
while ( i < m ) {
ans . push ( a [ i ++ ]);
}
while ( j < n ) {
ans . push ( b [ j ++ ]);
}
return ans ;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66 // Definition for a binary tree node.
// #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
// pub struct TreeNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// }
//
// impl TreeNode {
// #[inline]
// pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// TreeNode {
// val,
// left: None,
// right: None
// }
// }
// }
use std :: cell :: RefCell ;
use std :: rc :: Rc ;
impl Solution {
pub fn get_all_elements (
root1 : Option < Rc < RefCell < TreeNode >>> ,
root2 : Option < Rc < RefCell < TreeNode >>> ,
) -> Vec < i32 > {
let mut a = Vec :: new ();
let mut b = Vec :: new ();
Solution :: dfs ( & root1 , & mut a );
Solution :: dfs ( & root2 , & mut b );
let mut ans = Vec :: new ();
let ( mut i , mut j ) = ( 0 , 0 );
while i < a . len () && j < b . len () {
if a [ i ] <= b [ j ] {
ans . push ( a [ i ]);
i += 1 ;
} else {
ans . push ( b [ j ]);
j += 1 ;
}
}
while i < a . len () {
ans . push ( a [ i ]);
i += 1 ;
}
while j < b . len () {
ans . push ( b [ j ]);
j += 1 ;
}
ans
}
fn dfs ( root : & Option < Rc < RefCell < TreeNode >>> , nums : & mut Vec < i32 > ) {
if let Some ( node ) = root {
let node = node . borrow ();
Solution :: dfs ( & node . left , nums );
nums . push ( node . val );
Solution :: dfs ( & node . right , nums );
}
}
}