二分查找
前缀和
哈希表
排序
数组
有序集合
题目描述
给你一个下标从 0 开始的二维整数数组 flowers ,其中 flowers[i] = [starti , endi ] 表示第 i 朵花的 花期 从 starti 到 endi (都 包含 )。同时给你一个下标从 0 开始大小为 n 的整数数组 people ,people[i] 是第 i 个人来看花的时间。
请你返回一个大小为 n 的整数数组 answer ,其中 answer[i]是第 i 个人到达时在花期内花的 数目 。
示例 1:
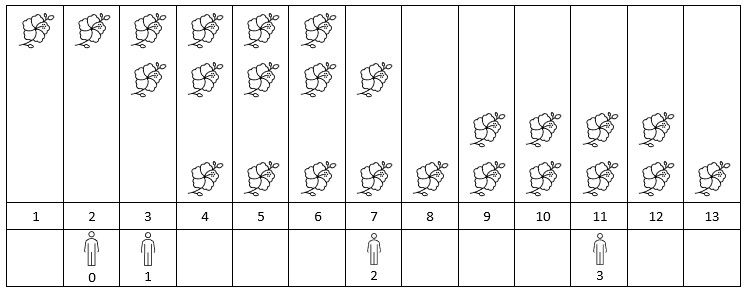
输入: flowers = [[1,6],[3,7],[9,12],[4,13]], people = [2,3,7,11]
输出: [1,2,2,2]
解释: 上图展示了每朵花的花期时间,和每个人的到达时间。
对每个人,我们返回他们到达时在花期内花的数目。
示例 2:
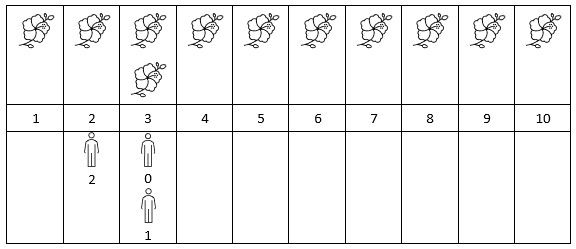
输入: flowers = [[1,10],[3,3]], people = [3,3,2]
输出: [2,2,1]
解释: 上图展示了每朵花的花期时间,和每个人的到达时间。
对每个人,我们返回他们到达时在花期内花的数目。
提示:
1 <= flowers.length <= 5 * 104 flowers[i].length == 21 <= starti <= endi <= 109 1 <= people.length <= 5 * 104 1 <= people[i] <= 109
解法
方法一:排序 + 二分查找
我们将花按照开始时间和结束时间分别排序,然后对于每个人,我们可以使用二分查找来找到他们到达时在花期内花的数目。就是说,找出在每个人到达时,已经开花的花的数目,减去在每个人到达时,已经凋谢的花的数目,即可得到答案。
时间复杂度 \(O((m + n) \times \log n)\) ,空间复杂度 \(O(n)\) 。其中 \(n\) 和 \(m\) 分别是数组 \(\textit{flowers}\) 和 \(\textit{people}\) 的长度。
Python3 Java C++ Go TypeScript Rust
class Solution :
def fullBloomFlowers (
self , flowers : List [ List [ int ]], people : List [ int ]
) -> List [ int ]:
start , end = sorted ( a for a , _ in flowers ), sorted ( b for _ , b in flowers )
return [ bisect_right ( start , p ) - bisect_left ( end , p ) for p in people ]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32 class Solution {
public int [] fullBloomFlowers ( int [][] flowers , int [] people ) {
int n = flowers . length ;
int [] start = new int [ n ] ;
int [] end = new int [ n ] ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; ++ i ) {
start [ i ] = flowers [ i ][ 0 ] ;
end [ i ] = flowers [ i ][ 1 ] ;
}
Arrays . sort ( start );
Arrays . sort ( end );
int m = people . length ;
int [] ans = new int [ m ] ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < m ; ++ i ) {
ans [ i ] = search ( start , people [ i ] + 1 ) - search ( end , people [ i ] );
}
return ans ;
}
private int search ( int [] nums , int x ) {
int l = 0 , r = nums . length ;
while ( l < r ) {
int mid = ( l + r ) >> 1 ;
if ( nums [ mid ] >= x ) {
r = mid ;
} else {
l = mid + 1 ;
}
}
return l ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21 class Solution {
public :
vector < int > fullBloomFlowers ( vector < vector < int >>& flowers , vector < int >& people ) {
int n = flowers . size ();
vector < int > start ;
vector < int > end ;
for ( auto & f : flowers ) {
start . push_back ( f [ 0 ]);
end . push_back ( f [ 1 ]);
}
sort ( start . begin (), start . end ());
sort ( end . begin (), end . end ());
vector < int > ans ;
for ( auto & p : people ) {
auto r = upper_bound ( start . begin (), start . end (), p ) - start . begin ();
auto l = lower_bound ( end . begin (), end . end (), p ) - end . begin ();
ans . push_back ( r - l );
}
return ans ;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17 func fullBloomFlowers ( flowers [][] int , people [] int ) ( ans [] int ) {
n := len ( flowers )
start := make ([] int , n )
end := make ([] int , n )
for i , f := range flowers {
start [ i ] = f [ 0 ]
end [ i ] = f [ 1 ]
}
sort . Ints ( start )
sort . Ints ( end )
for _ , p := range people {
r := sort . SearchInts ( start , p + 1 )
l := sort . SearchInts ( end , p )
ans = append ( ans , r - l )
}
return
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32 function fullBloomFlowers ( flowers : number [][], people : number []) : number [] {
const n = flowers . length ;
const start = new Array ( n ). fill ( 0 );
const end = new Array ( n ). fill ( 0 );
for ( let i = 0 ; i < n ; ++ i ) {
start [ i ] = flowers [ i ][ 0 ];
end [ i ] = flowers [ i ][ 1 ];
}
start . sort (( a , b ) => a - b );
end . sort (( a , b ) => a - b );
const ans : number [] = [];
for ( const p of people ) {
const r = search ( start , p + 1 );
const l = search ( end , p );
ans . push ( r - l );
}
return ans ;
}
function search ( nums : number [], x : number ) : number {
let l = 0 ;
let r = nums . length ;
while ( l < r ) {
const mid = ( l + r ) >> 1 ;
if ( nums [ mid ] >= x ) {
r = mid ;
} else {
l = mid + 1 ;
}
}
return l ;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44 use std :: collections :: BTreeMap ;
impl Solution {
#[allow(dead_code)]
pub fn full_bloom_flowers ( flowers : Vec < Vec < i32 >> , people : Vec < i32 > ) -> Vec < i32 > {
let n = people . len ();
// First sort the people vector based on the first item
let mut people : Vec < ( usize , i32 ) > = people . into_iter (). enumerate (). map ( | x | x ). collect ();
people . sort_by ( | lhs , rhs | lhs . 1. cmp ( & rhs . 1 ));
// Initialize the difference vector
let mut diff = BTreeMap :: new ();
let mut ret = vec! [ 0 ; n ];
for f in flowers {
let ( left , right ) = ( f [ 0 ], f [ 1 ]);
diff . entry ( left )
. and_modify ( | x | {
* x += 1 ;
})
. or_insert ( 1 );
diff . entry ( right + 1 )
. and_modify ( | x | {
* x -= 1 ;
})
. or_insert ( - 1 );
}
let mut sum = 0 ;
let mut i = 0 ;
for ( k , v ) in diff {
while i < n && people [ i ]. 1 < k {
ret [ people [ i ]. 0 ] += sum ;
i += 1 ;
}
sum += v ;
}
ret
}
}
方法二:差分 + 排序 + 离线查询
我们可以利用差分来维护每个时间点的花的数目。接下来,我们将 \(people\) 按照到达时间从小到大排序,在每个人到达时,我们对差分数组进行前缀和运算,就可以得到答案。
时间复杂度 \(O(m \times \log m + n \times \log n)\) ,空间复杂度 \(O(n + m)\) 。其中 \(n\) 和 \(m\) 分别是数组 \(\textit{flowers}\) 和 \(\textit{people}\) 的长度。
Python3 Java C++ Go TypeScript
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18 class Solution :
def fullBloomFlowers (
self , flowers : List [ List [ int ]], people : List [ int ]
) -> List [ int ]:
d = defaultdict ( int )
for st , ed in flowers :
d [ st ] += 1
d [ ed + 1 ] -= 1
ts = sorted ( d )
s = i = 0
m = len ( people )
ans = [ 0 ] * m
for t , j in sorted ( zip ( people , range ( m ))):
while i < len ( ts ) and ts [ i ] <= t :
s += d [ ts [ i ]]
i += 1
ans [ j ] = s
return ans
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25 class Solution {
public int [] fullBloomFlowers ( int [][] flowers , int [] people ) {
TreeMap < Integer , Integer > d = new TreeMap <> ();
for ( int [] f : flowers ) {
d . merge ( f [ 0 ] , 1 , Integer :: sum );
d . merge ( f [ 1 ] + 1 , - 1 , Integer :: sum );
}
int s = 0 ;
int m = people . length ;
Integer [] idx = new Integer [ m ] ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < m ; i ++ ) {
idx [ i ] = i ;
}
Arrays . sort ( idx , Comparator . comparingInt ( i -> people [ i ] ));
int [] ans = new int [ m ] ;
for ( int i : idx ) {
int t = people [ i ] ;
while ( ! d . isEmpty () && d . firstKey () <= t ) {
s += d . pollFirstEntry (). getValue ();
}
ans [ i ] = s ;
}
return ans ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27 class Solution {
public :
vector < int > fullBloomFlowers ( vector < vector < int >>& flowers , vector < int >& people ) {
map < int , int > d ;
for ( auto & f : flowers ) {
d [ f [ 0 ]] ++ ;
d [ f [ 1 ] + 1 ] -- ;
}
int m = people . size ();
vector < int > idx ( m );
iota ( idx . begin (), idx . end (), 0 );
sort ( idx . begin (), idx . end (), [ & ]( int i , int j ) {
return people [ i ] < people [ j ];
});
vector < int > ans ( m );
int s = 0 ;
for ( int i : idx ) {
int t = people [ i ];
while ( ! d . empty () && d . begin () -> first <= t ) {
s += d . begin () -> second ;
d . erase ( d . begin ());
}
ans [ i ] = s ;
}
return ans ;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29 func fullBloomFlowers ( flowers [][] int , people [] int ) [] int {
d := map [ int ] int {}
for _ , f := range flowers {
d [ f [ 0 ]] ++
d [ f [ 1 ] + 1 ] --
}
ts := [] int {}
for t := range d {
ts = append ( ts , t )
}
sort . Ints ( ts )
m := len ( people )
idx := make ([] int , m )
for i := range idx {
idx [ i ] = i
}
sort . Slice ( idx , func ( i , j int ) bool { return people [ idx [ i ]] < people [ idx [ j ]] })
ans := make ([] int , m )
s , i := 0 , 0
for _ , j := range idx {
t := people [ j ]
for i < len ( ts ) && ts [ i ] <= t {
s += d [ ts [ i ]]
i ++
}
ans [ j ] = s
}
return ans
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22 function fullBloomFlowers ( flowers : number [][], people : number []) : number [] {
const d : Map < number , number > = new Map ();
for ( const [ st , ed ] of flowers ) {
d . set ( st , ( d . get ( st ) || 0 ) + 1 );
d . set ( ed + 1 , ( d . get ( ed + 1 ) || 0 ) - 1 );
}
const ts = [... d . keys ()]. sort (( a , b ) => a - b );
let s = 0 ;
let i = 0 ;
const m = people . length ;
const idx : number [] = [... Array ( m )]. map (( _ , i ) => i ). sort (( a , b ) => people [ a ] - people [ b ]);
const ans = Array ( m ). fill ( 0 );
for ( const j of idx ) {
const t = people [ j ];
while ( i < ts . length && ts [ i ] <= t ) {
s += d . get ( ts [ i ]) ! ;
++ i ;
}
ans [ j ] = s ;
}
return ans ;
}