
题目描述
给定一个数组 trees,其中 trees[i] = [xi, yi] 表示树在花园中的位置。
你被要求用最短长度的绳子把整个花园围起来,因为绳子很贵。只有把 所有的树都围起来,花园才围得很好。
返回恰好位于围栏周边的树木的坐标。
示例 1:
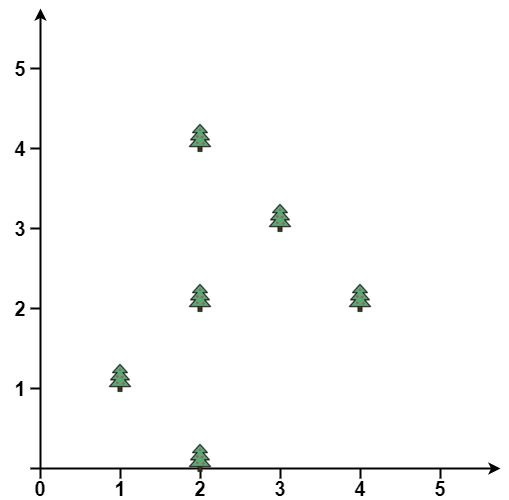
输入: points = [[1,1],[2,2],[2,0],[2,4],[3,3],[4,2]]
输出: [[1,1],[2,0],[3,3],[2,4],[4,2]]
示例 2:
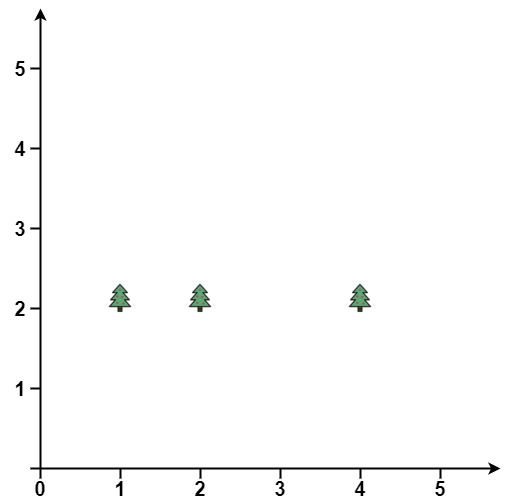
输入: points = [[1,2],[2,2],[4,2]]
输出: [[4,2],[2,2],[1,2]]
注意:
1 <= points.length <= 3000points[i].length == 20 <= xi, yi <= 100-
所有给定的点都是 唯一 的。
解法
方法一:Andrew 算法
原理:
利用夹角,让整个图形保持左转。先将最左边的前两个点加入栈中,每次加入新点时判断是否左拐(叉积大于 0),如果是就将新点直接加入;如果不是,就弹出栈顶,直到左拐,将新点加入栈中。
流程:
- 将所有点
(x, y) 进行排序,以 x 为第一关键字,y 为第二关键字升序排序;
- 先从左至右维护凸包的下半部分,然后再从右至左维护上半部分;
- 将第一个点放入栈中,这个点一定时凸包的最左边的点了,是不会清理掉的,然后再将第二个点放入栈中。当栈中元素大于等于 2 的时候,就要判断栈顶元素是否还要保留:
- 如果新点在栈顶元素和次栈顶元素所组成的直线的逆时针方向上,那么直接将新点加入栈中;
- 否则,将栈顶元素不断弹出,直至新点的位置出现在栈顶元素与次栈顶元素所在直线的逆时针方向。
这个过程,是从左往右走的,并且得到的凸包是凸壳的下半部分。求上半部分的时候,从右往左遍历。
时间复杂度 O(nlogn)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26 | class Solution:
def outerTrees(self, trees: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
def cross(i, j, k):
a, b, c = trees[i], trees[j], trees[k]
return (b[0] - a[0]) * (c[1] - b[1]) - (b[1] - a[1]) * (c[0] - b[0])
n = len(trees)
if n < 4:
return trees
trees.sort()
vis = [False] * n
stk = [0]
for i in range(1, n):
while len(stk) > 1 and cross(stk[-2], stk[-1], i) < 0:
vis[stk.pop()] = False
vis[i] = True
stk.append(i)
m = len(stk)
for i in range(n - 2, -1, -1):
if vis[i]:
continue
while len(stk) > m and cross(stk[-2], stk[-1], i) < 0:
stk.pop()
stk.append(i)
stk.pop()
return [trees[i] for i in stk]
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38 | class Solution {
public int[][] outerTrees(int[][] trees) {
int n = trees.length;
if (n < 4) {
return trees;
}
Arrays.sort(trees, (a, b) -> { return a[0] == b[0] ? a[1] - b[1] : a[0] - b[0]; });
boolean[] vis = new boolean[n];
int[] stk = new int[n + 10];
int cnt = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
while (cnt > 1 && cross(trees[stk[cnt - 1]], trees[stk[cnt - 2]], trees[i]) < 0) {
vis[stk[--cnt]] = false;
}
vis[i] = true;
stk[cnt++] = i;
}
int m = cnt;
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
if (vis[i]) {
continue;
}
while (cnt > m && cross(trees[stk[cnt - 1]], trees[stk[cnt - 2]], trees[i]) < 0) {
--cnt;
}
stk[cnt++] = i;
}
int[][] ans = new int[cnt - 1][2];
for (int i = 0; i < ans.length; ++i) {
ans[i] = trees[stk[i]];
}
return ans;
}
private int cross(int[] a, int[] b, int[] c) {
return (b[0] - a[0]) * (c[1] - b[1]) - (b[1] - a[1]) * (c[0] - b[0]);
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29 | class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> outerTrees(vector<vector<int>>& trees) {
int n = trees.size();
if (n < 4) return trees;
sort(trees.begin(), trees.end());
vector<int> vis(n);
vector<int> stk(n + 10);
int cnt = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
while (cnt > 1 && cross(trees[stk[cnt - 1]], trees[stk[cnt - 2]], trees[i]) < 0) vis[stk[--cnt]] = false;
vis[i] = true;
stk[cnt++] = i;
}
int m = cnt;
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
if (vis[i]) continue;
while (cnt > m && cross(trees[stk[cnt - 1]], trees[stk[cnt - 2]], trees[i]) < 0) --cnt;
stk[cnt++] = i;
}
vector<vector<int>> ans;
for (int i = 0; i < cnt - 1; ++i) ans.push_back(trees[stk[i]]);
return ans;
}
int cross(vector<int>& a, vector<int>& b, vector<int>& c) {
return (b[0] - a[0]) * (c[1] - b[1]) - (b[1] - a[1]) * (c[0] - b[0]);
}
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41 | func outerTrees(trees [][]int) [][]int {
n := len(trees)
if n < 4 {
return trees
}
sort.Slice(trees, func(i, j int) bool {
if trees[i][0] == trees[j][0] {
return trees[i][1] < trees[j][1]
}
return trees[i][0] < trees[j][0]
})
cross := func(i, j, k int) int {
a, b, c := trees[i], trees[j], trees[k]
return (b[0]-a[0])*(c[1]-b[1]) - (b[1]-a[1])*(c[0]-b[0])
}
vis := make([]bool, n)
stk := []int{0}
for i := 1; i < n; i++ {
for len(stk) > 1 && cross(stk[len(stk)-1], stk[len(stk)-2], i) < 0 {
vis[stk[len(stk)-1]] = false
stk = stk[:len(stk)-1]
}
vis[i] = true
stk = append(stk, i)
}
m := len(stk)
for i := n - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
if vis[i] {
continue
}
for len(stk) > m && cross(stk[len(stk)-1], stk[len(stk)-2], i) < 0 {
stk = stk[:len(stk)-1]
}
stk = append(stk, i)
}
var ans [][]int
for i := 0; i < len(stk)-1; i++ {
ans = append(ans, trees[stk[i]])
}
return ans
}
|


