
题目描述
迷宫中有一个球,它有空地 (表示为 0) 和墙 (表示为 1)。球可以向上、向下、向左或向右滚过空地,但直到撞上墙之前它都不会停止滚动。当球停止时,它才可以选择下一个滚动方向。
给定 m × n 的迷宫(maze),球的起始位置 (start = [startrow, startcol]) 和目的地 (destination = [destinationrow, destinationcol]),返回球在目的地 (destination) 停止的最短距离。如果球不能在目的地 (destination) 停止,返回 -1。
距离是指球从起始位置 ( 不包括 ) 到终点 ( 包括 ) 所经过的空地数。
你可以假设迷宫的边界都是墙 ( 见例子 )。
示例 1:
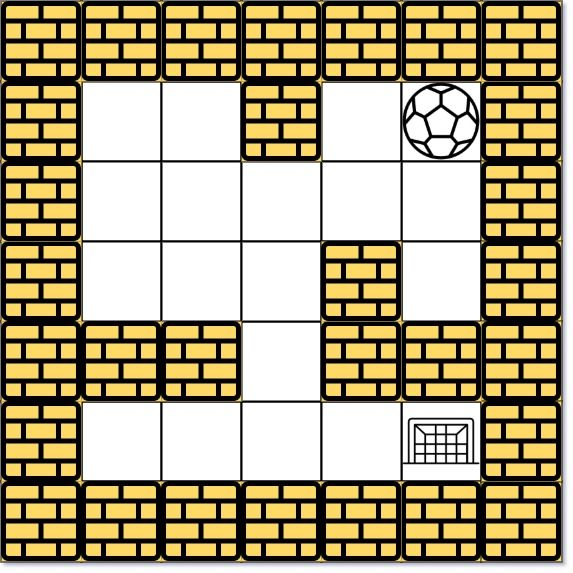
输入: maze = [[0,0,1,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,1,0],[1,1,0,1,1],[0,0,0,0,0]], start = [0,4], destination = [4,4]
输出: 12
解析: 一条最短路径 : left -> down -> left -> down -> right -> down -> right。
总距离为 1 + 1 + 3 + 1 + 2 + 2 + 2 = 12。
示例 2:
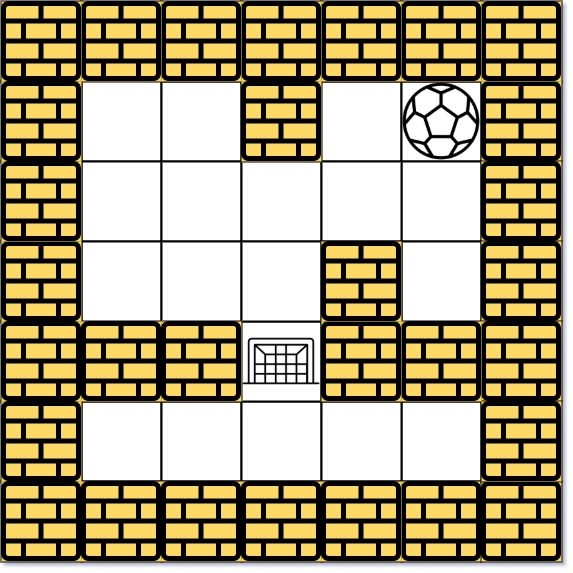
输入: maze = [[0,0,1,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,1,0],[1,1,0,1,1],[0,0,0,0,0]], start = [0,4], destination = [3,2]
输出: -1
解析: 球不可能在目的地停下来。注意,你可以经过目的地,但不能在那里停下来。
示例 3:
输入: maze = [[0,0,0,0,0],[1,1,0,0,1],[0,0,0,0,0],[0,1,0,0,1],[0,1,0,0,0]], start = [4,3], destination = [0,1]
输出: -1
注意:
m == maze.lengthn == maze[i].length1 <= m, n <= 100maze[i][j] 是 0 或 1.start.length == 2destination.length == 20 <= startrow, destinationrow < m0 <= startcol, destinationcol < n- 球和目的地都存在于一个空地中,它们最初不会处于相同的位置。
-
迷宫至少包含两个空地。
解法
方法一:BFS
我们定义一个二维数组 \(dist\),其中 \(dist[i][j]\) 表示从起始位置到达 \((i,j)\) 的最短路径长度。初始时,\(dist\) 中的所有元素都被初始化为一个很大的数,除了起始位置,因为起始位置到自身的距离是 \(0\)。
然后,我们定义一个队列 \(q\),将起始位置加入队列。随后不断进行以下操作:弹出队列中的首元素,将其四个方向上可以到达的位置加入队列中,并且在 \(dist\) 中记录这些位置的距离,直到队列为空。
最后,如果终点位置的距离仍然是一个很大的数,说明从起始位置无法到达终点位置,返回 \(-1\),否则返回终点位置的距离。
时间复杂度 \(O(m \times n \times \max(m, n))\),空间复杂度 \(O(m \times n)\)。其中 \(m\) 和 \(n\) 分别是迷宫的行数和列数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21 | class Solution:
def shortestDistance(
self, maze: List[List[int]], start: List[int], destination: List[int]
) -> int:
m, n = len(maze), len(maze[0])
dirs = (-1, 0, 1, 0, -1)
si, sj = start
di, dj = destination
q = deque([(si, sj)])
dist = [[inf] * n for _ in range(m)]
dist[si][sj] = 0
while q:
i, j = q.popleft()
for a, b in pairwise(dirs):
x, y, k = i, j, dist[i][j]
while 0 <= x + a < m and 0 <= y + b < n and maze[x + a][y + b] == 0:
x, y, k = x + a, y + b, k + 1
if k < dist[x][y]:
dist[x][y] = k
q.append((x, y))
return -1 if dist[di][dj] == inf else dist[di][dj]
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35 | class Solution {
public int shortestDistance(int[][] maze, int[] start, int[] destination) {
int m = maze.length, n = maze[0].length;
final int inf = 1 << 30;
int[][] dist = new int[m][n];
for (var row : dist) {
Arrays.fill(row, inf);
}
int si = start[0], sj = start[1];
int di = destination[0], dj = destination[1];
dist[si][sj] = 0;
Deque<int[]> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
q.offer(new int[] {si, sj});
int[] dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
var p = q.poll();
int i = p[0], j = p[1];
for (int d = 0; d < 4; ++d) {
int x = i, y = j, k = dist[i][j];
int a = dirs[d], b = dirs[d + 1];
while (
x + a >= 0 && x + a < m && y + b >= 0 && y + b < n && maze[x + a][y + b] == 0) {
x += a;
y += b;
++k;
}
if (k < dist[x][y]) {
dist[x][y] = k;
q.offer(new int[] {x, y});
}
}
}
return dist[di][dj] == inf ? -1 : dist[di][dj];
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32 | class Solution {
public:
int shortestDistance(vector<vector<int>>& maze, vector<int>& start, vector<int>& destination) {
int m = maze.size(), n = maze[0].size();
int dist[m][n];
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof(dist));
int si = start[0], sj = start[1];
int di = destination[0], dj = destination[1];
dist[si][sj] = 0;
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.emplace(si, sj);
int dirs[5] = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
while (!q.empty()) {
auto [i, j] = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int d = 0; d < 4; ++d) {
int x = i, y = j, k = dist[i][j];
int a = dirs[d], b = dirs[d + 1];
while (x + a >= 0 && x + a < m && y + b >= 0 && y + b < n && maze[x + a][y + b] == 0) {
x += a;
y += b;
++k;
}
if (k < dist[x][y]) {
dist[x][y] = k;
q.emplace(x, y);
}
}
}
return dist[di][dj] == 0x3f3f3f3f ? -1 : dist[di][dj];
}
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35 | func shortestDistance(maze [][]int, start []int, destination []int) int {
m, n := len(maze), len(maze[0])
dist := make([][]int, m)
const inf = 1 << 30
for i := range dist {
dist[i] = make([]int, n)
for j := range dist[i] {
dist[i][j] = inf
}
}
dist[start[0]][start[1]] = 0
q := [][]int{start}
dirs := [5]int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}
for len(q) > 0 {
p := q[0]
q = q[1:]
i, j := p[0], p[1]
for d := 0; d < 4; d++ {
x, y, k := i, j, dist[i][j]
a, b := dirs[d], dirs[d+1]
for x+a >= 0 && x+a < m && y+b >= 0 && y+b < n && maze[x+a][y+b] == 0 {
x, y, k = x+a, y+b, k+1
}
if k < dist[x][y] {
dist[x][y] = k
q = append(q, []int{x, y})
}
}
}
di, dj := destination[0], destination[1]
if dist[di][dj] == inf {
return -1
}
return dist[di][dj]
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29 | function shortestDistance(maze: number[][], start: number[], destination: number[]): number {
const m = maze.length;
const n = maze[0].length;
const dist: number[][] = Array.from({ length: m }, () =>
Array.from({ length: n }, () => Infinity),
);
const [si, sj] = start;
const [di, dj] = destination;
dist[si][sj] = 0;
const q: number[][] = [[si, sj]];
const dirs = [-1, 0, 1, 0, -1];
while (q.length) {
const [i, j] = q.shift()!;
for (let d = 0; d < 4; ++d) {
let [x, y, k] = [i, j, dist[i][j]];
const [a, b] = [dirs[d], dirs[d + 1]];
while (x + a >= 0 && x + a < m && y + b >= 0 && y + b < n && maze[x + a][y + b] === 0) {
x += a;
y += b;
++k;
}
if (k < dist[x][y]) {
dist[x][y] = k;
q.push([x, y]);
}
}
}
return dist[di][dj] === Infinity ? -1 : dist[di][dj];
}
|


