
题目描述
存在一个不含 0 的 环形 数组 nums ,每个 nums[i] 都表示位于下标 i 的角色应该向前或向后移动的下标个数:
- 如果
nums[i] 是正数,向前(下标递增方向)移动 |nums[i]| 步
- 如果
nums[i] 是负数,向后(下标递减方向)移动 |nums[i]| 步
因为数组是 环形 的,所以可以假设从最后一个元素向前移动一步会到达第一个元素,而第一个元素向后移动一步会到达最后一个元素。
数组中的 循环 由长度为 k 的下标序列 seq 标识:
- 遵循上述移动规则将导致一组重复下标序列
seq[0] -> seq[1] -> ... -> seq[k - 1] -> seq[0] -> ...
- 所有
nums[seq[j]] 应当不是 全正 就是 全负
k > 1
如果 nums 中存在循环,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:
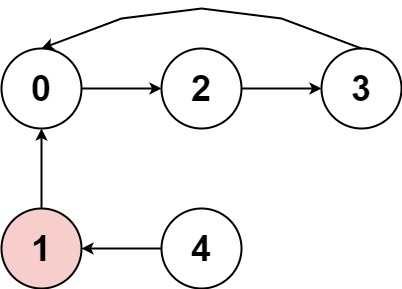
输入:nums = [2,-1,1,2,2]
输出:true
解释:图片展示了节点间如何连接。白色节点向前跳跃,而红色节点向后跳跃。
我们可以看到存在循环,按下标 0 -> 2 -> 3 -> 0 --> ...,并且其中的所有节点都是白色(以相同方向跳跃)。
示例 2:
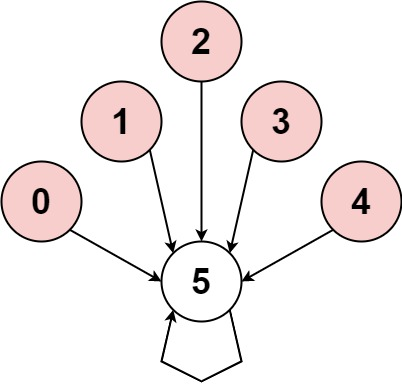
输入:nums = [-1,-2,-3,-4,-5,6]
输出:false
解释:图片展示了节点间如何连接。白色节点向前跳跃,而红色节点向后跳跃。
唯一的循环长度为 1,所以返回 false。
示例 3:
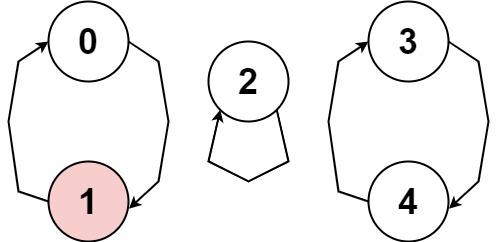
输入:nums = [1,-1,5,1,4]
输出:true
解释:图片展示了节点间如何连接。白色节点向前跳跃,而红色节点向后跳跃。
我们可以看到存在循环,按下标 0 --> 1 --> 0 --> ...,当它的大小大于 1 时,它有一个向前跳的节点和一个向后跳的节点,所以 它不是一个循环。
我们可以看到存在循环,按下标 3 --> 4 --> 3 --> ...,并且其中的所有节点都是白色(以相同方向跳跃)。
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 5000-1000 <= nums[i] <= 1000nums[i] != 0
进阶:你能设计一个时间复杂度为 O(n) 且额外空间复杂度为 O(1) 的算法吗?
解法
方法一
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22 | class Solution:
def circularArrayLoop(self, nums: List[int]) -> bool:
n = len(nums)
def next(i):
return (i + nums[i] % n + n) % n
for i in range(n):
if nums[i] == 0:
continue
slow, fast = i, next(i)
while nums[slow] * nums[fast] > 0 and nums[slow] * nums[next(fast)] > 0:
if slow == fast:
if slow != next(slow):
return True
break
slow, fast = next(slow), next(next(fast))
j = i
while nums[j] * nums[next(j)] > 0:
nums[j] = 0
j = next(j)
return False
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35 | class Solution {
private int n;
private int[] nums;
public boolean circularArrayLoop(int[] nums) {
n = nums.length;
this.nums = nums;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (nums[i] == 0) {
continue;
}
int slow = i, fast = next(i);
while (nums[slow] * nums[fast] > 0 && nums[slow] * nums[next(fast)] > 0) {
if (slow == fast) {
if (slow != next(slow)) {
return true;
}
break;
}
slow = next(slow);
fast = next(next(fast));
}
int j = i;
while (nums[j] * nums[next(j)] > 0) {
nums[j] = 0;
j = next(j);
}
}
return false;
}
private int next(int i) {
return (i + nums[i] % n + n) % n;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29 | class Solution {
public:
bool circularArrayLoop(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (!nums[i]) continue;
int slow = i, fast = next(nums, i);
while (nums[slow] * nums[fast] > 0 && nums[slow] * nums[next(nums, fast)] > 0) {
if (slow == fast) {
if (slow != next(nums, slow)) return true;
break;
}
slow = next(nums, slow);
fast = next(nums, next(nums, fast));
}
int j = i;
while (nums[j] * nums[next(nums, j)] > 0) {
nums[j] = 0;
j = next(nums, j);
}
}
return false;
}
int next(vector<int>& nums, int i) {
int n = nums.size();
return (i + nums[i] % n + n) % n;
}
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28 | func circularArrayLoop(nums []int) bool {
for i, num := range nums {
if num == 0 {
continue
}
slow, fast := i, next(nums, i)
for nums[slow]*nums[fast] > 0 && nums[slow]*nums[next(nums, fast)] > 0 {
if slow == fast {
if slow != next(nums, slow) {
return true
}
break
}
slow, fast = next(nums, slow), next(nums, next(nums, fast))
}
j := i
for nums[j]*nums[next(nums, j)] > 0 {
nums[j] = 0
j = next(nums, j)
}
}
return false
}
func next(nums []int, i int) int {
n := len(nums)
return (i + nums[i]%n + n) % n
}
|



