二叉树
动态规划
树
深度优先搜索
题目描述
小偷又发现了一个新的可行窃的地区。这个地区只有一个入口,我们称之为root 。
除了root 之外,每栋房子有且只有一个“父“房子与之相连。一番侦察之后,聪明的小偷意识到“这个地方的所有房屋的排列类似于一棵二叉树”。 如果 两个直接相连的房子在同一天晚上被打劫 ,房屋将自动报警。
给定二叉树的 root 。返回 在不触动警报的情况下 ,小偷能够盗取的最高金额
示例 1:
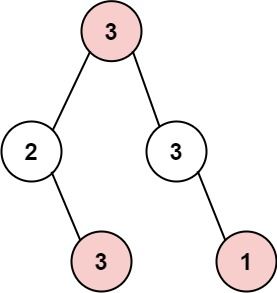
输入: root = [3,2,3,null,3,null,1]
输出: 7
解释: 小偷一晚能够盗取的最高金额 3 + 3 + 1 = 7
示例 2:
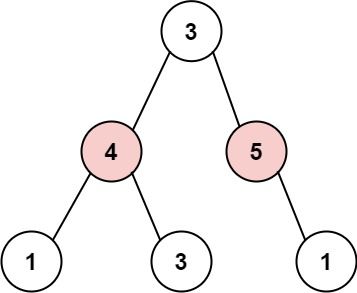
输入: root = [3,4,5,1,3,null,1]
输出: 9
解释: 小偷一晚能够盗取的最高金额 4 + 5 = 9
提示:
树的节点数在 [1, 104 ] 范围内
0 <= Node.val <= 104
解法
方法一:树形 DP
我们定义一个函数 \(dfs(root)\) ,表示偷取以 \(root\) 为根的二叉树的最大金额。该函数返回一个二元组 \((a, b)\) ,其中 \(a\) 表示偷取 \(root\) 节点时能得到的最大金额,而 \(b\) 表示不偷取 \(root\) 节点时能得到的最大金额。
函数 \(dfs(root)\) 的计算过程如下:
如果 \(root\) 为空,那么显然有 \(dfs(root) = (0, 0)\) 。
否则,我们首先计算出左右子节点的结果,即 \(dfs(root.left)\) 和 \(dfs(root.right)\) ,这样就得到了两对值 \((l_a, l_b)\) 以及 \((r_a, r_b)\) 。对于 \(dfs(root)\) 的结果,我们可以分为两种情况:
如果偷取 \(root\) 节点,那么不能偷取其左右子节点,结果为 \(root.val + l_b + r_b\) ;
如果不偷取 \(root\) 节点,那么可以偷取其左右子节点,结果为 \(\max(l_a, l_b) + \max(r_a, r_b)\) 。
在主函数中,我们可以直接返回 \(dfs(root)\) 的较大值,即 \(\max(dfs(root))\) 。
时间复杂度 \(O(n)\) ,空间复杂度 \(O(n)\) 。其中 \(n\) 是二叉树的节点数。
Python3 Java C++ Go TypeScript
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16 # Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution :
def rob ( self , root : Optional [ TreeNode ]) -> int :
def dfs ( root : Optional [ TreeNode ]) -> ( int , int ):
if root is None :
return 0 , 0
la , lb = dfs ( root . left )
ra , rb = dfs ( root . right )
return root . val + lb + rb , max ( la , lb ) + max ( ra , rb )
return max ( dfs ( root ))
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int rob ( TreeNode root ) {
int [] ans = dfs ( root );
return Math . max ( ans [ 0 ] , ans [ 1 ] );
}
private int [] dfs ( TreeNode root ) {
if ( root == null ) {
return new int [ 2 ] ;
}
int [] l = dfs ( root . left );
int [] r = dfs ( root . right );
return new int [] { root . val + l [ 1 ] + r [ 1 ] , Math . max ( l [ 0 ] , l [ 1 ] ) + Math . max ( r [ 0 ] , r [ 1 ] )};
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public :
int rob ( TreeNode * root ) {
function < pair < int , int > ( TreeNode * ) > dfs = [ & ]( TreeNode * root ) -> pair < int , int > {
if ( ! root ) {
return make_pair ( 0 , 0 );
}
auto [ la , lb ] = dfs ( root -> left );
auto [ ra , rb ] = dfs ( root -> right );
return make_pair ( root -> val + lb + rb , max ( la , lb ) + max ( ra , rb ));
};
auto [ a , b ] = dfs ( root );
return max ( a , b );
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func rob ( root * TreeNode ) int {
var dfs func ( * TreeNode ) ( int , int )
dfs = func ( root * TreeNode ) ( int , int ) {
if root == nil {
return 0 , 0
}
la , lb := dfs ( root . Left )
ra , rb := dfs ( root . Right )
return root . Val + lb + rb , max ( la , lb ) + max ( ra , rb )
}
a , b := dfs ( root )
return max ( a , b )
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function rob ( root : TreeNode | null ) : number {
const dfs = ( root : TreeNode | null ) : [ number , number ] => {
if ( ! root ) {
return [ 0 , 0 ];
}
const [ la , lb ] = dfs ( root . left );
const [ ra , rb ] = dfs ( root . right );
return [ root . val + lb + rb , Math . max ( la , lb ) + Math . max ( ra , rb )];
};
return Math . max (... dfs ( root ));
}
GitHub