


题目描述
给你一个整数数组 colors 和一个整数 k ,colors表示一个由红色和蓝色瓷砖组成的环,第 i 块瓷砖的颜色为 colors[i] :
colors[i] == 0 表示第 i 块瓷砖的颜色是 红色 。colors[i] == 1 表示第 i 块瓷砖的颜色是 蓝色 。
环中连续 k 块瓷砖的颜色如果是 交替 颜色(也就是说除了第一块和最后一块瓷砖以外,中间瓷砖的颜色与它 左边 和 右边 的颜色都不同),那么它被称为一个 交替 组。
请你返回 交替 组的数目。
注意 ,由于 colors 表示一个 环 ,第一块 瓷砖和 最后一块 瓷砖是相邻的。
示例 1:
输入:colors = [0,1,0,1,0], k = 3
输出:3
解释:
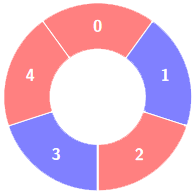
交替组包括:
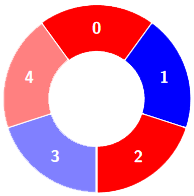
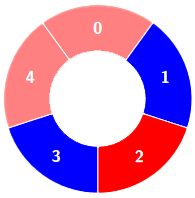
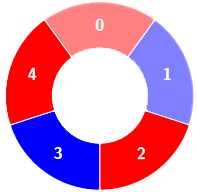
示例 2:
输入:colors = [0,1,0,0,1,0,1], k = 6
输出:2
解释:
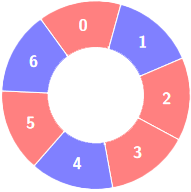
交替组包括:
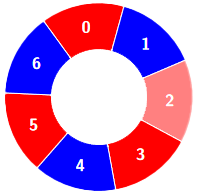
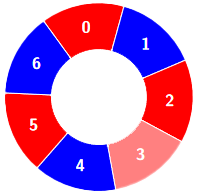
示例 3:
输入:colors = [1,1,0,1], k = 4
输出:0
解释:
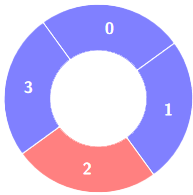
提示:
3 <= colors.length <= 1050 <= colors[i] <= 13 <= k <= colors.length
解法
方法一:一次遍历
我们可以将环展开成一个长度为 \(2n\) 的数组,然后从左到右遍历这个数组,用一个变量 \(\textit{cnt}\) 记录当前交替组的长度,如果遇到了相同的颜色,就将 \(\textit{cnt}\) 重置为 \(1\),否则将 \(\textit{cnt}\) 加一。如果 \(\textit{cnt} \ge k\),并且当前位置 \(i\) 大于等于 \(n\),那么就找到了一个交替组,答案加一。
遍历结束后,返回答案即可。
时间复杂度 \(O(n)\),其中 \(n\) 为数组 \(\textit{colors}\) 的长度。空间复杂度 \(O(1)\)。
| class Solution:
def numberOfAlternatingGroups(self, colors: List[int], k: int) -> int:
n = len(colors)
ans = cnt = 0
for i in range(n << 1):
if i and colors[i % n] == colors[(i - 1) % n]:
cnt = 1
else:
cnt += 1
ans += i >= n and cnt >= k
return ans
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15 | class Solution {
public int numberOfAlternatingGroups(int[] colors, int k) {
int n = colors.length;
int ans = 0, cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n << 1; ++i) {
if (i > 0 && colors[i % n] == colors[(i - 1) % n]) {
cnt = 1;
} else {
++cnt;
}
ans += i >= n && cnt >= k ? 1 : 0;
}
return ans;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16 | class Solution {
public:
int numberOfAlternatingGroups(vector<int>& colors, int k) {
int n = colors.size();
int ans = 0, cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n << 1; ++i) {
if (i && colors[i % n] == colors[(i - 1) % n]) {
cnt = 1;
} else {
++cnt;
}
ans += i >= n && cnt >= k ? 1 : 0;
}
return ans;
}
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15 | func numberOfAlternatingGroups(colors []int, k int) (ans int) {
n := len(colors)
cnt := 0
for i := 0; i < n<<1; i++ {
if i > 0 && colors[i%n] == colors[(i-1)%n] {
cnt = 1
} else {
cnt++
}
if i >= n && cnt >= k {
ans++
}
}
return
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13 | function numberOfAlternatingGroups(colors: number[], k: number): number {
const n = colors.length;
let [ans, cnt] = [0, 0];
for (let i = 0; i < n << 1; ++i) {
if (i && colors[i % n] === colors[(i - 1) % n]) {
cnt = 1;
} else {
++cnt;
}
ans += i >= n && cnt >= k ? 1 : 0;
}
return ans;
}
|










