
题目描述
给定一个二维整数数组 edges,表示一个有 n 个节点的树,节点编号从 0 到 n - 1,以节点 0 为根,其中 edges[i] = [ui, vi] 表示节点 vi 和 ui 之间存在一条边。
还给定一个 下标从 0 开始,大小为 n 的整数数组 colors,其中 colors[i] 表示节点 i 分配的颜色。
我们希望找到一个节点 v,使得 v 的子树中的每个节点具有 相同 的颜色。
返回 具有 尽可能多 节点 且 符合上述要求的子树大小。
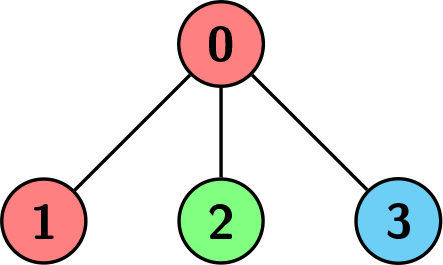
示例 1:
输入:edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3]], colors = [1,1,2,3]
输出:1
解释:每种颜色分别对应为:1 -> 红色,2 -> 绿色,3 -> 蓝色。我们可以看到以节点 0 为根的子树具有不同颜色的子节点。任何其他子树都是相同颜色的,并且大小为 1。因此,我们返回 1。
示例 2:
输入:edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3]], colors = [1,1,1,1]
输出:4
解释:整个树具有相同的颜色,以节点 0 为根的子树具有节点数最多,为 4。因此,我们返回 4。
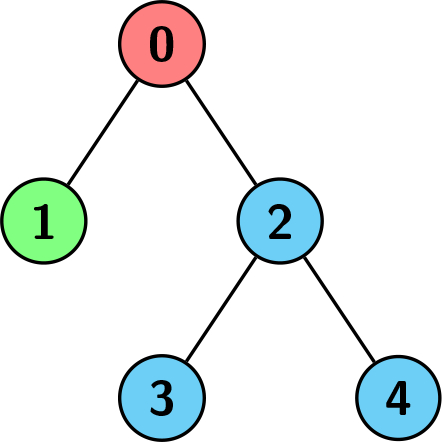
示例 3:
输入:edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[2,3],[2,4]], colors = [1,2,3,3,3]
输出:3
解释:每种颜色分别对应为:1 -> 红色,2 -> 绿色,3 -> 蓝色。我们可以看到以节点 0 为根的子树有不同颜色的子节点。其他任何子树都是相同颜色的,但以节点 2 为根的子树的大小为 3,这是最大的。因此,我们返回 3。
提示:
n == edges.length + 11 <= n <= 5 * 104edges[i] == [ui, vi]0 <= ui, vi < ncolors.length == n1 <= colors[i] <= 105- 输入被生成,使得由
edges 表示的图是一棵树。
解法
方法一:DFS
我们先根据题目给定的边的信息,构建一个邻接表 \(g\),其中 \(g[a]\) 表示节点 \(a\) 的所有相邻节点。然后我们创建一个长度为 \(n\) 的数组 \(size\),其中 \(size[a]\) 表示以节点 \(a\) 为根的子树的节点数。
接下来,我们设计一个函数 \(dfs(a, fa)\),它将返回以节点 \(a\) 为根的子树是否满足题目要求。函数 \(dfs(a, fa)\) 的执行过程如下:
- 首先,我们用一个变量 \(ok\) 记录以节点 \(a\) 为根的子树是否满足题目要求,初始时 \(ok\) 为 \(true\)。
- 接着,我们遍历节点 \(a\) 的所有相邻节点 \(b\),如果 \(b\) 不是 \(a\) 的父节点 \(fa\),那么我们递归调用 \(dfs(b, a)\),并将返回值保存到变量 \(t\) 中,并且更新 \(ok\) 为 \(ok\) 与 \(colors[a] = colors[b] \land t\) 的值,其中 \(\land\) 表示逻辑与运算。然后,我们更新 \(size[a] = size[a] + size[b]\)。
- 然后,我们判断 \(ok\) 的值,如果 \(ok\) 为 \(true\),那么我们更新答案 \(ans = \max(ans, size[a])\)。
- 最后,我们返回 \(ok\) 的值。
我们调用 \(dfs(0, -1)\),其中 \(0\) 表示根节点的编号,\(-1\) 表示根节点没有父节点。最终的答案即为 \(ans\)。
时间复杂度 \(O(n)\),空间复杂度 \(O(n)\)。其中 \(n\) 是节点的数量。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23 | class Solution:
def maximumSubtreeSize(self, edges: List[List[int]], colors: List[int]) -> int:
def dfs(a: int, fa: int) -> bool:
ok = True
for b in g[a]:
if b != fa:
t = dfs(b, a)
ok = ok and colors[a] == colors[b] and t
size[a] += size[b]
if ok:
nonlocal ans
ans = max(ans, size[a])
return ok
n = len(edges) + 1
g = [[] for _ in range(n)]
size = [1] * n
for a, b in edges:
g[a].append(b)
g[b].append(a)
ans = 0
dfs(0, -1)
return ans
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37 | class Solution {
private List<Integer>[] g;
private int[] colors;
private int[] size;
private int ans;
public int maximumSubtreeSize(int[][] edges, int[] colors) {
int n = edges.length + 1;
g = new List[n];
size = new int[n];
this.colors = colors;
Arrays.fill(size, 1);
Arrays.setAll(g, i -> new ArrayList<>());
for (var e : edges) {
int a = e[0], b = e[1];
g[a].add(b);
g[b].add(a);
}
dfs(0, -1);
return ans;
}
private boolean dfs(int a, int fa) {
boolean ok = true;
for (int b : g[a]) {
if (b != fa) {
boolean t = dfs(b, a);
ok = ok && colors[a] == colors[b] && t;
size[a] += size[b];
}
}
if (ok) {
ans = Math.max(ans, size[a]);
}
return ok;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30 | class Solution {
public:
int maximumSubtreeSize(vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<int>& colors) {
int n = edges.size() + 1;
vector<int> g[n];
vector<int> size(n, 1);
for (auto& e : edges) {
int a = e[0], b = e[1];
g[a].push_back(b);
g[b].push_back(a);
}
int ans = 0;
function<bool(int, int)> dfs = [&](int a, int fa) {
bool ok = true;
for (int b : g[a]) {
if (b != fa) {
bool t = dfs(b, a);
ok = ok && colors[a] == colors[b] && t;
size[a] += size[b];
}
}
if (ok) {
ans = max(ans, size[a]);
}
return ok;
};
dfs(0, -1);
return ans;
}
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28 | func maximumSubtreeSize(edges [][]int, colors []int) (ans int) {
n := len(edges) + 1
g := make([][]int, n)
for _, e := range edges {
a, b := e[0], e[1]
g[a] = append(g[a], b)
g[b] = append(g[b], a)
}
size := make([]int, n)
var dfs func(int, int) bool
dfs = func(a, fa int) bool {
size[a] = 1
ok := true
for _, b := range g[a] {
if b != fa {
t := dfs(b, a)
ok = ok && t && colors[a] == colors[b]
size[a] += size[b]
}
}
if ok {
ans = max(ans, size[a])
}
return ok
}
dfs(0, -1)
return
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26 | function maximumSubtreeSize(edges: number[][], colors: number[]): number {
const n = edges.length + 1;
const g: number[][] = Array.from({ length: n }, () => []);
for (const [a, b] of edges) {
g[a].push(b);
g[b].push(a);
}
const size: number[] = Array(n).fill(1);
let ans = 0;
const dfs = (a: number, fa: number): boolean => {
let ok = true;
for (const b of g[a]) {
if (b !== fa) {
const t = dfs(b, a);
ok = ok && t && colors[a] === colors[b];
size[a] += size[b];
}
}
if (ok) {
ans = Math.max(ans, size[a]);
}
return ok;
};
dfs(0, -1);
return ans;
}
|


