


题目描述
给你一个长度为 n 的整数数组 nums ,下标从 0 开始。
如果在下标 i 处 分割 数组,其中 0 <= i <= n - 2 ,使前 i + 1 个元素的乘积和剩余元素的乘积互质,则认为该分割 有效 。
- 例如,如果
nums = [2, 3, 3] ,那么在下标 i = 0 处的分割有效,因为 2 和 9 互质,而在下标 i = 1 处的分割无效,因为 6 和 3 不互质。在下标 i = 2 处的分割也无效,因为 i == n - 1 。
返回可以有效分割数组的最小下标 i ,如果不存在有效分割,则返回 -1 。
当且仅当 gcd(val1, val2) == 1 成立时,val1 和 val2 这两个值才是互质的,其中 gcd(val1, val2) 表示 val1 和 val2 的最大公约数。
示例 1:
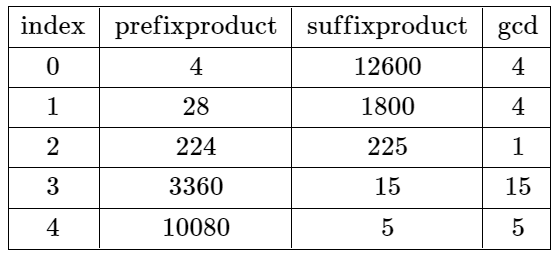
输入:nums = [4,7,8,15,3,5]
输出:2
解释:上表展示了每个下标 i 处的前 i + 1 个元素的乘积、剩余元素的乘积和它们的最大公约数的值。
唯一一个有效分割位于下标 2 。
示例 2:
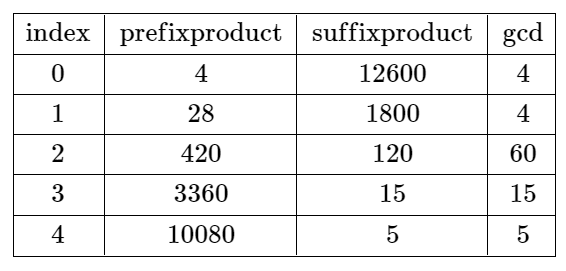
输入:nums = [4,7,15,8,3,5]
输出:-1
解释:上表展示了每个下标 i 处的前 i + 1 个元素的乘积、剩余元素的乘积和它们的最大公约数的值。
不存在有效分割。
提示:
n == nums.length1 <= n <= 1041 <= nums[i] <= 106
解法
方法一:质因数分解
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27 | class Solution:
def findValidSplit(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
first = {}
n = len(nums)
last = list(range(n))
for i, x in enumerate(nums):
j = 2
while j <= x // j:
if x % j == 0:
if j in first:
last[first[j]] = i
else:
first[j] = i
while x % j == 0:
x //= j
j += 1
if x > 1:
if x in first:
last[first[x]] = i
else:
first[x] = i
mx = last[0]
for i, x in enumerate(last):
if mx < i:
return mx
mx = max(mx, x)
return -1
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40 | class Solution {
public int findValidSplit(int[] nums) {
Map<Integer, Integer> first = new HashMap<>();
int n = nums.length;
int[] last = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
last[i] = i;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int x = nums[i];
for (int j = 2; j <= x / j; ++j) {
if (x % j == 0) {
if (first.containsKey(j)) {
last[first.get(j)] = i;
} else {
first.put(j, i);
}
while (x % j == 0) {
x /= j;
}
}
}
if (x > 1) {
if (first.containsKey(x)) {
last[first.get(x)] = i;
} else {
first.put(x, i);
}
}
}
int mx = last[0];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (mx < i) {
return mx;
}
mx = Math.max(mx, last[i]);
}
return -1;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39 | class Solution {
public:
int findValidSplit(vector<int>& nums) {
unordered_map<int, int> first;
int n = nums.size();
vector<int> last(n);
iota(last.begin(), last.end(), 0);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int x = nums[i];
for (int j = 2; j <= x / j; ++j) {
if (x % j == 0) {
if (first.count(j)) {
last[first[j]] = i;
} else {
first[j] = i;
}
while (x % j == 0) {
x /= j;
}
}
}
if (x > 1) {
if (first.count(x)) {
last[first[x]] = i;
} else {
first[x] = i;
}
}
}
int mx = last[0];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (mx < i) {
return mx;
}
mx = max(mx, last[i]);
}
return -1;
}
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37 | func findValidSplit(nums []int) int {
first := map[int]int{}
n := len(nums)
last := make([]int, n)
for i := range last {
last[i] = i
}
for i, x := range nums {
for j := 2; j <= x/j; j++ {
if x%j == 0 {
if k, ok := first[j]; ok {
last[k] = i
} else {
first[j] = i
}
for x%j == 0 {
x /= j
}
}
}
if x > 1 {
if k, ok := first[x]; ok {
last[k] = i
} else {
first[x] = i
}
}
}
mx := last[0]
for i, x := range last {
if mx < i {
return mx
}
mx = max(mx, x)
}
return -1
}
|




