
题目描述
编写一个高效的算法来搜索 m x n 矩阵 matrix 中的一个目标值 target 。该矩阵具有以下特性:
- 每行的元素从左到右升序排列。
- 每列的元素从上到下升序排列。
示例 1:
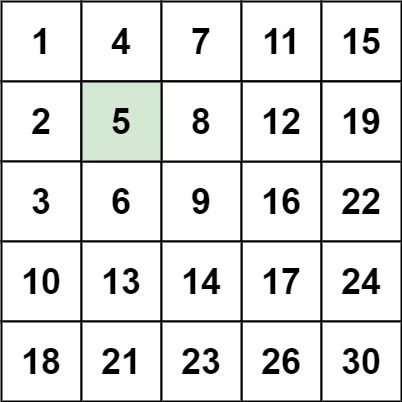
输入:matrix = [[1,4,7,11,15],[2,5,8,12,19],[3,6,9,16,22],[10,13,14,17,24],[18,21,23,26,30]], target = 5
输出:true
示例 2:
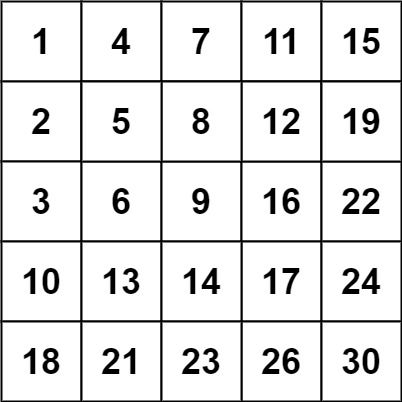
输入:matrix = [[1,4,7,11,15],[2,5,8,12,19],[3,6,9,16,22],[10,13,14,17,24],[18,21,23,26,30]], target = 20
输出:false
提示:
m == matrix.lengthn == matrix[i].length1 <= n, m <= 300-109 <= matrix[i][j] <= 109- 每行的所有元素从左到右升序排列
- 每列的所有元素从上到下升序排列
-109 <= target <= 109
解法
方法一:二分查找
由于每一行的所有元素升序排列,因此,对于每一行,我们可以使用二分查找找到第一个大于等于 \(\textit{target}\) 的元素,然后判断该元素是否等于 \(\textit{target}\)。如果等于 \(\textit{target}\),说明找到了目标值,直接返回 \(\text{true}\)。如果不等于 \(\textit{target}\),说明这一行的所有元素都小于 \(\textit{target}\),应该继续搜索下一行。
如果所有行都搜索完了,都没有找到目标值,说明目标值不存在,返回 \(\text{false}\)。
时间复杂度 \(O(m \times \log n)\),其中 \(m\) 和 \(n\) 分别为矩阵的行数和列数。空间复杂度 \(O(1)\)。
| class Solution:
def searchMatrix(self, matrix: List[List[int]], target: int) -> bool:
for row in matrix:
j = bisect_left(row, target)
if j < len(matrix[0]) and row[j] == target:
return True
return False
|
| class Solution {
public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {
for (var row : matrix) {
int j = Arrays.binarySearch(row, target);
if (j >= 0) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12 | class Solution {
public:
bool searchMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& matrix, int target) {
for (auto& row : matrix) {
int j = lower_bound(row.begin(), row.end(), target) - row.begin();
if (j < matrix[0].size() && row[j] == target) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
};
|
| func searchMatrix(matrix [][]int, target int) bool {
for _, row := range matrix {
j := sort.SearchInts(row, target)
if j < len(matrix[0]) && row[j] == target {
return true
}
}
return false
}
|
| function searchMatrix(matrix: number[][], target: number): boolean {
const n = matrix[0].length;
for (const row of matrix) {
const j = _.sortedIndex(row, target);
if (j < n && row[j] === target) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24 | use std::cmp::Ordering;
impl Solution {
pub fn search_matrix(matrix: Vec<Vec<i32>>, target: i32) -> bool {
let m = matrix.len();
let n = matrix[0].len();
let mut i = 0;
let mut j = n;
while i < m && j > 0 {
match target.cmp(&matrix[i][j - 1]) {
Ordering::Less => {
j -= 1;
}
Ordering::Greater => {
i += 1;
}
Ordering::Equal => {
return true;
}
}
}
false
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15 | /**
* @param {number[][]} matrix
* @param {number} target
* @return {boolean}
*/
var searchMatrix = function (matrix, target) {
const n = matrix[0].length;
for (const row of matrix) {
const j = _.sortedIndex(row, target);
if (j < n && row[j] == target) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
};
|
| public class Solution {
public bool SearchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {
foreach (int[] row in matrix) {
int j = Array.BinarySearch(row, target);
if (j >= 0) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
|
方法二:从左下角或右上角搜索
这里我们以左下角或右上角作为起始搜索点,往右上或左下方向开始搜索。比较当前元素 \(\textit{matrix}[i][j]\) 与 \(\textit{target}\) 的大小关系:
- 若 \(\textit{matrix}[i][j] = \textit{target}\),说明找到了目标值,直接返回 \(\text{true}\)。
- 若 \(\textit{matrix}[i][j] > \textit{target}\),说明这一列从当前位置开始往上的所有元素均大于 \(\textit{target}\),应该让 \(i\) 指针往上移动,即 \(i \leftarrow i - 1\)。
- 若 \(\textit{matrix}[i][j] < \textit{target}\),说明这一行从当前位置开始往右的所有元素均小于 \(\textit{target}\),应该让 \(j\) 指针往右移动,即 \(j \leftarrow j + 1\)。
若搜索结束依然找不到 \(\textit{target}\),返回 \(\text{false}\)。
时间复杂度 \(O(m + n)\),其中 \(m\) 和 \(n\) 分别为矩阵的行数和列数。空间复杂度 \(O(1)\)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12 | class Solution:
def searchMatrix(self, matrix: List[List[int]], target: int) -> bool:
m, n = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
i, j = m - 1, 0
while i >= 0 and j < n:
if matrix[i][j] == target:
return True
if matrix[i][j] > target:
i -= 1
else:
j += 1
return False
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17 | class Solution {
public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {
int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
int i = m - 1, j = 0;
while (i >= 0 && j < n) {
if (matrix[i][j] == target) {
return true;
}
if (matrix[i][j] > target) {
--i;
} else {
++j;
}
}
return false;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18 | class Solution {
public:
bool searchMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& matrix, int target) {
int m = matrix.size(), n = matrix[0].size();
int i = m - 1, j = 0;
while (i >= 0 && j < n) {
if (matrix[i][j] == target) {
return true;
}
if (matrix[i][j] > target) {
--i;
} else {
++j;
}
}
return false;
}
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15 | func searchMatrix(matrix [][]int, target int) bool {
m, n := len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
i, j := m-1, 0
for i >= 0 && j < n {
if matrix[i][j] == target {
return true
}
if matrix[i][j] > target {
i--
} else {
j++
}
}
return false
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15 | function searchMatrix(matrix: number[][], target: number): boolean {
const [m, n] = [matrix.length, matrix[0].length];
let [i, j] = [m - 1, 0];
while (i >= 0 && j < n) {
if (matrix[i][j] === target) {
return true;
}
if (matrix[i][j] > target) {
--i;
} else {
++j;
}
}
return false;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22 | impl Solution {
pub fn search_matrix(matrix: Vec<Vec<i32>>, target: i32) -> bool {
let m = matrix.len();
let n = matrix[0].len();
let mut i = m - 1;
let mut j = 0;
while i >= 0 && j < n {
if matrix[i][j] == target {
return true;
}
if matrix[i][j] > target {
if i == 0 {
break;
}
i -= 1;
} else {
j += 1;
}
}
false
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17 | public class Solution {
public bool SearchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {
int m = matrix.Length, n = matrix[0].Length;
int i = m - 1, j = 0;
while (i >= 0 && j < n) {
if (matrix[i][j] == target) {
return true;
}
if (matrix[i][j] > target) {
--i;
} else {
++j;
}
}
return false;
}
}
|


