递归
链表
题目描述
给你一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后链表的头节点。你必须在不修改节点内部的值的情况下完成本题(即,只能进行节点交换)。
示例 1:
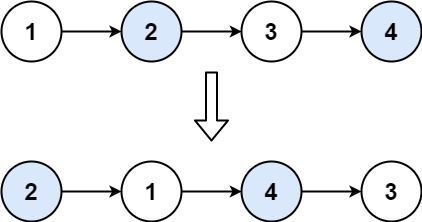
输入: head = [1,2,3,4]
输出: [2,1,4,3]
示例 2:
输入: head = []
输出: []
示例 3:
输入: head = [1]
输出: [1]
提示:
链表中节点的数目在范围 [0, 100] 内
0 <= Node.val <= 100
解法
方法一:递归
我们可以通过递归的方式实现两两交换链表中的节点。
递归的终止条件是链表中没有节点,或者链表中只有一个节点,此时无法进行交换,直接返回该节点。
否则,我们递归交换链表 \(head.next.next\) ,记交换后的头节点为 \(t\) ,然后我们记 \(head\) 的下一个节点为 \(p\) ,然后令 \(p\) 指向 \(head\) ,而 \(head\) 指向 \(t\) ,最后返回 \(p\) 。
时间复杂度 \(O(n)\) ,空间复杂度 \(O(n)\) ,其中 \(n\) 是链表的长度。
Python3 Java C++ Go TypeScript Rust JavaScript C# Ruby
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14 # Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution :
def swapPairs ( self , head : Optional [ ListNode ]) -> Optional [ ListNode ]:
if head is None or head . next is None :
return head
t = self . swapPairs ( head . next . next )
p = head . next
p . next = head
head . next = t
return p
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22 /**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs ( ListNode head ) {
if ( head == null || head . next == null ) {
return head ;
}
ListNode t = swapPairs ( head . next . next );
ListNode p = head . next ;
p . next = head ;
head . next = t ;
return p ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23 /**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public :
ListNode * swapPairs ( ListNode * head ) {
if ( ! head || ! head -> next ) {
return head ;
}
ListNode * t = swapPairs ( head -> next -> next );
ListNode * p = head -> next ;
p -> next = head ;
head -> next = t ;
return p ;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17 /**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func swapPairs ( head * ListNode ) * ListNode {
if head == nil || head . Next == nil {
return head
}
t := swapPairs ( head . Next . Next )
p := head . Next
p . Next = head
head . Next = t
return p
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22 /**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* val: number
* next: ListNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
* }
*/
function swapPairs ( head : ListNode | null ) : ListNode | null {
if ( ! head || ! head . next ) {
return head ;
}
const t = swapPairs ( head . next . next );
const p = head . next ;
p . next = head ;
head . next = t ;
return p ;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33 // Definition for singly-linked list.
// #[derive(PartialEq, Eq, Clone, Debug)]
// pub struct ListNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub next: Option<Box<ListNode>>
// }
//
// impl ListNode {
// #[inline]
// fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// ListNode {
// next: None,
// val
// }
// }
// }
impl Solution {
pub fn swap_pairs ( head : Option < Box < ListNode >> ) -> Option < Box < ListNode >> {
let mut dummy = Some ( Box :: new ( ListNode { val : 0 , next : head }));
let mut cur = dummy . as_mut (). unwrap ();
while cur . next . is_some () && cur . next . as_ref (). unwrap (). next . is_some () {
cur . next = {
let mut b = cur . next . as_mut (). unwrap (). next . take ();
cur . next . as_mut (). unwrap (). next = b . as_mut (). unwrap (). next . take ();
let a = cur . next . take ();
b . as_mut (). unwrap (). next = a ;
b
};
cur = cur . next . as_mut (). unwrap (). next . as_mut (). unwrap ();
}
dummy . unwrap (). next
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21 /**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var swapPairs = function ( head ) {
if ( ! head || ! head . next ) {
return head ;
}
const t = swapPairs ( head . next . next );
const p = head . next ;
p . next = head ;
head . next = t ;
return p ;
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23 /**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* public int val;
* public ListNode next;
* public ListNode(int val=0, ListNode next=null) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = next;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode SwapPairs ( ListNode head ) {
if ( head is null || head . next is null ) {
return head ;
}
ListNode t = SwapPairs ( head . next . next );
ListNode p = head . next ;
p . next = head ;
head . next = t ;
return p ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24 # Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode
# attr_accessor :val, :next
# def initialize(val = 0, _next = nil)
# @val = val
# @next = _next
# end
# end
# @param {ListNode} head
# @return {ListNode}
def swap_pairs ( head )
dummy = ListNode . new ( 0 , head )
pre = dummy
cur = head
while ! cur . nil? && ! cur . next . nil?
t = cur . next
cur . next = t . next
t . next = cur
pre . next = t
pre = cur
cur = cur . next
end
dummy . next
end
方法二:迭代
我们设置一个虚拟头节点 \(dummy\) ,初始时指向 \(head\) ,然后设置两个指针 \(pre\) 和 \(cur\) ,初始时 \(pre\) 指向 \(dummy\) ,而 \(cur\) 指向 \(head\) 。
接下来,我们遍历链表,每次需要交换 \(pre\) 后面的两个节点,因此我们先判断 \(cur\) 和 \(cur.next\) 是否为空,若不为空,则进行交换,否则终止循环。
时间复杂度 \(O(n)\) ,空间复杂度 \(O(1)\) ,其中 \(n\) 是链表的长度。
Python3 Java C++ Go TypeScript JavaScript C# PHP
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16 # Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution :
def swapPairs ( self , head : Optional [ ListNode ]) -> Optional [ ListNode ]:
dummy = ListNode ( next = head )
pre , cur = dummy , head
while cur and cur . next :
t = cur . next
cur . next = t . next
t . next = cur
pre . next = t
pre , cur = cur , cur . next
return dummy . next
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26 /**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs ( ListNode head ) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode ( 0 , head );
ListNode pre = dummy ;
ListNode cur = head ;
while ( cur != null && cur . next != null ) {
ListNode t = cur . next ;
cur . next = t . next ;
t . next = cur ;
pre . next = t ;
pre = cur ;
cur = cur . next ;
}
return dummy . next ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27 /**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public :
ListNode * swapPairs ( ListNode * head ) {
ListNode * dummy = new ListNode ( 0 , head );
ListNode * pre = dummy ;
ListNode * cur = head ;
while ( cur && cur -> next ) {
ListNode * t = cur -> next ;
cur -> next = t -> next ;
t -> next = cur ;
pre -> next = t ;
pre = cur ;
cur = cur -> next ;
}
return dummy -> next ;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19 /**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func swapPairs ( head * ListNode ) * ListNode {
dummy := & ListNode { Next : head }
pre , cur := dummy , head
for cur != nil && cur . Next != nil {
t := cur . Next
cur . Next = t . Next
t . Next = cur
pre . Next = t
pre , cur = cur , cur . Next
}
return dummy . Next
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24 /**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* val: number
* next: ListNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
* }
*/
function swapPairs ( head : ListNode | null ) : ListNode | null {
const dummy = new ListNode ( 0 , head );
let [ pre , cur ] = [ dummy , head ];
while ( cur && cur . next ) {
const t = cur . next ;
cur . next = t . next ;
t . next = cur ;
pre . next = t ;
[ pre , cur ] = [ cur , cur . next ];
}
return dummy . next ;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23 /**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var swapPairs = function ( head ) {
const dummy = new ListNode ( 0 , head );
let [ pre , cur ] = [ dummy , head ];
while ( cur && cur . next ) {
const t = cur . next ;
cur . next = t . next ;
t . next = cur ;
pre . next = t ;
[ pre , cur ] = [ cur , cur . next ];
}
return dummy . next ;
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27 /**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* public int val;
* public ListNode next;
* public ListNode(int val=0, ListNode next=null) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = next;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode SwapPairs ( ListNode head ) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode ( 0 , head );
ListNode pre = dummy ;
ListNode cur = head ;
while ( cur is not null && cur . next is not null ) {
ListNode t = cur . next ;
cur . next = t . next ;
t . next = cur ;
pre . next = t ;
pre = cur ;
cur = cur . next ;
}
return dummy . next ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37 # Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode {
# public $val;
# public $next;
# public function __construct($val = 0, $next = null)
# {
# $this->val = $val;
# $this->next = $next;
# }
# }
class Solution {
/**
* @param ListNode $head
* @return ListNode
*/
function swapPairs($head) {
$dummy = new ListNode(0);
$dummy->next = $head;
$prev = $dummy;
while ($head !== null && $head->next !== null) {
$first = $head;
$second = $head->next;
$first->next = $second->next;
$second->next = $first;
$prev->next = $second;
$prev = $first;
$head = $first->next;
}
return $dummy->next;
}
}