


题目描述
有一棵根节点为 0 的 家族树 ,总共包含 n 个节点,节点编号为 0 到 n - 1 。给你一个下标从 0 开始的整数数组 parents ,其中 parents[i] 是节点 i 的父节点。由于节点 0 是 根 ,所以 parents[0] == -1 。
总共有 105 个基因值,每个基因值都用 闭区间 [1, 105] 中的一个整数表示。给你一个下标从 0 开始的整数数组 nums ,其中 nums[i] 是节点 i 的基因值,且基因值 互不相同 。
请你返回一个数组 ans ,长度为 n ,其中 ans[i] 是以节点 i 为根的子树内 缺失 的 最小 基因值。
节点 x 为根的 子树 包含节点 x 和它所有的 后代 节点。
示例 1:
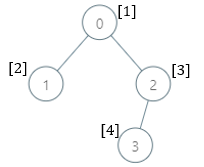
输入:parents = [-1,0,0,2], nums = [1,2,3,4]
输出:[5,1,1,1]
解释:每个子树答案计算结果如下:
- 0:子树包含节点 [0,1,2,3] ,基因值分别为 [1,2,3,4] 。5 是缺失的最小基因值。
- 1:子树只包含节点 1 ,基因值为 2 。1 是缺失的最小基因值。
- 2:子树包含节点 [2,3] ,基因值分别为 [3,4] 。1 是缺失的最小基因值。
- 3:子树只包含节点 3 ,基因值为 4 。1是缺失的最小基因值。
示例 2:
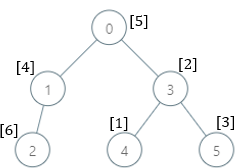
输入:parents = [-1,0,1,0,3,3], nums = [5,4,6,2,1,3]
输出:[7,1,1,4,2,1]
解释:每个子树答案计算结果如下:
- 0:子树内包含节点 [0,1,2,3,4,5] ,基因值分别为 [5,4,6,2,1,3] 。7 是缺失的最小基因值。
- 1:子树内包含节点 [1,2] ,基因值分别为 [4,6] 。 1 是缺失的最小基因值。
- 2:子树内只包含节点 2 ,基因值为 6 。1 是缺失的最小基因值。
- 3:子树内包含节点 [3,4,5] ,基因值分别为 [2,1,3] 。4 是缺失的最小基因值。
- 4:子树内只包含节点 4 ,基因值为 1 。2 是缺失的最小基因值。
- 5:子树内只包含节点 5 ,基因值为 3 。1 是缺失的最小基因值。
示例 3:
输入:parents = [-1,2,3,0,2,4,1], nums = [2,3,4,5,6,7,8]
输出:[1,1,1,1,1,1,1]
解释:所有子树都缺失基因值 1 。
提示:
n == parents.length == nums.length2 <= n <= 105- 对于
i != 0 ,满足 0 <= parents[i] <= n - 1
parents[0] == -1parents 表示一棵合法的树。1 <= nums[i] <= 105nums[i] 互不相同。
解法
方法一:DFS
我们注意到,每个节点的基因值互不相同,因此,我们只需要找到基因值为 \(1\) 的节点 \(idx\),那么除了从节点 \(idx\) 到根节点 \(0\) 的每个节点,其它节点的答案都是 \(1\)。
因此,我们初始化答案数组 \(ans\) 为 \([1,1,...,1]\),然后我们的重点就在于求出节点 \(idx\) 到根节点 \(0\) 的路径上的每个节点的答案。
我们可以从节点 \(idx\) 开始,通过深度优先搜索的方式,标记以 \(idx\) 作为根节点的子树中出现过的基因值,记录在数组 \(has\) 中。搜索过程中,我们用一个数组 \(vis\) 标记已经访问过的节点,防止重复访问。
接下来,我们从 \(i=2\) 开始,不断向后寻找第一个没有出现过的基因值,即为节点 \(idx\) 的答案。这里 \(i\) 是严格递增的,因为基因值互不相同,所以我们一定能在 \([1,..n+1]\) 中找到一个没有出现过的基因值。
然后,我们更新节点 \(idx\) 的答案,即 \(ans[idx]=i\),并将 \(idx\) 更新为其父节点,继续上述过程,直到 \(idx=-1\),即到达了根节点 \(0\)。
最后,我们返回答案数组 \(ans\) 即可。
时间复杂度 \(O(n)\),空间复杂度 \(O(n)\)。其中 \(n\) 是节点的数量。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34 | class Solution:
def smallestMissingValueSubtree(
self, parents: List[int], nums: List[int]
) -> List[int]:
def dfs(i: int):
if vis[i]:
return
vis[i] = True
if nums[i] < len(has):
has[nums[i]] = True
for j in g[i]:
dfs(j)
n = len(nums)
ans = [1] * n
g = [[] for _ in range(n)]
idx = -1
for i, p in enumerate(parents):
if i:
g[p].append(i)
if nums[i] == 1:
idx = i
if idx == -1:
return ans
vis = [False] * n
has = [False] * (n + 2)
i = 2
while idx != -1:
dfs(idx)
while has[i]:
i += 1
ans[idx] = i
idx = parents[idx]
return ans
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50 | class Solution {
private List<Integer>[] g;
private boolean[] vis;
private boolean[] has;
private int[] nums;
public int[] smallestMissingValueSubtree(int[] parents, int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
this.nums = nums;
g = new List[n];
vis = new boolean[n];
has = new boolean[n + 2];
Arrays.setAll(g, i -> new ArrayList<>());
int idx = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (i > 0) {
g[parents[i]].add(i);
}
if (nums[i] == 1) {
idx = i;
}
}
int[] ans = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(ans, 1);
if (idx == -1) {
return ans;
}
for (int i = 2; idx != -1; idx = parents[idx]) {
dfs(idx);
while (has[i]) {
++i;
}
ans[idx] = i;
}
return ans;
}
private void dfs(int i) {
if (vis[i]) {
return;
}
vis[i] = true;
if (nums[i] < has.length) {
has[nums[i]] = true;
}
for (int j : g[i]) {
dfs(j);
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44 | class Solution {
public:
vector<int> smallestMissingValueSubtree(vector<int>& parents, vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
vector<int> g[n];
bool vis[n];
bool has[n + 2];
memset(vis, false, sizeof(vis));
memset(has, false, sizeof(has));
int idx = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (i) {
g[parents[i]].push_back(i);
}
if (nums[i] == 1) {
idx = i;
}
}
vector<int> ans(n, 1);
if (idx == -1) {
return ans;
}
function<void(int)> dfs = [&](int i) {
if (vis[i]) {
return;
}
vis[i] = true;
if (nums[i] < n + 2) {
has[nums[i]] = true;
}
for (int j : g[i]) {
dfs(j);
}
};
for (int i = 2; ~idx; idx = parents[idx]) {
dfs(idx);
while (has[i]) {
++i;
}
ans[idx] = i;
}
return ans;
}
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41 | func smallestMissingValueSubtree(parents []int, nums []int) []int {
n := len(nums)
g := make([][]int, n)
vis := make([]bool, n)
has := make([]bool, n+2)
idx := -1
ans := make([]int, n)
for i, p := range parents {
if i > 0 {
g[p] = append(g[p], i)
}
if nums[i] == 1 {
idx = i
}
ans[i] = 1
}
if idx < 0 {
return ans
}
var dfs func(int)
dfs = func(i int) {
if vis[i] {
return
}
vis[i] = true
if nums[i] < len(has) {
has[nums[i]] = true
}
for _, j := range g[i] {
dfs(j)
}
}
for i := 2; idx != -1; idx = parents[idx] {
dfs(idx)
for has[i] {
i++
}
ans[idx] = i
}
return ans
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39 | function smallestMissingValueSubtree(parents: number[], nums: number[]): number[] {
const n = nums.length;
const g: number[][] = Array.from({ length: n }, () => []);
const vis: boolean[] = Array(n).fill(false);
const has: boolean[] = Array(n + 2).fill(false);
const ans: number[] = Array(n).fill(1);
let idx = -1;
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (i) {
g[parents[i]].push(i);
}
if (nums[i] === 1) {
idx = i;
}
}
if (idx === -1) {
return ans;
}
const dfs = (i: number): void => {
if (vis[i]) {
return;
}
vis[i] = true;
if (nums[i] < has.length) {
has[nums[i]] = true;
}
for (const j of g[i]) {
dfs(j);
}
};
for (let i = 2; ~idx; idx = parents[idx]) {
dfs(idx);
while (has[i]) {
++i;
}
ans[idx] = i;
}
return ans;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51 | impl Solution {
pub fn smallest_missing_value_subtree(parents: Vec<i32>, nums: Vec<i32>) -> Vec<i32> {
fn dfs(
i: usize,
vis: &mut Vec<bool>,
has: &mut Vec<bool>,
g: &Vec<Vec<usize>>,
nums: &Vec<i32>,
) {
if vis[i] {
return;
}
vis[i] = true;
if nums[i] < (has.len() as i32) {
has[nums[i] as usize] = true;
}
for &j in &g[i] {
dfs(j, vis, has, g, nums);
}
}
let n = nums.len();
let mut ans = vec![1; n];
let mut g: Vec<Vec<usize>> = vec![vec![]; n];
let mut idx = -1;
for (i, &p) in parents.iter().enumerate() {
if i > 0 {
g[p as usize].push(i);
}
if nums[i] == 1 {
idx = i as i32;
}
}
if idx == -1 {
return ans;
}
let mut vis = vec![false; n];
let mut has = vec![false; (n + 2) as usize];
let mut i = 2;
let mut idx_mut = idx;
while idx_mut != -1 {
dfs(idx_mut as usize, &mut vis, &mut has, &g, &nums);
while has[i] {
i += 1;
}
ans[idx_mut as usize] = i as i32;
idx_mut = parents[idx_mut as usize];
}
ans
}
}
|




