数学
递归
链表
题目描述
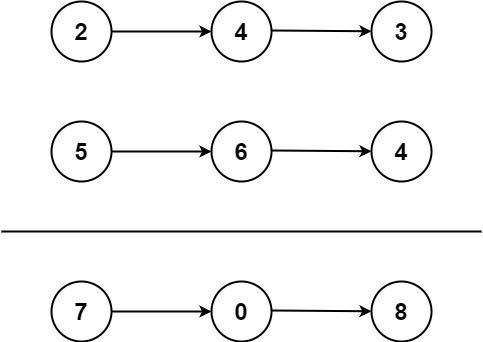
给你两个 非空 的链表,表示两个非负的整数。它们每位数字都是按照 逆序 的方式存储的,并且每个节点只能存储 一位 数字。
请你将两个数相加,并以相同形式返回一个表示和的链表。
你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数都不会以 0 开头。
示例 1:
输入: l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4]
输出: [7,0,8]
解释: 342 + 465 = 807.
示例 2:
输入: l1 = [0], l2 = [0]
输出: [0]
示例 3:
输入: l1 = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9], l2 = [9,9,9,9]
输出: [8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]
提示:
每个链表中的节点数在范围 [1, 100] 内
0 <= Node.val <= 9题目数据保证列表表示的数字不含前导零
解法
方法一:模拟
我们同时遍历两个链表 \(l_1\) 和 \(l_2\) ,并使用变量 \(carry\) 表示当前是否有进位。
每次遍历时,我们取出对应链表的当前位,计算它们与进位 \(carry\) 的和,然后更新进位的值,最后将当前位的值加入答案链表。如果两个链表都遍历完了,并且进位为 \(0\) 时,遍历结束。
最后我们返回答案链表的头节点即可。
时间复杂度 \(O(\max(m, n))\) ,其中 \(m\) 和 \(n\) 分别为两个链表的长度。我们需要遍历两个链表的全部位置,而处理每个位置只需要 \(O(1)\) 的时间。忽略答案的空间消耗,空间复杂度 \(O(1)\) 。
Python3 Java C++ Go TypeScript Rust JavaScript C# PHP Swift Ruby Nim
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19 # Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution :
def addTwoNumbers (
self , l1 : Optional [ ListNode ], l2 : Optional [ ListNode ]
) -> Optional [ ListNode ]:
dummy = ListNode ()
carry , curr = 0 , dummy
while l1 or l2 or carry :
s = ( l1 . val if l1 else 0 ) + ( l2 . val if l2 else 0 ) + carry
carry , val = divmod ( s , 10 )
curr . next = ListNode ( val )
curr = curr . next
l1 = l1 . next if l1 else None
l2 = l2 . next if l2 else None
return dummy . next
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26 /**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers ( ListNode l1 , ListNode l2 ) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode ( 0 );
int carry = 0 ;
ListNode cur = dummy ;
while ( l1 != null || l2 != null || carry != 0 ) {
int s = ( l1 == null ? 0 : l1 . val ) + ( l2 == null ? 0 : l2 . val ) + carry ;
carry = s / 10 ;
cur . next = new ListNode ( s % 10 );
cur = cur . next ;
l1 = l1 == null ? null : l1 . next ;
l2 = l2 == null ? null : l2 . next ;
}
return dummy . next ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27 /**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public :
ListNode * addTwoNumbers ( ListNode * l1 , ListNode * l2 ) {
ListNode * dummy = new ListNode ();
int carry = 0 ;
ListNode * cur = dummy ;
while ( l1 || l2 || carry ) {
int s = ( l1 ? l1 -> val : 0 ) + ( l2 ? l2 -> val : 0 ) + carry ;
carry = s / 10 ;
cur -> next = new ListNode ( s % 10 );
cur = cur -> next ;
l1 = l1 ? l1 -> next : nullptr ;
l2 = l2 ? l2 -> next : nullptr ;
}
return dummy -> next ;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31 /**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func addTwoNumbers ( l1 * ListNode , l2 * ListNode ) * ListNode {
dummy := & ListNode {}
carry := 0
cur := dummy
for l1 != nil || l2 != nil || carry != 0 {
s := carry
if l1 != nil {
s += l1 . Val
}
if l2 != nil {
s += l2 . Val
}
carry = s / 10
cur . Next = & ListNode { s % 10 , nil }
cur = cur . Next
if l1 != nil {
l1 = l1 . Next
}
if l2 != nil {
l2 = l2 . Next
}
}
return dummy . Next
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31 /**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* val: number
* next: ListNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
* }
*/
function addTwoNumbers ( l1 : ListNode | null , l2 : ListNode | null ) : ListNode | null {
const dummy = new ListNode ();
let cur = dummy ;
let sum = 0 ;
while ( l1 != null || l2 != null || sum !== 0 ) {
if ( l1 != null ) {
sum += l1 . val ;
l1 = l1 . next ;
}
if ( l2 != null ) {
sum += l2 . val ;
l2 = l2 . next ;
}
cur . next = new ListNode ( sum % 10 );
cur = cur . next ;
sum = Math . floor ( sum / 10 );
}
return dummy . next ;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40 // Definition for singly-linked list.
// #[derive(PartialEq, Eq, Clone, Debug)]
// pub struct ListNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub next: Option<Box<ListNode>>
// }
//
// impl ListNode {
// #[inline]
// fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// ListNode {
// next: None,
// val
// }
// }
// }
impl Solution {
pub fn add_two_numbers (
mut l1 : Option < Box < ListNode >> ,
mut l2 : Option < Box < ListNode >> ,
) -> Option < Box < ListNode >> {
let mut dummy = Some ( Box :: new ( ListNode :: new ( 0 )));
let mut cur = & mut dummy ;
let mut sum = 0 ;
while l1 . is_some () || l2 . is_some () || sum != 0 {
if let Some ( node ) = l1 {
sum += node . val ;
l1 = node . next ;
}
if let Some ( node ) = l2 {
sum += node . val ;
l2 = node . next ;
}
cur . as_mut (). unwrap (). next = Some ( Box :: new ( ListNode :: new ( sum % 10 )));
cur = & mut cur . as_mut (). unwrap (). next ;
sum /= 10 ;
}
dummy . unwrap (). next . take ()
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26 /**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} l1
* @param {ListNode} l2
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var addTwoNumbers = function ( l1 , l2 ) {
const dummy = new ListNode ();
let carry = 0 ;
let cur = dummy ;
while ( l1 || l2 || carry ) {
const s = ( l1 ? . val || 0 ) + ( l2 ? . val || 0 ) + carry ;
carry = Math . floor ( s / 10 );
cur . next = new ListNode ( s % 10 );
cur = cur . next ;
l1 = l1 ? . next ;
l2 = l2 ? . next ;
}
return dummy . next ;
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27 /**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* public int val;
* public ListNode next;
* public ListNode(int val=0, ListNode next=null) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = next;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode AddTwoNumbers ( ListNode l1 , ListNode l2 ) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode ();
int carry = 0 ;
ListNode cur = dummy ;
while ( l1 != null || l2 != null || carry != 0 ) {
int s = ( l1 == null ? 0 : l1 . val ) + ( l2 == null ? 0 : l2 . val ) + carry ;
carry = s / 10 ;
cur . next = new ListNode ( s % 10 );
cur = cur . next ;
l1 = l1 == null ? null : l1 . next ;
l2 = l2 == null ? null : l2 . next ;
}
return dummy . next ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47 /**
* Definition for a singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* public $val = 0;
* public $next = null;
* function __construct($val = 0, $next = null) {
* $this->val = $val;
* $this->next = $next;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
/**
* @param ListNode $l1
* @param ListNode $l2
* @return ListNode
*/
function addTwoNumbers($l1, $l2) {
$dummy = new ListNode(0);
$current = $dummy;
$carry = 0;
while ($l1 !== null || $l2 !== null) {
$x = $l1 !== null ? $l1->val : 0;
$y = $l2 !== null ? $l2->val : 0;
$sum = $x + $y + $carry;
$carry = (int) ($sum / 10);
$current->next = new ListNode($sum % 10);
$current = $current->next;
if ($l1 !== null) {
$l1 = $l1->next;
}
if ($l2 !== null) {
$l2 = $l2->next;
}
}
if ($carry > 0) {
$current->next = new ListNode($carry);
}
return $dummy->next;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28 /**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* public var val: Int
* public var next: ListNode?
* public init() { self.val = 0; self.next = nil; }
* public init(_ val: Int) { self.val = val; self.next = nil; }
* public init(_ val: Int, _ next: ListNode?) { self.val = val; self.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
func addTwoNumbers ( _ l1 : ListNode ?, _ l2 : ListNode ?) -> ListNode ? {
var dummy = ListNode . init ()
var carry = 0
var l1 = l1
var l2 = l2
var cur = dummy
while l1 != nil || l2 != nil || carry != 0 {
let s = ( l1 ?. val ?? 0 ) + ( l2 ?. val ?? 0 ) + carry
carry = s / 10
cur . next = ListNode . init ( s % 10 )
cur = cur . next !
l1 = l1 ?. next
l2 = l2 ?. next
}
return dummy . next
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25 # Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode
# attr_accessor :val, :next
# def initialize(val = 0, _next = nil)
# @val = val
# @next = _next
# end
# end
# @param {ListNode} l1
# @param {ListNode} l2
# @return {ListNode}
def add_two_numbers ( l1 , l2 )
dummy = ListNode . new ()
carry = 0
cur = dummy
while ! l1 . nil? || ! l2 . nil? || carry > 0
s = ( l1 . nil? ? 0 : l1 . val ) + ( l2 . nil? ? 0 : l2 . val ) + carry
carry = s / 10
cur . next = ListNode . new ( s % 10 )
cur = cur . next
l1 = l1 . nil? ? l1 : l1 . next
l2 = l2 . nil? ? l2 : l2 . next
end
dummy . next
end
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31 #[
# Driver code in the solution file
# Definition for singly-linked list.
type
Node[int] = ref object
value: int
next: Node[int]
SinglyLinkedList[T] = object
head, tail: Node[T]
]#
# More efficient code churning ...
proc addTwoNumbers ( l1 : var SinglyLinkedList , l2 : var SinglyLinkedList ): SinglyLinkedList [ int ] =
var
aggregate : SinglyLinkedList
psum : seq [ char ]
temp_la , temp_lb : seq [ int ]
while not l1 . head . isNil :
temp_la . add ( l1 . head . value )
l1 . head = l1 . head . next
while not l2 . head . isNil :
temp_lb . add ( l2 . head . value )
l2 . head = l2 . head . next
psum = reversed ( $ ( reversed ( temp_la ). join ( "" ). parseInt () + reversed ( temp_lb ). join ( "" ). parseInt ()))
for i in psum : aggregate . append (( $ i ). parseInt ())
result = aggregate