
题目描述
有一个具有 n 个顶点的 双向 图,其中每个顶点标记从 0 到 n - 1(包含 0 和 n - 1)。图中的边用一个二维整数数组 edges 表示,其中 edges[i] = [ui, vi] 表示顶点 ui 和顶点 vi 之间的双向边。 每个顶点对由 最多一条 边连接,并且没有顶点存在与自身相连的边。
请你确定是否存在从顶点 source 开始,到顶点 destination 结束的 有效路径 。
给你数组 edges 和整数 n、source 和 destination,如果从 source 到 destination 存在 有效路径 ,则返回 true,否则返回 false 。
示例 1:
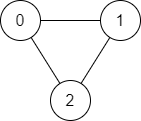
输入:n = 3, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,0]], source = 0, destination = 2
输出:true
解释:存在由顶点 0 到顶点 2 的路径:
- 0 → 1 → 2
- 0 → 2
示例 2:
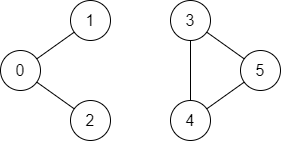
输入:n = 6, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[3,5],[5,4],[4,3]], source = 0, destination = 5
输出:false
解释:不存在由顶点 0 到顶点 5 的路径.
提示:
1 <= n <= 2 * 1050 <= edges.length <= 2 * 105edges[i].length == 20 <= ui, vi <= n - 1ui != vi0 <= source, destination <= n - 1- 不存在重复边
- 不存在指向顶点自身的边
解法
方法一:DFS
我们首先将 \(\textit{edges}\) 转换成邻接表 \(g\),然后使用 DFS,判断是否存在从 \(\textit{source}\) 到 \(\textit{destination}\) 的路径。
过程中,我们用数组 \(\textit{vis}\) 记录已经访问过的顶点,避免重复访问。
时间复杂度 \(O(n + m)\),空间复杂度 \(O(n + m)\)。其中 \(n\) 和 \(m\) 分别是节点数和边数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19 | class Solution:
def validPath(
self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]], source: int, destination: int
) -> bool:
def dfs(i: int) -> bool:
if i == destination:
return True
vis.add(i)
for j in g[i]:
if j not in vis and dfs(j):
return True
return False
g = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for u, v in edges:
g[u].append(v)
g[v].append(u)
vis = set()
return dfs(source)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31 | class Solution {
private int destination;
private boolean[] vis;
private List<Integer>[] g;
public boolean validPath(int n, int[][] edges, int source, int destination) {
this.destination = destination;
vis = new boolean[n];
g = new List[n];
Arrays.setAll(g, i -> new ArrayList<>());
for (var e : edges) {
int u = e[0], v = e[1];
g[u].add(v);
g[v].add(u);
}
return dfs(source);
}
private boolean dfs(int i) {
if (i == destination) {
return true;
}
vis[i] = true;
for (var j : g[i]) {
if (!vis[j] && dfs(j)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25 | class Solution {
public:
bool validPath(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, int source, int destination) {
vector<int> g[n];
vector<bool> vis(n);
for (const auto& e : edges) {
int u = e[0], v = e[1];
g[u].push_back(v);
g[v].push_back(u);
}
function<bool(int)> dfs = [&](int i) -> bool {
if (i == destination) {
return true;
}
vis[i] = true;
for (int j : g[i]) {
if (!vis[j] && dfs(j)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
};
return dfs(source);
}
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23 | func validPath(n int, edges [][]int, source int, destination int) bool {
vis := make([]bool, n)
g := make([][]int, n)
for _, e := range edges {
u, v := e[0], e[1]
g[u] = append(g[u], v)
g[v] = append(g[v], u)
}
var dfs func(int) bool
dfs = func(i int) bool {
if i == destination {
return true
}
vis[i] = true
for _, j := range g[i] {
if !vis[j] && dfs(j) {
return true
}
}
return false
}
return dfs(source)
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19 | function validPath(n: number, edges: number[][], source: number, destination: number): boolean {
const g: number[][] = Array.from({ length: n }, () => []);
for (const [u, v] of edges) {
g[u].push(v);
g[v].push(u);
}
const vis = new Set<number>();
const dfs = (i: number) => {
if (i === destination) {
return true;
}
if (vis.has(i)) {
return false;
}
vis.add(i);
return g[i].some(dfs);
};
return dfs(source);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32 | impl Solution {
pub fn valid_path(n: i32, edges: Vec<Vec<i32>>, source: i32, destination: i32) -> bool {
let n = n as usize;
let source = source as usize;
let destination = destination as usize;
let mut g = vec![Vec::new(); n];
let mut vis = vec![false; n];
for e in edges {
let u = e[0] as usize;
let v = e[1] as usize;
g[u].push(v);
g[v].push(u);
}
fn dfs(g: &Vec<Vec<usize>>, vis: &mut Vec<bool>, i: usize, destination: usize) -> bool {
if i == destination {
return true;
}
vis[i] = true;
for &j in &g[i] {
if !vis[j] && dfs(g, vis, j, destination) {
return true;
}
}
false
}
dfs(&g, &mut vis, source, destination)
}
}
|
方法二:BFS
我们也可以使用 BFS,判断是否存在从 \(\textit{source}\) 到 \(\textit{destination}\) 的路径。
具体地,我们定义一个队列 \(q\),初始时将 \(\textit{source}\) 加入队列。另外,我们用一个集合 \(\textit{vis}\) 记录已经访问过的顶点,避免重复访问。
接下来,我们不断从队列中取出顶点 \(i\),如果 \(i = \textit{destination}\),则说明存在从 \(\textit{source}\) 到 \(\textit{destination}\) 的路径,返回 \(\textit{true}\)。否则,我们遍历 \(i\) 的所有邻接顶点 \(j\),如果 \(j\) 没有被访问过,我们将 \(j\) 加入队列 \(q\),并且标记 \(j\) 为已访问。
最后,如果队列为空,说明不存在从 \(\textit{source}\) 到 \(\textit{destination}\) 的路径,返回 \(\textit{false}\)。
时间复杂度 \(O(n + m)\),空间复杂度 \(O(n + m)\)。其中 \(n\) 和 \(m\) 分别是节点数和边数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19 | class Solution:
def validPath(
self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]], source: int, destination: int
) -> bool:
g = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for u, v in edges:
g[u].append(v)
g[v].append(u)
q = deque([source])
vis = {source}
while q:
i = q.popleft()
if i == destination:
return True
for j in g[i]:
if j not in vis:
vis.add(j)
q.append(j)
return False
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28 | class Solution {
public boolean validPath(int n, int[][] edges, int source, int destination) {
List<Integer>[] g = new List[n];
Arrays.setAll(g, k -> new ArrayList<>());
for (var e : edges) {
int u = e[0], v = e[1];
g[u].add(v);
g[v].add(u);
}
Deque<Integer> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
q.offer(source);
boolean[] vis = new boolean[n];
vis[source] = true;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int i = q.poll();
if (i == destination) {
return true;
}
for (int j : g[i]) {
if (!vis[j]) {
vis[j] = true;
q.offer(j);
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28 | class Solution {
public:
bool validPath(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, int source, int destination) {
vector<vector<int>> g(n);
for (const auto& e : edges) {
int u = e[0], v = e[1];
g[u].push_back(v);
g[v].push_back(u);
}
queue<int> q{{source}};
vector<bool> vis(n);
vis[source] = true;
while (q.size()) {
int i = q.front();
q.pop();
if (i == destination) {
return true;
}
for (int j : g[i]) {
if (!vis[j]) {
vis[j] = true;
q.push(j);
}
}
}
return false;
}
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25 | func validPath(n int, edges [][]int, source int, destination int) bool {
g := make([][]int, n)
for _, e := range edges {
u, v := e[0], e[1]
g[u] = append(g[u], v)
g[v] = append(g[v], u)
}
q := []int{source}
vis := make([]bool, n)
vis[source] = true
for len(q) > 0 {
i := q[0]
q = q[1:]
if i == destination {
return true
}
for _, j := range g[i] {
if !vis[j] {
vis[j] = true
q = append(q, j)
}
}
}
return false
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22 | function validPath(n: number, edges: number[][], source: number, destination: number): boolean {
const g: number[][] = Array.from({ length: n }, () => []);
for (const [u, v] of edges) {
g[u].push(v);
g[v].push(u);
}
const vis = new Set<number>([source]);
const q = [source];
while (q.length) {
const i = q.pop()!;
if (i === destination) {
return true;
}
for (const j of g[i]) {
if (!vis.has(j)) {
vis.add(j);
q.push(j);
}
}
}
return false;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36 | use std::collections::{HashSet, VecDeque};
impl Solution {
pub fn valid_path(n: i32, edges: Vec<Vec<i32>>, source: i32, destination: i32) -> bool {
let n = n as usize;
let source = source as usize;
let destination = destination as usize;
let mut g = vec![Vec::new(); n];
for edge in edges {
let u = edge[0] as usize;
let v = edge[1] as usize;
g[u].push(v);
g[v].push(u);
}
let mut q = VecDeque::new();
let mut vis = HashSet::new();
q.push_back(source);
vis.insert(source);
while let Some(i) = q.pop_front() {
if i == destination {
return true;
}
for &j in &g[i] {
if !vis.contains(&j) {
vis.insert(j);
q.push_back(j);
}
}
}
false
}
}
|
方法三:并查集
并查集是一种树形的数据结构,顾名思义,它用于处理一些不交集的合并及查询问题。 它支持两种操作:
- 查找(Find):确定某个元素处于哪个子集,单次操作时间复杂度 \(O(\alpha(n))\)
- 合并(Union):将两个子集合并成一个集合,单次操作时间复杂度 \(O(\alpha(n))\)
对于本题,我们可以利用并查集,将 edges 中的边进行合并,然后判断 source 和 destination 是否在同一个集合中。
时间复杂度 \(O(n \log n + m)\) 或 \(O(n \alpha(n) + m)\),空间复杂度 \(O(n)\)。其中 \(n\) 和 \(m\) 分别是节点数和边数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31 | class UnionFind:
def __init__(self, n):
self.p = list(range(n))
self.size = [1] * n
def find(self, x):
if self.p[x] != x:
self.p[x] = self.find(self.p[x])
return self.p[x]
def union(self, a, b):
pa, pb = self.find(a), self.find(b)
if pa == pb:
return False
if self.size[pa] > self.size[pb]:
self.p[pb] = pa
self.size[pa] += self.size[pb]
else:
self.p[pa] = pb
self.size[pb] += self.size[pa]
return True
class Solution:
def validPath(
self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]], source: int, destination: int
) -> bool:
uf = UnionFind(n)
for u, v in edges:
uf.union(u, v)
return uf.find(source) == uf.find(destination)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43 | class UnionFind {
private int[] p;
private int[] size;
public UnionFind(int n) {
p = new int[n];
size = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
p[i] = i;
size[i] = 1;
}
}
public int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x) {
p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
}
public void union(int a, int b) {
int pa = find(a), pb = find(b);
if (pa != pb) {
if (size[pa] > size[pb]) {
p[pb] = pa;
size[pa] += size[pb];
} else {
p[pa] = pb;
size[pb] += size[pa];
}
}
}
}
class Solution {
public boolean validPath(int n, int[][] edges, int source, int destination) {
UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(n);
for (var e : edges) {
uf.union(e[0], e[1]);
}
return uf.find(source) == uf.find(destination);
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42 | class UnionFind {
public:
UnionFind(int n) {
p = vector<int>(n);
size = vector<int>(n, 1);
iota(p.begin(), p.end(), 0);
}
void unite(int a, int b) {
int pa = find(a), pb = find(b);
if (pa != pb) {
if (size[pa] > size[pb]) {
p[pb] = pa;
size[pa] += size[pb];
} else {
p[pa] = pb;
size[pb] += size[pa];
}
}
}
int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x) {
p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
}
private:
vector<int> p, size;
};
class Solution {
public:
bool validPath(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, int source, int destination) {
UnionFind uf(n);
for (const auto& e : edges) {
uf.unite(e[0], e[1]);
}
return uf.find(source) == uf.find(destination);
}
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43 | type unionFind struct {
p, size []int
}
func newUnionFind(n int) *unionFind {
p := make([]int, n)
size := make([]int, n)
for i := range p {
p[i] = i
size[i] = 1
}
return &unionFind{p, size}
}
func (uf *unionFind) find(x int) int {
if uf.p[x] != x {
uf.p[x] = uf.find(uf.p[x])
}
return uf.p[x]
}
func (uf *unionFind) union(a, b int) bool {
pa, pb := uf.find(a), uf.find(b)
if pa == pb {
return false
}
if uf.size[pa] > uf.size[pb] {
uf.p[pb] = pa
uf.size[pa] += uf.size[pb]
} else {
uf.p[pa] = pb
uf.size[pb] += uf.size[pa]
}
return true
}
func validPath(n int, edges [][]int, source int, destination int) bool {
uf := newUnionFind(n)
for _, e := range edges {
uf.union(e[0], e[1])
}
return uf.find(source) == uf.find(destination)
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38 | class UnionFind {
p: number[];
size: number[];
constructor(n: number) {
this.p = Array(n)
.fill(0)
.map((_, i) => i);
this.size = Array(n).fill(1);
}
find(x: number): number {
if (this.p[x] !== x) {
this.p[x] = this.find(this.p[x]);
}
return this.p[x];
}
union(a: number, b: number): boolean {
const [pa, pb] = [this.find(a), this.find(b)];
if (pa === pb) {
return false;
}
if (this.size[pa] > this.size[pb]) {
this.p[pb] = pa;
this.size[pa] += this.size[pb];
} else {
this.p[pa] = pb;
this.size[pb] += this.size[pa];
}
return true;
}
}
function validPath(n: number, edges: number[][], source: number, destination: number): boolean {
const uf = new UnionFind(n);
edges.forEach(([u, v]) => uf.union(u, v));
return uf.find(source) === uf.find(destination);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48 | struct UnionFind {
p: Vec<usize>,
size: Vec<usize>,
}
impl UnionFind {
fn new(n: usize) -> Self {
let p = (0..n).collect();
let size = vec![1; n];
UnionFind { p, size }
}
fn find(&mut self, x: usize) -> usize {
if self.p[x] != x {
self.p[x] = self.find(self.p[x]);
}
self.p[x]
}
fn union(&mut self, a: usize, b: usize) {
let pa = self.find(a);
let pb = self.find(b);
if pa != pb {
if self.size[pa] > self.size[pb] {
self.p[pb] = pa;
self.size[pa] += self.size[pb];
} else {
self.p[pa] = pb;
self.size[pb] += self.size[pa];
}
}
}
}
impl Solution {
pub fn valid_path(n: i32, edges: Vec<Vec<i32>>, source: i32, destination: i32) -> bool {
let n = n as usize;
let mut uf = UnionFind::new(n);
for e in edges {
let u = e[0] as usize;
let v = e[1] as usize;
uf.union(u, v);
}
uf.find(source as usize) == uf.find(destination as usize)
}
}
|


