


题目描述
给你一个 m x n 的迷宫矩阵 maze (下标从 0 开始),矩阵中有空格子(用 '.' 表示)和墙(用 '+' 表示)。同时给你迷宫的入口 entrance ,用 entrance = [entrancerow, entrancecol] 表示你一开始所在格子的行和列。
每一步操作,你可以往 上,下,左 或者 右 移动一个格子。你不能进入墙所在的格子,你也不能离开迷宫。你的目标是找到离 entrance 最近 的出口。出口 的含义是 maze 边界 上的 空格子。entrance 格子 不算 出口。
请你返回从 entrance 到最近出口的最短路径的 步数 ,如果不存在这样的路径,请你返回 -1 。
示例 1:
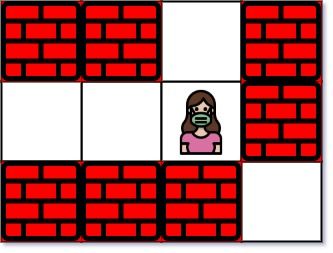
输入:maze = [["+","+",".","+"],[".",".",".","+"],["+","+","+","."]], entrance = [1,2]
输出:1
解释:总共有 3 个出口,分别位于 (1,0),(0,2) 和 (2,3) 。
一开始,你在入口格子 (1,2) 处。
- 你可以往左移动 2 步到达 (1,0) 。
- 你可以往上移动 1 步到达 (0,2) 。
从入口处没法到达 (2,3) 。
所以,最近的出口是 (0,2) ,距离为 1 步。
示例 2:
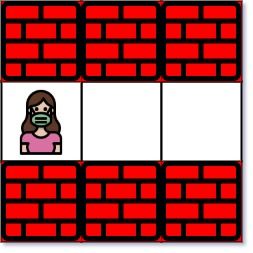
输入:maze = [["+","+","+"],[".",".","."],["+","+","+"]], entrance = [1,0]
输出:2
解释:迷宫中只有 1 个出口,在 (1,2) 处。
(1,0) 不算出口,因为它是入口格子。
初始时,你在入口与格子 (1,0) 处。
- 你可以往右移动 2 步到达 (1,2) 处。
所以,最近的出口为 (1,2) ,距离为 2 步。
示例 3:

输入:maze = [[".","+"]], entrance = [0,0]
输出:-1
解释:这个迷宫中没有出口。
提示:
maze.length == mmaze[i].length == n1 <= m, n <= 100maze[i][j] 要么是 '.' ,要么是 '+' 。entrance.length == 20 <= entrancerow < m0 <= entrancecol < nentrance 一定是空格子。
解法
方法一:BFS
我们可以从入口开始,进行广度优先搜索,每次搜索到一个新的空格子,就将其标记为已访问,并将其加入队列,直到找到一个边界上的空格子,返回步数。
具体地,我们定义一个队列 \(q\),初始时我们将 \(\textit{entrance}\) 加入队列。定义一个变量 \(\textit{ans}\) 记录步数,初始为 \(1\)。然后我们开始进行广度优先搜索,每一轮我们取出队列中的所有元素,遍历这些元素,对于每个元素,我们尝试向四个方向移动,如果移动后的位置是一个空格子,我们将其加入队列,并将其标记为已访问。如果移动后的位置是边界上的空格子,我们返回 \(\textit{ans}\)。如果队列为空,我们返回 \(-1\)。这一轮搜索结束后,我们将 \(\textit{ans}\) 加一,继续进行下一轮搜索。
遍历结束后,如果我们没有找到边界上的空格子,我们返回 \(-1\)。
时间复杂度 \(O(m \times n)\),空间复杂度 \(O(m \times n)\)。其中 \(m\) 和 \(n\) 分别是迷宫的行数和列数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19 | class Solution:
def nearestExit(self, maze: List[List[str]], entrance: List[int]) -> int:
m, n = len(maze), len(maze[0])
i, j = entrance
q = deque([(i, j)])
maze[i][j] = "+"
ans = 0
while q:
ans += 1
for _ in range(len(q)):
i, j = q.popleft()
for a, b in [[0, -1], [0, 1], [-1, 0], [1, 0]]:
x, y = i + a, j + b
if 0 <= x < m and 0 <= y < n and maze[x][y] == ".":
if x == 0 or x == m - 1 or y == 0 or y == n - 1:
return ans
q.append((x, y))
maze[x][y] = "+"
return -1
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25 | class Solution {
public int nearestExit(char[][] maze, int[] entrance) {
int m = maze.length, n = maze[0].length;
final int[] dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
Deque<int[]> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
q.offer(entrance);
maze[entrance[0]][entrance[1]] = '+';
for (int ans = 1; !q.isEmpty(); ++ans) {
for (int k = q.size(); k > 0; --k) {
var p = q.poll();
for (int d = 0; d < 4; ++d) {
int x = p[0] + dirs[d], y = p[1] + dirs[d + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && maze[x][y] == '.') {
if (x == 0 || x == m - 1 || y == 0 || y == n - 1) {
return ans;
}
maze[x][y] = '+';
q.offer(new int[] {x, y});
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27 | class Solution {
public:
int nearestExit(vector<vector<char>>& maze, vector<int>& entrance) {
int m = maze.size(), n = maze[0].size();
int dirs[5] = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.emplace(entrance[0], entrance[1]);
maze[entrance[0]][entrance[1]] = '+';
for (int ans = 1; !q.empty(); ++ans) {
for (int k = q.size(); k; --k) {
auto [i, j] = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int d = 0; d < 4; ++d) {
int x = i + dirs[d], y = j + dirs[d + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && maze[x][y] == '.') {
if (x == 0 || x == m - 1 || y == 0 || y == n - 1) {
return ans;
}
maze[x][y] = '+';
q.emplace(x, y);
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23 | func nearestExit(maze [][]byte, entrance []int) int {
m, n := len(maze), len(maze[0])
q := [][2]int{{entrance[0], entrance[1]}}
maze[entrance[0]][entrance[1]] = '+'
dirs := []int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}
for ans := 1; len(q) > 0; ans++ {
for k := len(q); k > 0; k-- {
p := q[0]
q = q[1:]
for l := 0; l < 4; l++ {
x, y := p[0]+dirs[l], p[1]+dirs[l+1]
if x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && maze[x][y] == '.' {
if x == 0 || x == m-1 || y == 0 || y == n-1 {
return ans
}
q = append(q, [2]int{x, y})
maze[x][y] = '+'
}
}
}
}
return -1
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19 | function nearestExit(maze: string[][], entrance: number[]): number {
const dir = [0, 1, 0, -1, 0];
const q = [[...entrance, 0]];
maze[entrance[0]][entrance[1]] = '+';
for (const [i, j, ans] of q) {
for (let d = 0; d < 4; d++) {
const [x, y] = [i + dir[d], j + dir[d + 1]];
const v = maze[x]?.[y];
if (!v && ans) {
return ans;
}
if (v === '.') {
q.push([x, y, ans + 1]);
maze[x][y] = '+';
}
}
}
return -1;
}
|





