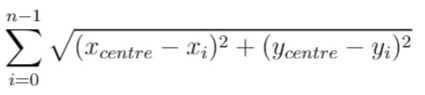题目描述
一家快递公司希望在新城市建立新的服务中心。公司统计了该城市所有客户在二维地图上的坐标,并希望能够以此为依据为新的服务中心选址:使服务中心 到所有客户的欧几里得距离的总和最小 。
给你一个数组 positions ,其中 positions[i] = [xi, yi] 表示第 i 个客户在二维地图上的位置,返回到所有客户的 欧几里得距离的最小总和 。
换句话说,请你为服务中心选址,该位置的坐标 [xcentre, ycentre] 需要使下面的公式取到最小值:
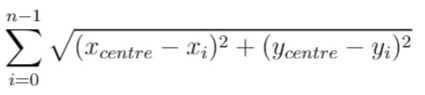
与真实值误差在 10-5之内的答案将被视作正确答案。
示例 1:
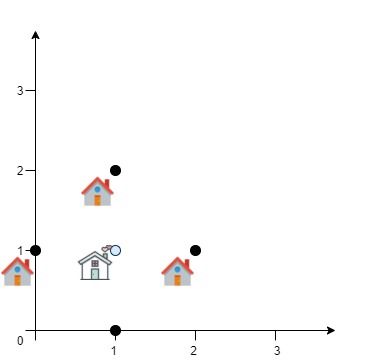
输入:positions = [[0,1],[1,0],[1,2],[2,1]]
输出:4.00000
解释:如图所示,你可以选 [xcentre, ycentre] = [1, 1] 作为新中心的位置,这样一来到每个客户的距离就都是 1,所有距离之和为 4 ,这也是可以找到的最小值。
示例 2:
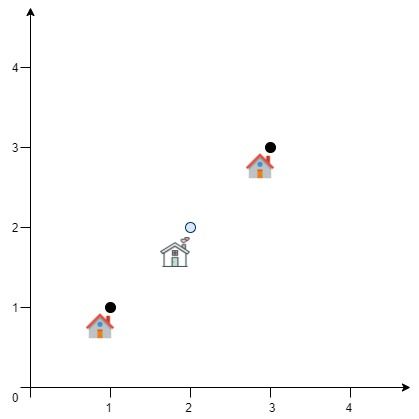
输入:positions = [[1,1],[3,3]]
输出:2.82843
解释:欧几里得距离可能的最小总和为 sqrt(2) + sqrt(2) = 2.82843
提示:
1 <= positions.length <= 50positions[i].length == 20 <= xi, yi <= 100
解法
方法一:梯度下降法
我们可以先设定一个初始的服务中心位置为所有客户坐标的几何中心 \((x, y)\)。接下来,使用梯度下降法不断迭代,设定一个学习率 \(\alpha=0.5\),衰减率 \(decay=0.999\)。每次一次迭代,计算当前位置到所有客户的距离之和,然后计算当前位置的梯度,最后更新当前位置。当梯度的绝对值都小于 \(10^{-6}\) 时,停止迭代,返回当前位置到所有客户的距离之和。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28 | class Solution:
def getMinDistSum(self, positions: List[List[int]]) -> float:
n = len(positions)
x = y = 0
for x1, y1 in positions:
x += x1
y += y1
x, y = x / n, y / n
decay = 0.999
eps = 1e-6
alpha = 0.5
while 1:
grad_x = grad_y = 0
dist = 0
for x1, y1 in positions:
a = x - x1
b = y - y1
c = sqrt(a * a + b * b)
grad_x += a / (c + 1e-8)
grad_y += b / (c + 1e-8)
dist += c
dx = grad_x * alpha
dy = grad_y * alpha
x -= dx
y -= dy
alpha *= decay
if abs(dx) <= eps and abs(dy) <= eps:
return dist
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33 | class Solution {
public double getMinDistSum(int[][] positions) {
int n = positions.length;
double x = 0, y = 0;
for (int[] p : positions) {
x += p[0];
y += p[1];
}
x /= n;
y /= n;
double decay = 0.999;
double eps = 1e-6;
double alpha = 0.5;
while (true) {
double gradX = 0, gradY = 0;
double dist = 0;
for (int[] p : positions) {
double a = x - p[0], b = y - p[1];
double c = Math.sqrt(a * a + b * b);
gradX += a / (c + 1e-8);
gradY += b / (c + 1e-8);
dist += c;
}
double dx = gradX * alpha, dy = gradY * alpha;
if (Math.abs(dx) <= eps && Math.abs(dy) <= eps) {
return dist;
}
x -= dx;
y -= dy;
alpha *= decay;
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34 | class Solution {
public:
double getMinDistSum(vector<vector<int>>& positions) {
int n = positions.size();
double x = 0, y = 0;
for (auto& p : positions) {
x += p[0];
y += p[1];
}
x /= n;
y /= n;
double decay = 0.999;
double eps = 1e-6;
double alpha = 0.5;
while (true) {
double gradX = 0, gradY = 0;
double dist = 0;
for (auto& p : positions) {
double a = x - p[0], b = y - p[1];
double c = sqrt(a * a + b * b);
gradX += a / (c + 1e-8);
gradY += b / (c + 1e-8);
dist += c;
}
double dx = gradX * alpha, dy = gradY * alpha;
if (abs(dx) <= eps && abs(dy) <= eps) {
return dist;
}
x -= dx;
y -= dy;
alpha *= decay;
}
}
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33 | func getMinDistSum(positions [][]int) float64 {
n := len(positions)
var x, y float64
for _, p := range positions {
x += float64(p[0])
y += float64(p[1])
}
x /= float64(n)
y /= float64(n)
const decay float64 = 0.999
const eps float64 = 1e-6
var alpha float64 = 0.5
for {
var gradX, gradY float64
var dist float64
for _, p := range positions {
a := x - float64(p[0])
b := y - float64(p[1])
c := math.Sqrt(a*a + b*b)
gradX += a / (c + 1e-8)
gradY += b / (c + 1e-8)
dist += c
}
dx := gradX * alpha
dy := gradY * alpha
if math.Abs(dx) <= eps && math.Abs(dy) <= eps {
return dist
}
x -= dx
y -= dy
alpha *= decay
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33 | function getMinDistSum(positions: number[][]): number {
const n = positions.length;
let [x, y] = [0, 0];
for (const [px, py] of positions) {
x += px;
y += py;
}
x /= n;
y /= n;
const decay = 0.999;
const eps = 1e-6;
let alpha = 0.5;
while (true) {
let [gradX, gradY] = [0, 0];
let dist = 0;
for (const [px, py] of positions) {
const a = x - px;
const b = y - py;
const c = Math.sqrt(a * a + b * b);
gradX += a / (c + 1e-8);
gradY += b / (c + 1e-8);
dist += c;
}
const dx = gradX * alpha;
const dy = gradY * alpha;
if (Math.abs(dx) <= eps && Math.abs(dy) <= eps) {
return dist;
}
x -= dx;
y -= dy;
alpha *= decay;
}
}
|