二叉树
栈
树
深度优先搜索
题目描述
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 后序遍历 。
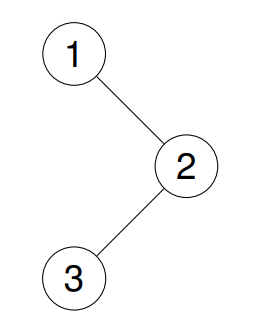
示例 1:
输入: root = [1,null,2,3]
输出: [3,2,1]
解释:
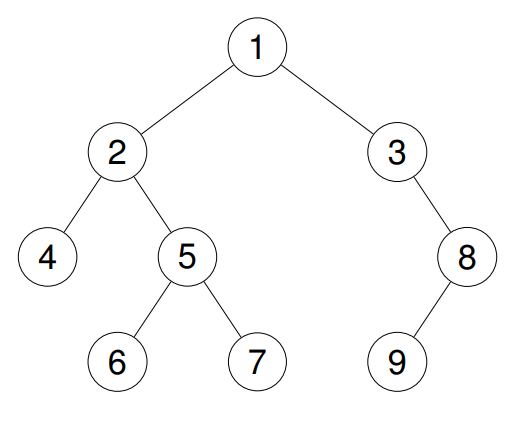
示例 2:
输入: root = [1,2,3,4,5,null,8,null,null,6,7,9]
输出: [4,6,7,5,2,9,8,3,1]
解释:
示例 3:
示例 4:
提示:
树中节点的数目在范围 [0, 100] 内
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
进阶: 递归算法很简单,你可以通过迭代算法完成吗?
解法
方法一:递归
我们先递归左右子树,然后再访问根节点。
时间复杂度 \(O(n)\) ,空间复杂度 \(O(n)\) 。其中 \(n\) 是二叉树的节点数,空间复杂度主要取决于递归调用的栈空间。
Python3 Java C++ Go TypeScript Rust
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18 # Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution :
def postorderTraversal ( self , root : Optional [ TreeNode ]) -> List [ int ]:
def dfs ( root ):
if root is None :
return
dfs ( root . left )
dfs ( root . right )
ans . append ( root . val )
ans = []
dfs ( root )
return ans
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private List < Integer > ans = new ArrayList <> ();
public List < Integer > postorderTraversal ( TreeNode root ) {
dfs ( root );
return ans ;
}
private void dfs ( TreeNode root ) {
if ( root == null ) {
return ;
}
dfs ( root . left );
dfs ( root . right );
ans . add ( root . val );
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public :
vector < int > postorderTraversal ( TreeNode * root ) {
vector < int > ans ;
function < void ( TreeNode * ) > dfs = [ & ]( TreeNode * root ) {
if ( ! root ) {
return ;
}
dfs ( root -> left );
dfs ( root -> right );
ans . push_back ( root -> val );
};
dfs ( root );
return ans ;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func postorderTraversal ( root * TreeNode ) ( ans [] int ) {
var dfs func ( * TreeNode )
dfs = func ( root * TreeNode ) {
if root == nil {
return
}
dfs ( root . Left )
dfs ( root . Right )
ans = append ( ans , root . Val )
}
dfs ( root )
return
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function postorderTraversal ( root : TreeNode | null ) : number [] {
const ans : number [] = [];
const dfs = ( root : TreeNode | null ) => {
if ( ! root ) {
return ;
}
dfs ( root . left );
dfs ( root . right );
ans . push ( root . val );
};
dfs ( root );
return ans ;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37 // Definition for a binary tree node.
// #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
// pub struct TreeNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// }
//
// impl TreeNode {
// #[inline]
// pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// TreeNode {
// val,
// left: None,
// right: None
// }
// }
// }
use std :: cell :: RefCell ;
use std :: rc :: Rc ;
impl Solution {
fn dfs ( root : & Option < Rc < RefCell < TreeNode >>> , ans : & mut Vec < i32 > ) {
if root . is_none () {
return ;
}
let node = root . as_ref (). unwrap (). borrow ();
Self :: dfs ( & node . left , ans );
Self :: dfs ( & node . right , ans );
ans . push ( node . val );
}
pub fn postorder_traversal ( root : Option < Rc < RefCell < TreeNode >>> ) -> Vec < i32 > {
let mut ans = vec! [];
Self :: dfs ( & root , & mut ans );
ans
}
}
方法二:栈实现后序遍历
先序遍历的顺序是:根、左、右,如果我们改变左右孩子的顺序,就能将顺序变成:根、右、左。最后再将结果反转一下,就得到了后序遍历的结果。
因此,栈实现非递归遍历的思路如下:
定义一个栈 \(stk\) ,先将根节点压入栈
若栈不为空,每次从栈中弹出一个节点
处理该节点
先把节点左孩子压入栈,接着把节点右孩子压入栈(如果有孩子节点)
重复 2-4
将结果反转,得到后序遍历的结果
时间复杂度 \(O(n)\) ,空间复杂度 \(O(n)\) 。其中 \(n\) 是二叉树的节点数,空间复杂度主要取决于栈空间。
Python3 Java C++ Go TypeScript
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20 # Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution :
def postorderTraversal ( self , root : Optional [ TreeNode ]) -> List [ int ]:
ans = []
if root is None :
return ans
stk = [ root ]
while stk :
node = stk . pop ()
ans . append ( node . val )
if node . left :
stk . append ( node . left )
if node . right :
stk . append ( node . right )
return ans [:: - 1 ]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List < Integer > postorderTraversal ( TreeNode root ) {
LinkedList < Integer > ans = new LinkedList <> ();
if ( root == null ) {
return ans ;
}
Deque < TreeNode > stk = new ArrayDeque <> ();
stk . push ( root );
while ( ! stk . isEmpty ()) {
TreeNode node = stk . pop ();
ans . addFirst ( node . val );
if ( node . left != null ) {
stk . push ( node . left );
}
if ( node . right != null ) {
stk . push ( node . right );
}
}
return ans ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public :
vector < int > postorderTraversal ( TreeNode * root ) {
vector < int > ans ;
if ( ! root ) {
return ans ;
}
stack < TreeNode *> stk ;
stk . push ( root );
while ( stk . size ()) {
auto node = stk . top ();
stk . pop ();
ans . push_back ( node -> val );
if ( node -> left ) {
stk . push ( node -> left );
}
if ( node -> right ) {
stk . push ( node -> right );
}
}
reverse ( ans . begin (), ans . end ());
return ans ;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func postorderTraversal ( root * TreeNode ) ( ans [] int ) {
if root == nil {
return
}
stk := [] * TreeNode { root }
for len ( stk ) > 0 {
node := stk [ len ( stk ) - 1 ]
stk = stk [: len ( stk ) - 1 ]
ans = append ( ans , node . Val )
if node . Left != nil {
stk = append ( stk , node . Left )
}
if node . Right != nil {
stk = append ( stk , node . Right )
}
}
for i , j := 0 , len ( ans ) - 1 ; i < j ; i , j = i + 1 , j - 1 {
ans [ i ], ans [ j ] = ans [ j ], ans [ i ]
}
return
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function postorderTraversal ( root : TreeNode | null ) : number [] {
const ans : number [] = [];
if ( ! root ) {
return ans ;
}
const stk : TreeNode [] = [ root ];
while ( stk . length ) {
const { left , right , val } = stk . pop ();
ans . push ( val );
left && stk . push ( left );
right && stk . push ( right );
}
ans . reverse ();
return ans ;
}
方法三:Morris 实现后序遍历
Morris 遍历无需使用栈,空间复杂度为 \(O(1)\) 。核心思想是:
遍历二叉树节点,
若当前节点 root 的右子树为空,将当前节点值添加至结果列表 \(ans\) 中,并将当前节点更新为 root.left
若当前节点 root 的右子树不为空,找到右子树的最左节点 next(也即是 root 节点在中序遍历下的后继节点):
若后继节点 next 的左子树为空,将当前节点值添加至结果列表 \(ans\) 中,然后将后继节点的左子树指向当前节点 root,并将当前节点更新为 root.right。
若后继节点 next 的左子树不为空,将后继节点左子树指向空(即解除 next 与 root 的指向关系),并将当前节点更新为 root.left。
循环以上步骤,直至二叉树节点为空,遍历结束。
最后返回结果列表的逆序即可。
Morris 后序遍历跟 Morris 前序遍历思路一致,只是将前序的“根左右”变为“根右左”,最后逆序结果即可变成“左右根”。
时间复杂度 \(O(n)\) ,其中 \(n\) 是二叉树的节点数。空间复杂度 \(O(1)\) 。
Python3 Java C++ Go TypeScript
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25 # Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution :
def postorderTraversal ( self , root : Optional [ TreeNode ]) -> List [ int ]:
ans = []
while root :
if root . right is None :
ans . append ( root . val )
root = root . left
else :
next = root . right
while next . left and next . left != root :
next = next . left
if next . left != root :
ans . append ( root . val )
next . left = root
root = root . right
else :
next . left = None
root = root . left
return ans [:: - 1 ]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List < Integer > postorderTraversal ( TreeNode root ) {
LinkedList < Integer > ans = new LinkedList <> ();
while ( root != null ) {
if ( root . right == null ) {
ans . addFirst ( root . val );
root = root . left ;
} else {
TreeNode next = root . right ;
while ( next . left != null && next . left != root ) {
next = next . left ;
}
if ( next . left == null ) {
ans . addFirst ( root . val );
next . left = root ;
root = root . right ;
} else {
next . left = null ;
root = root . left ;
}
}
}
return ans ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public :
vector < int > postorderTraversal ( TreeNode * root ) {
vector < int > ans ;
while ( root ) {
if ( ! root -> right ) {
ans . push_back ( root -> val );
root = root -> left ;
} else {
TreeNode * next = root -> right ;
while ( next -> left && next -> left != root ) {
next = next -> left ;
}
if ( next -> left != root ) {
ans . push_back ( root -> val );
next -> left = root ;
root = root -> right ;
} else {
next -> left = nullptr ;
root = root -> left ;
}
}
}
reverse ( ans . begin (), ans . end ());
return ans ;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func postorderTraversal ( root * TreeNode ) ( ans [] int ) {
for root != nil {
if root . Right == nil {
ans = append ([] int { root . Val }, ans ... )
root = root . Left
} else {
next := root . Right
for next . Left != nil && next . Left != root {
next = next . Left
}
if next . Left == nil {
ans = append ([] int { root . Val }, ans ... )
next . Left = root
root = root . Right
} else {
next . Left = nil
root = root . Left
}
}
}
return
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function postorderTraversal ( root : TreeNode | null ) : number [] {
const ans : number [] = [];
while ( root !== null ) {
const { val , left , right } = root ;
if ( right === null ) {
ans . push ( val );
root = left ;
} else {
let next = right ;
while ( next . left !== null && next . left !== root ) {
next = next . left ;
}
if ( next . left === null ) {
ans . push ( val );
next . left = root ;
root = right ;
} else {
next . left = null ;
root = left ;
}
}
}
return ans . reverse ();
}